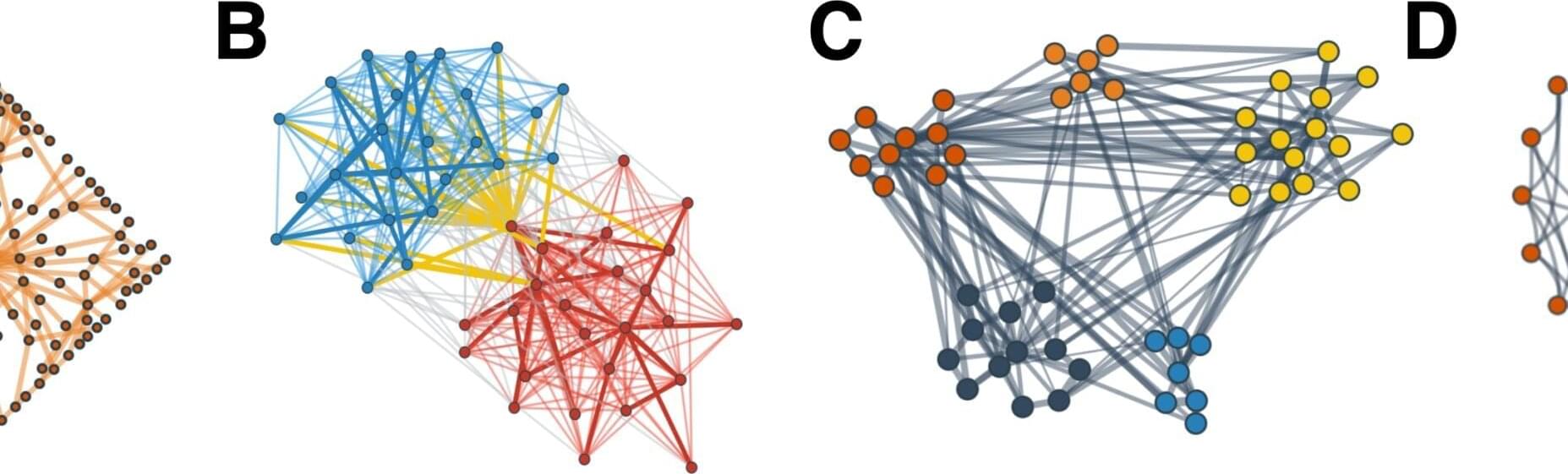
When large language models (LLMs) make decisions about networking and friendship, the models tend to act like people, across both synthetic simulations and real-world network contexts.
Marios Papachristou and Yuan Yuan developed a framework to study network formation behaviors of multiple LLM agents and compared these behaviors against human behaviors. The paper is published in the journal PNAS Nexus.