Researchers announced that they have achieved the world’s first elucidation of how hydrogen produces free electrons through the interaction with certain defects in silicon. The achievement has the potential to improve how insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) are designed and manufactured, making them more efficient and reducing their power loss. It is also expected to open up possibilities for future devices using ultra-wide bandgap (UWBG) materials.
In the global drive toward carbon neutrality, efforts to make power electronics more efficient and energy-saving are accelerating worldwide. IGBTs are key components responsible for power conversion, so improving their efficiency is a major priority. While hydrogen ion implantation has been used for about half a century to control electron concentration in silicon, the underlying mechanism has remained unclear until now.
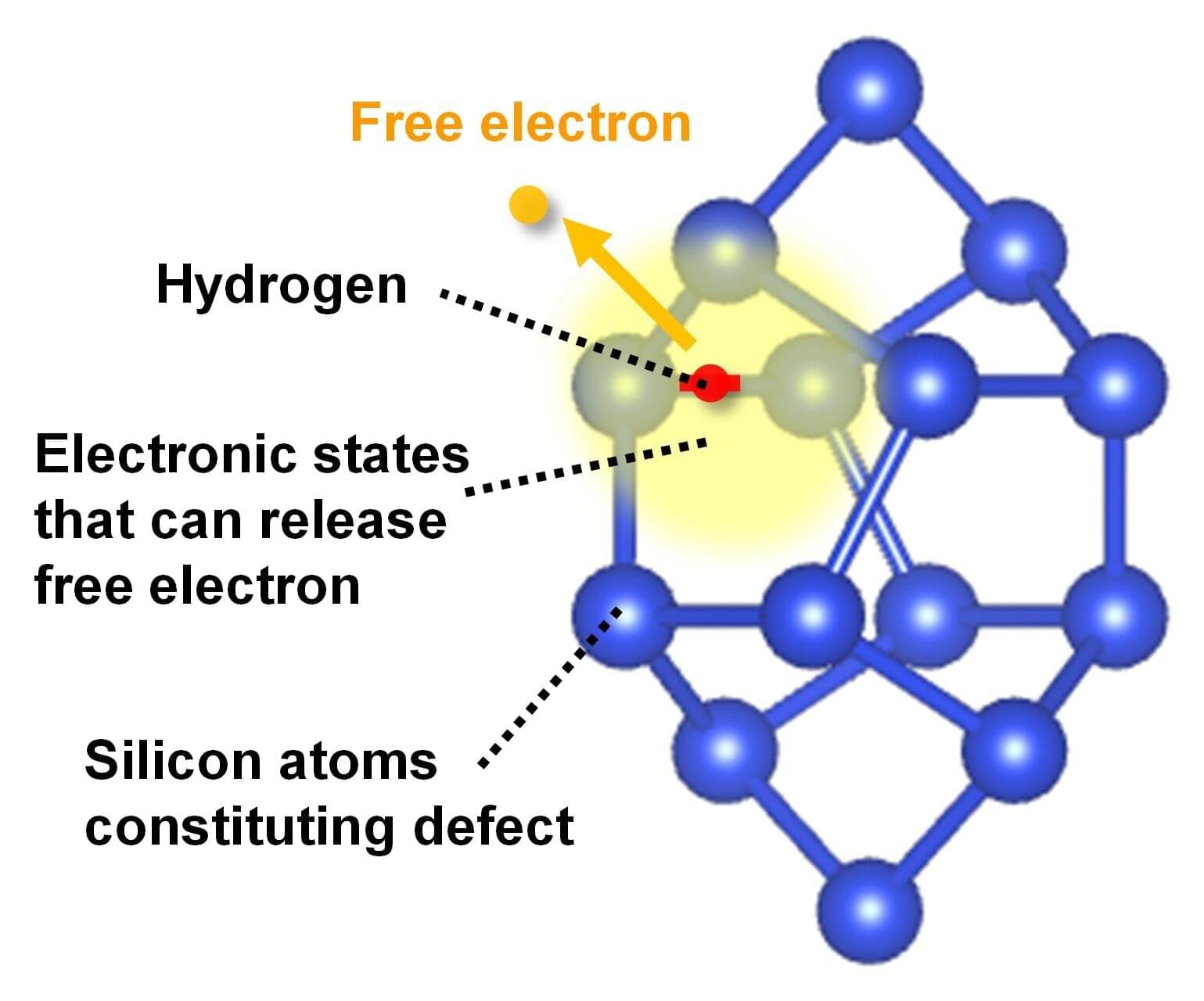
In 2023, Mitsubishi Electric and University of Tsukuba jointly discovered a defect complex in silicon that contributes to increasing electron concentration. They confirmed that this complex is formed when an interstitial silicon pair and hydrogen bind, but the reason why free electrons are newly generated in this process was still unclear.