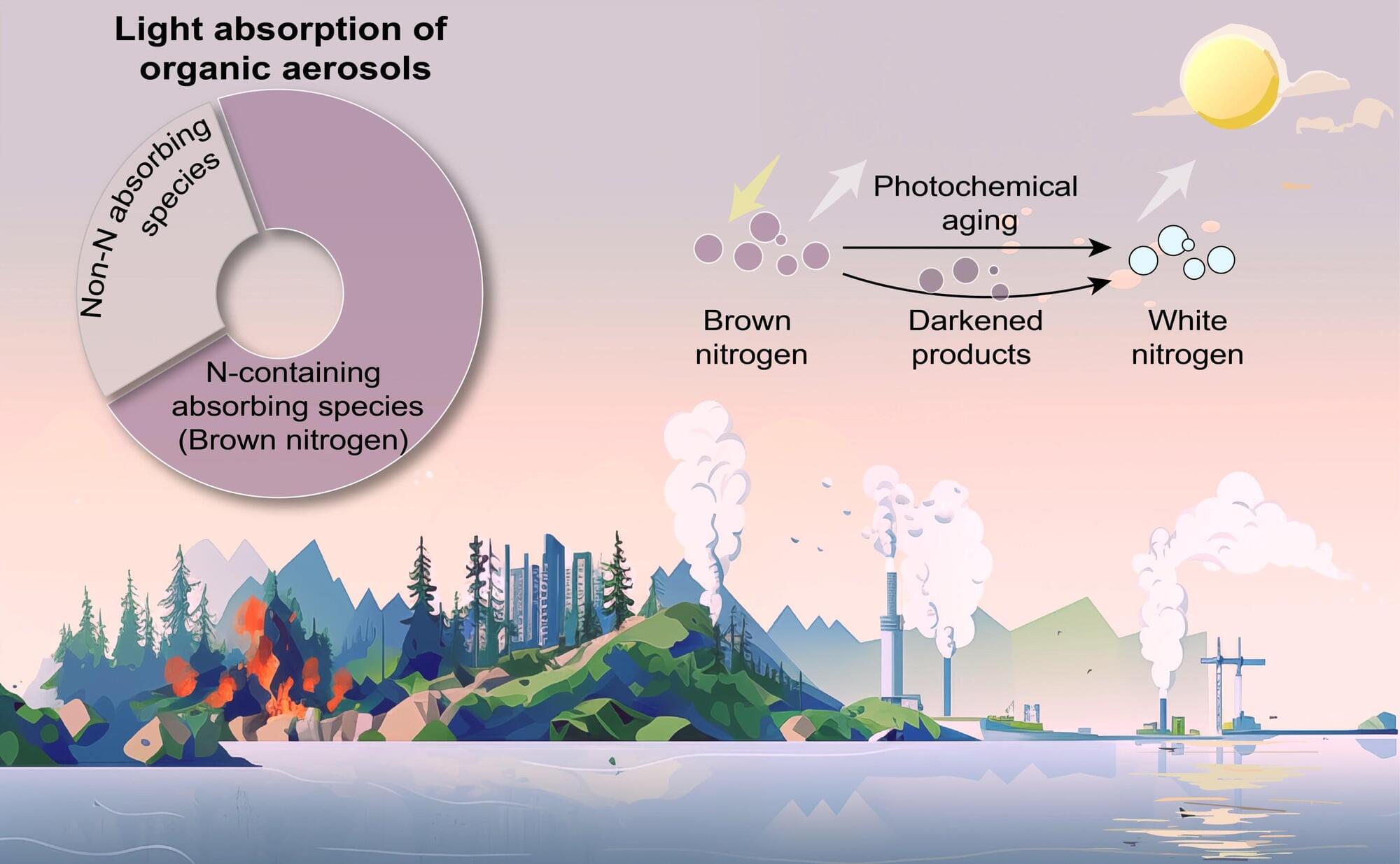
A collaborative research team has introduced a nitrogen-centric framework that explains the light-absorbing effects of atmospheric organic aerosols. Published in Science, this study reveals that nitrogen-containing compounds play a dominant role in the absorption of sunlight by atmospheric organic aerosols worldwide. This discovery signifies a major step towards improving climate models and developing more targeted strategies to mitigate the climate impact of airborne particles.
Atmospheric organic aerosols influence climate by absorbing and scattering sunlight, particularly within the near-ultraviolet to visible range. Due to their complex composition and continuous chemical transformation in the atmosphere, accurately assessing their climate effects has remained a challenge.
The study was jointly led by Prof. Fu Tzung-May, Professor of the School of Environmental Science and Engineering at Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech) and National Center for Applied Mathematics Shenzhen (NCAMS), and Prof. Yu Jianzhen, Chair Professor of the Department of Chemistry and the Division of Environment and Sustainability at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST).