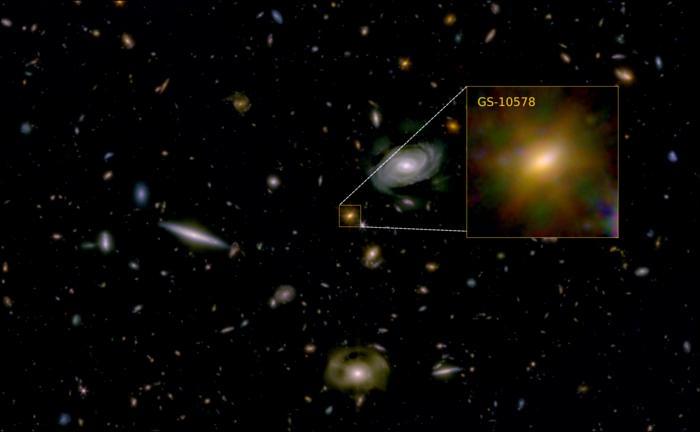
Dr. Francesco D’Eugenio: “The galaxy looks like a calm, rotating disc. That tells us it didn’t suffer a major, disruptive merger with another galaxy.”
What were galaxies like in the early universe? This is what a recent study published in Nature Astronomy hopes to address as an international team of scientists investigated the formation and evolution of the first galaxies after the Big Bang. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand the conditions of the early universe and what this could mean for the development of life throughout the cosmos.
For the study, the researchers used a combination of data obtained from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) located in Chile to examine “Pablo’s Galaxy” (officially designated as GS-10578) and is estimated to have existed approximately three billion years after the Big Bang. For context, the Big Bang is estimated to have occurred approximately 13.8 billion years ago. Using this data, the researchers discovered that Pablo’s Galaxy had a very short lifespan due to a lack of star formation from the galaxy’s black hole heated all of the cold gas, preventing new stars from forming.