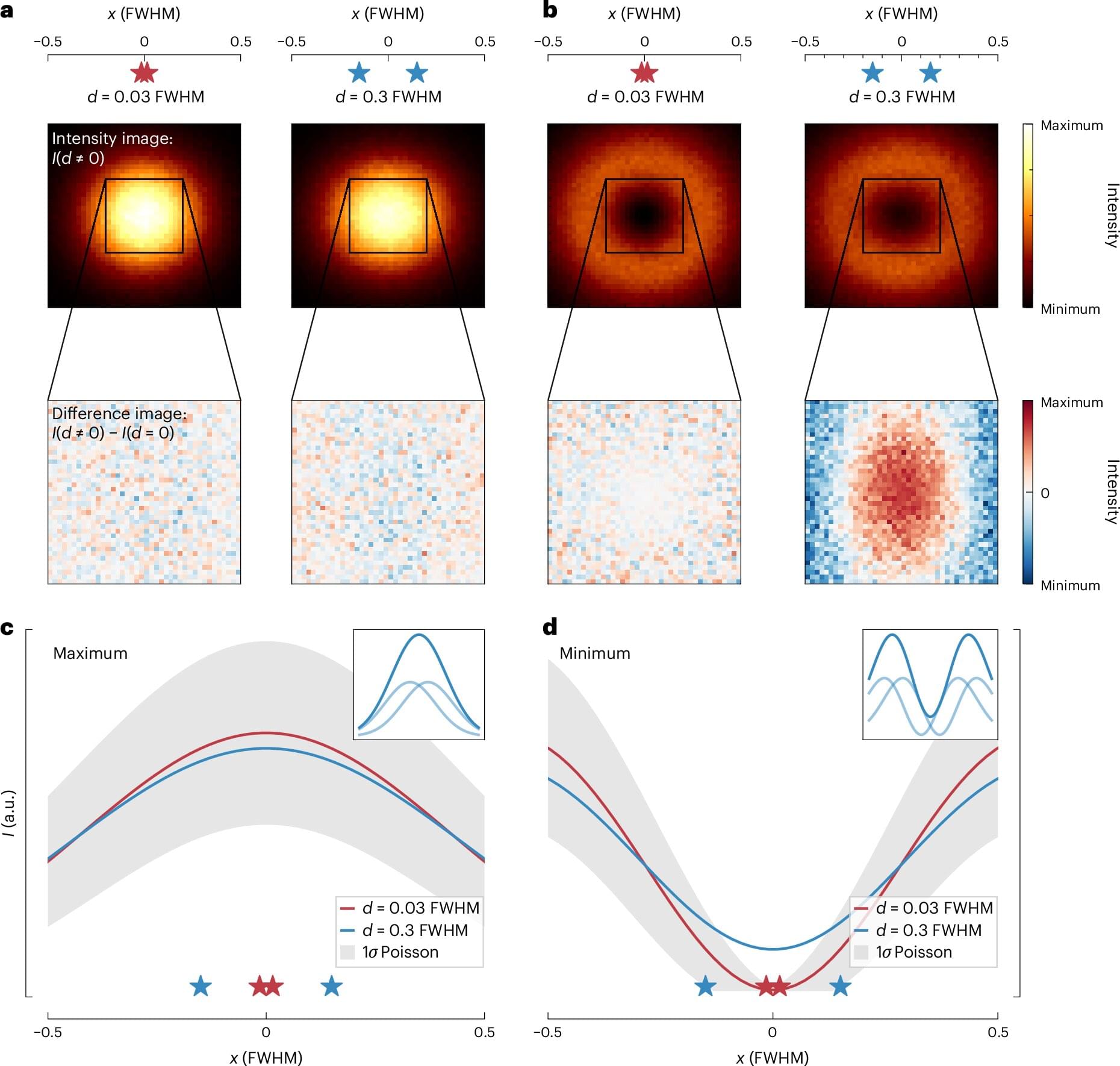
Overcoming the resolution limit in a light microscope of around half a wavelength of light (about 250 nanometers) is one of the most significant developments in optics. Due to the wave nature of light, even the best lens cannot produce a light spot smaller than 250 nanometers in diameter. All molecules within this bright spot are illuminated at the same time, light up together, and therefore, appear inseparable as a blurred whole.
In the early 1990s, Stefan Hell realized that molecules could be separated by briefly switching the molecular signal “OFF” and “ON” in such a way that closely neighboring molecules are forced to signal consecutively. Molecules that signal consecutively can be readily distinguished.
In fluorescence microscopy, this ON/OFF separation principle could be implemented to perfection, since molecular fluorescence can be easily switched on and off. In fact, STED and PALM/STORM, as well as the more recent super-resolution fluorescence microscopes, are all based on this ON/OFF principle.