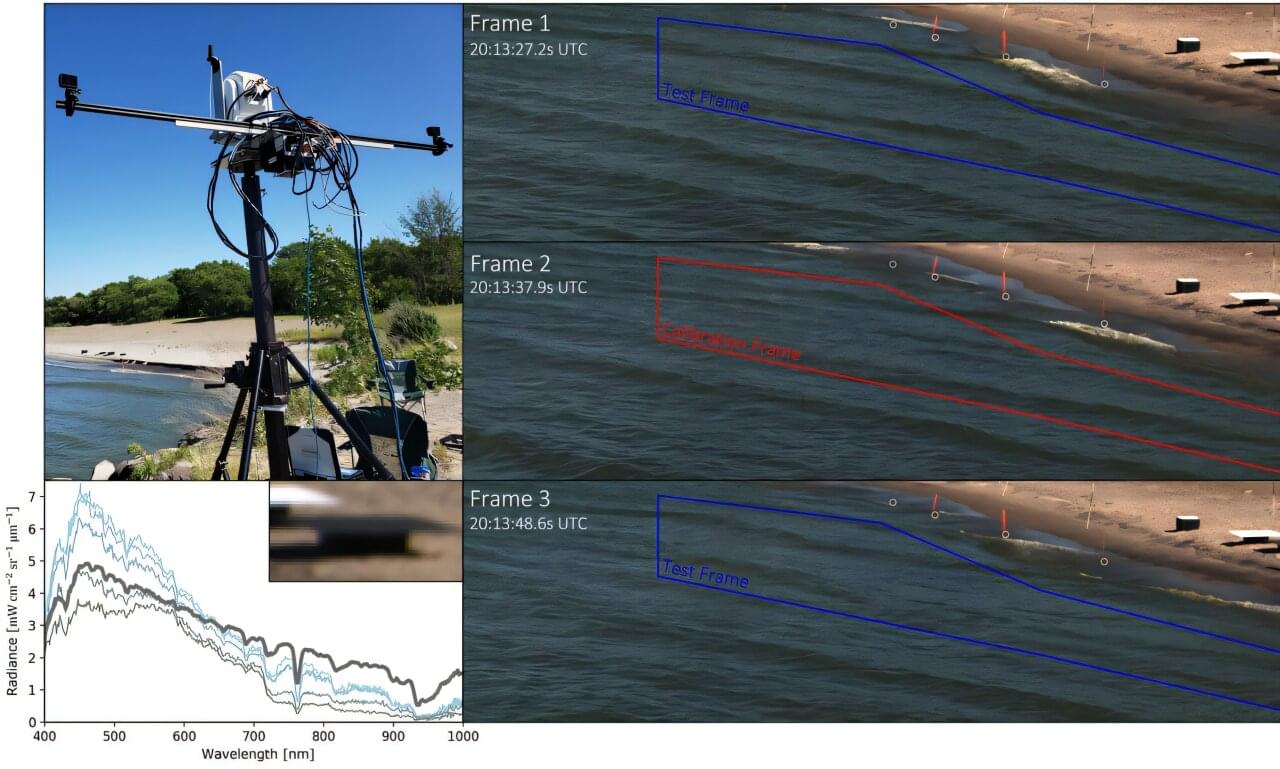
Hyperspectral imaging (HSI), or imaging spectroscopy, captures detailed information across the electromagnetic spectrum by acquiring a spectrum for each pixel in an image. This enables precise identification of materials through their spectral signatures.
HSI supports Earth remote sensing applications such as automated classification, abundance mapping, and estimation of physical and biological properties like soil moisture, sediment density, water quality, biomass, leaf area, and pigment content.
Although HSI offers detailed insight into a remote sensing scene, HSI data may not be readily available for an intended application. Recent studies have attempted to combine HSI with traditional red-green-blue (RGB) video acquisition to lower costs and improve performance. However, this fusion technology still faces technical challenges.