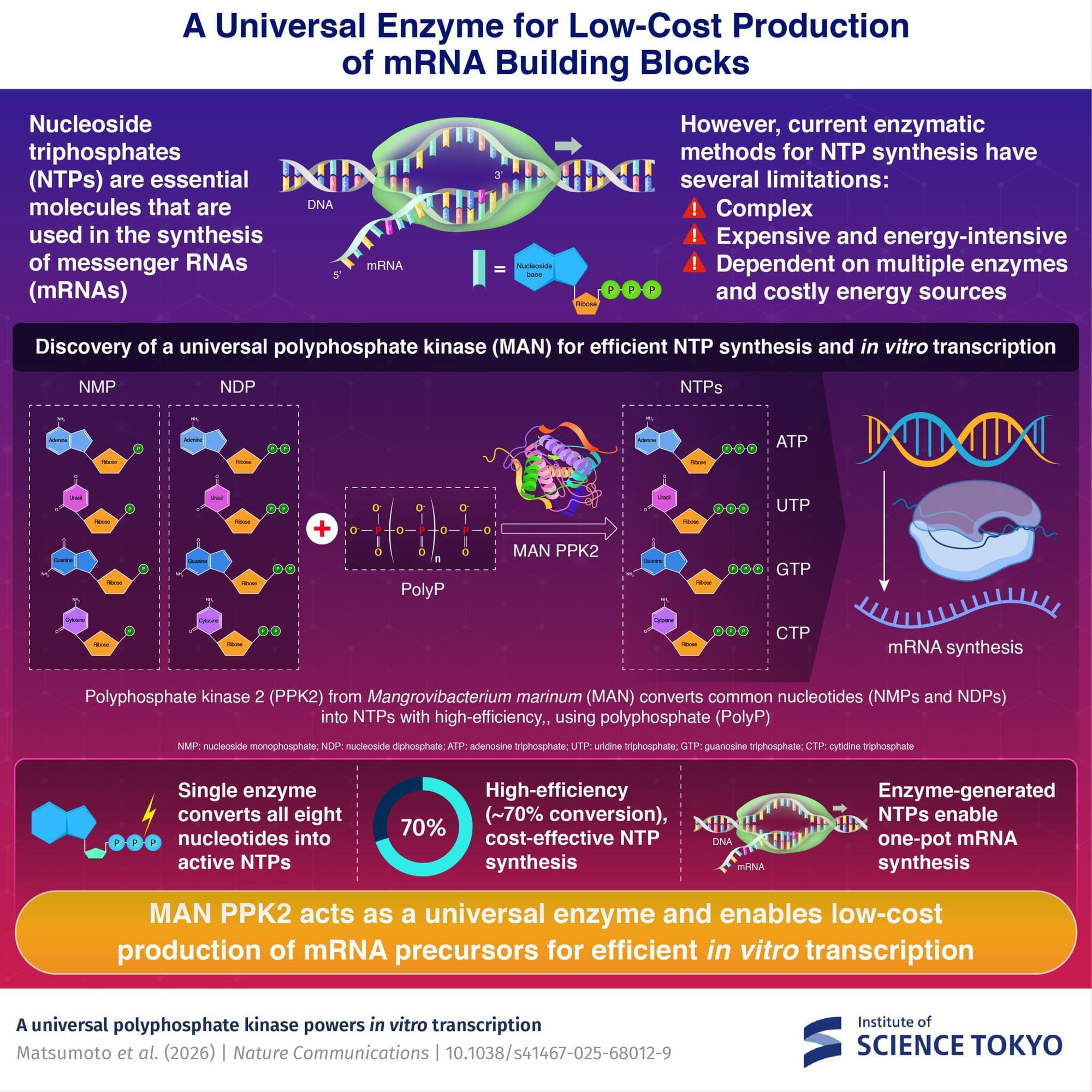
A single enzyme that can generate all four nucleoside triphosphates, the building blocks of ribonucleic acid (RNA), has been identified by researchers at the Institute of Science Tokyo. The study was published online in the journal Nature Communications.
By using polyphosphate as a phosphate donor, the enzyme efficiently converts inexpensive nucleotide precursors into the active forms required for RNA synthesis. Overall, the method dramatically simplifies the process of nucleotide production—offering a low-cost, efficient option for the in vitro synthesis of RNA.