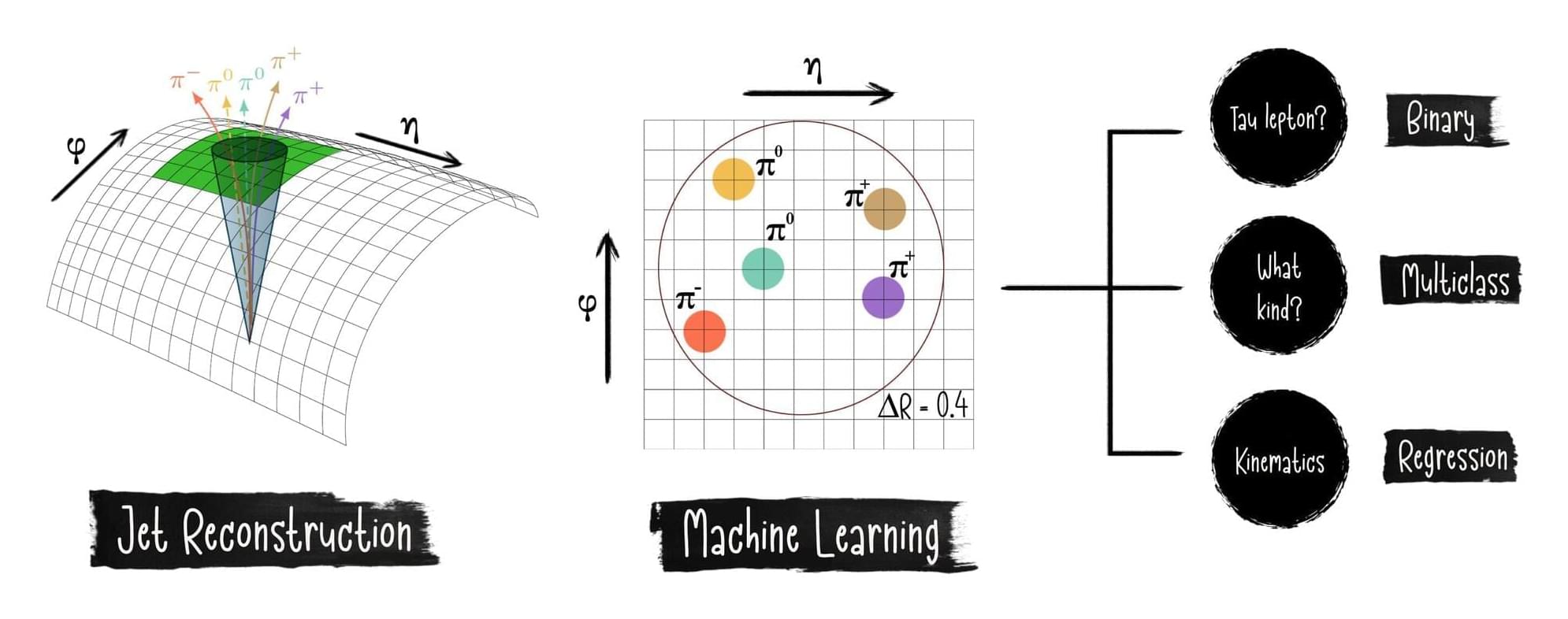
In order to find rare processes from collider data, scientists use computer algorithms to determine the type and properties of particles based on the faint signals that they leave in the detector. One such particle is the tau lepton, which is produced, for example, in the decay of the Higgs boson.
The tau lepton leaves a spray or jet of low-energy particles, the subtle pattern of which in the jet allows one to distinguish them from jets produced by other particles. The jet also contains information about the energy of the tau lepton, which is distributed among the daughter particles, and on the way is decayed. Currently, the best algorithms use multiple steps of combinatorics and computer vision.
ChatGPT has shown much stronger performance in rejecting backgrounds than computer-vision based methods. In this paper, researchers showed that such language-based models can find the tau leptons from the jet patterns, and also determine the energy and decay properties more accurately than before.