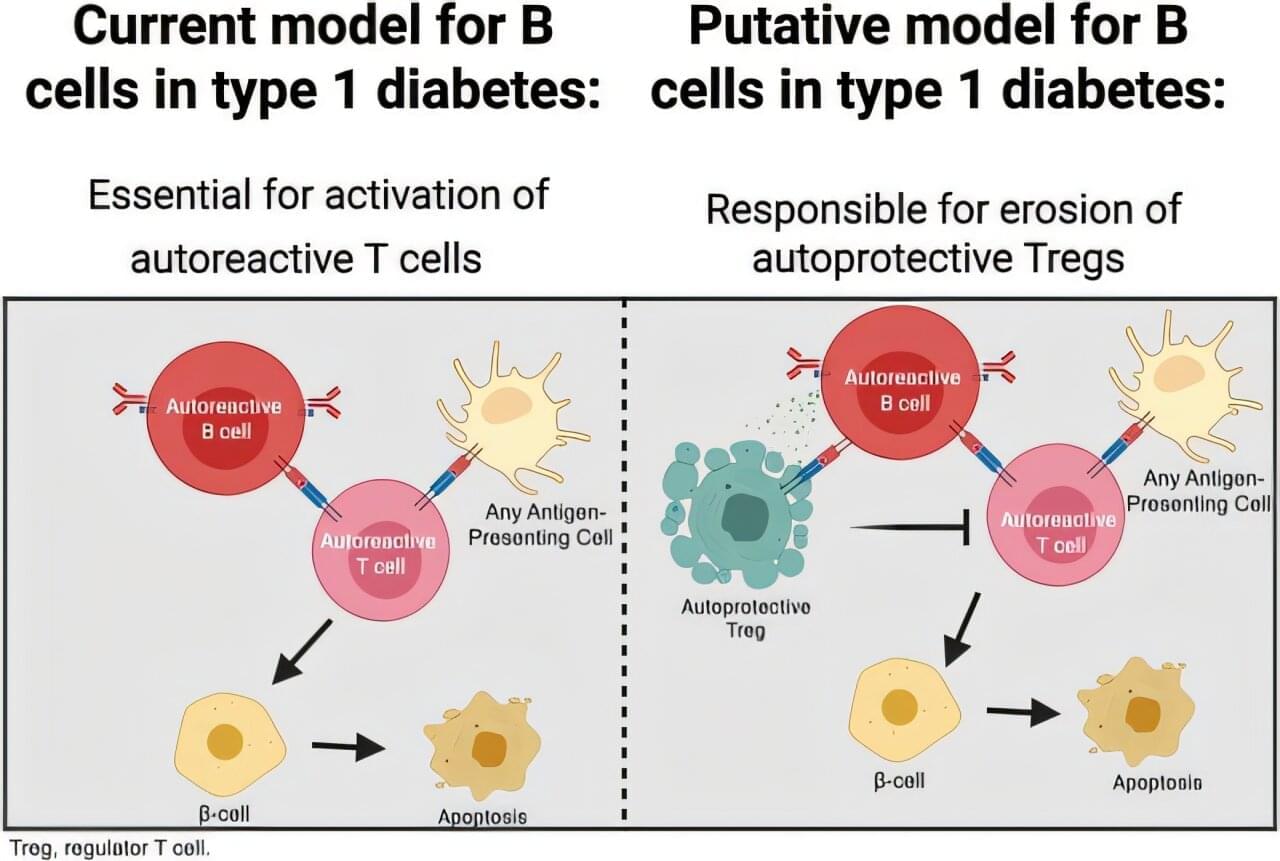
A recent study by Vanderbilt Health researchers has revealed a greater, detrimental role for B lymphocytes (B cells) in the progression of type 1 diabetes (T1D).
B cells are immune cells thought to drive the immune system’s attack on insulin-producing beta cells by activating anti-islet T cells. The study published in Diabetes suggests they play an even more sinister role by also interfering with and limiting the function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) that help calm the immune system.
“Our study showed B cells can weaken the body’s natural defenses by interfering with Tregs, which normally behave as peacekeepers to ward off immune attacks on the pancreas and the insulin-producing beta cells,” said Daniel Moore, MD, PhD, associate professor of Pediatrics at Vanderbilt Health and the study’s corresponding author.