Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is the most common cardiovascular disease worldwide, threatening human health, quality of life and longevity. Aging is a dominant risk factor for CAD. This study aims to investigate the potential mechanisms of aging-related genes and CAD, and to make molecular drug predictions that will contribute to the diagnosis and treatment.
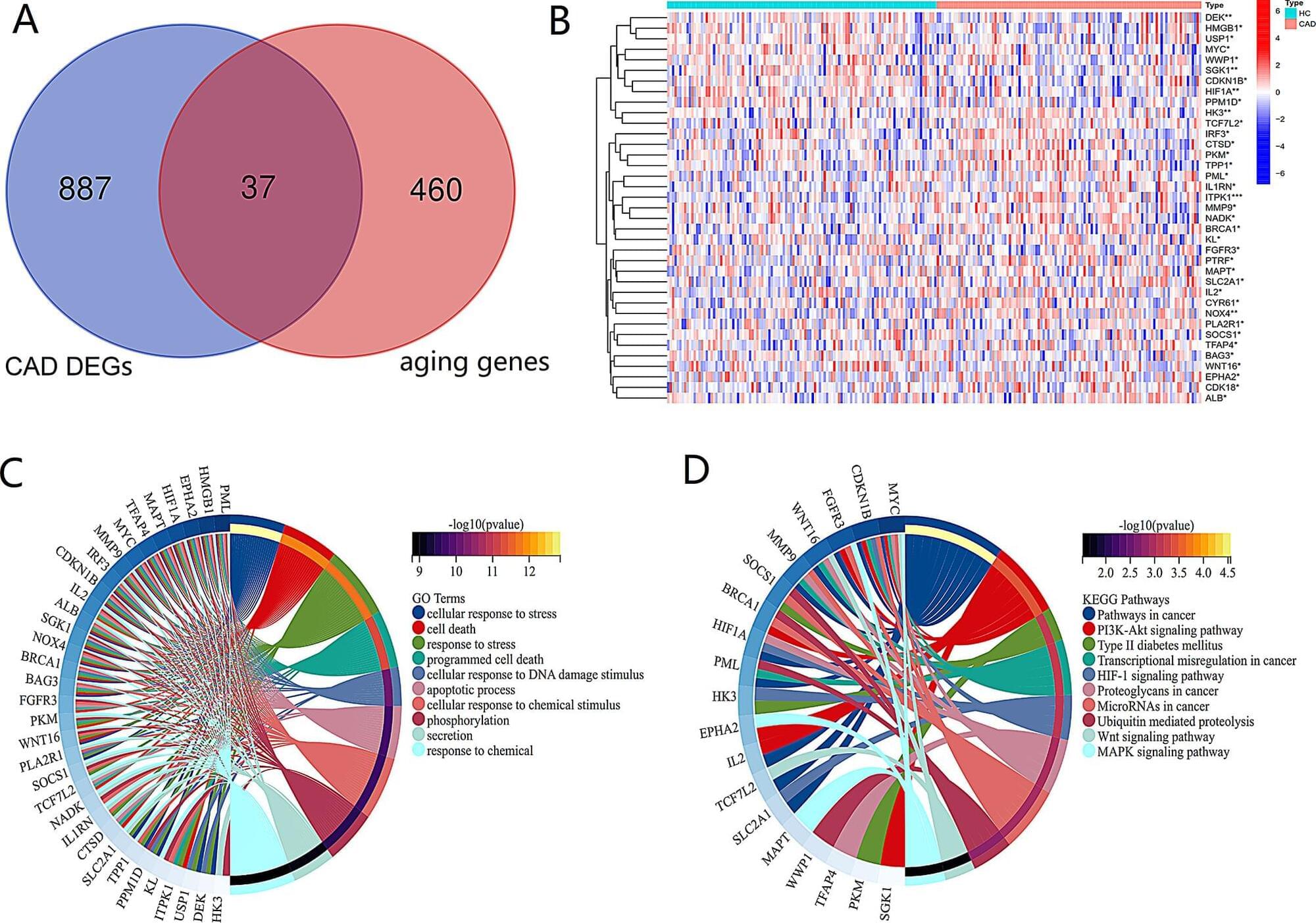
We downloaded the gene expression profile of circulating leukocytes in CAD patients (GSE12288) from Gene Expression Omnibus database, obtained differentially expressed aging genes through “limma” package and GenaCards database, and tested their biological functions. Further screening of aging related characteristic genes (ARCGs) using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator and random forest, generating nomogram charts and ROC curves for evaluating diagnostic efficacy. Immune cells were estimated by ssGSEA, and then combine ARCGs with immune cells and clinical indicators based on Pearson correlation analysis. Unsupervised cluster analysis was used to construct molecular clusters based on ARCGs and to assess functional characteristics between clusters. The DSigDB database was employed to explore the potential targeted drugs of ARCGs, and the molecular docking was carried out through Autodock Vina.