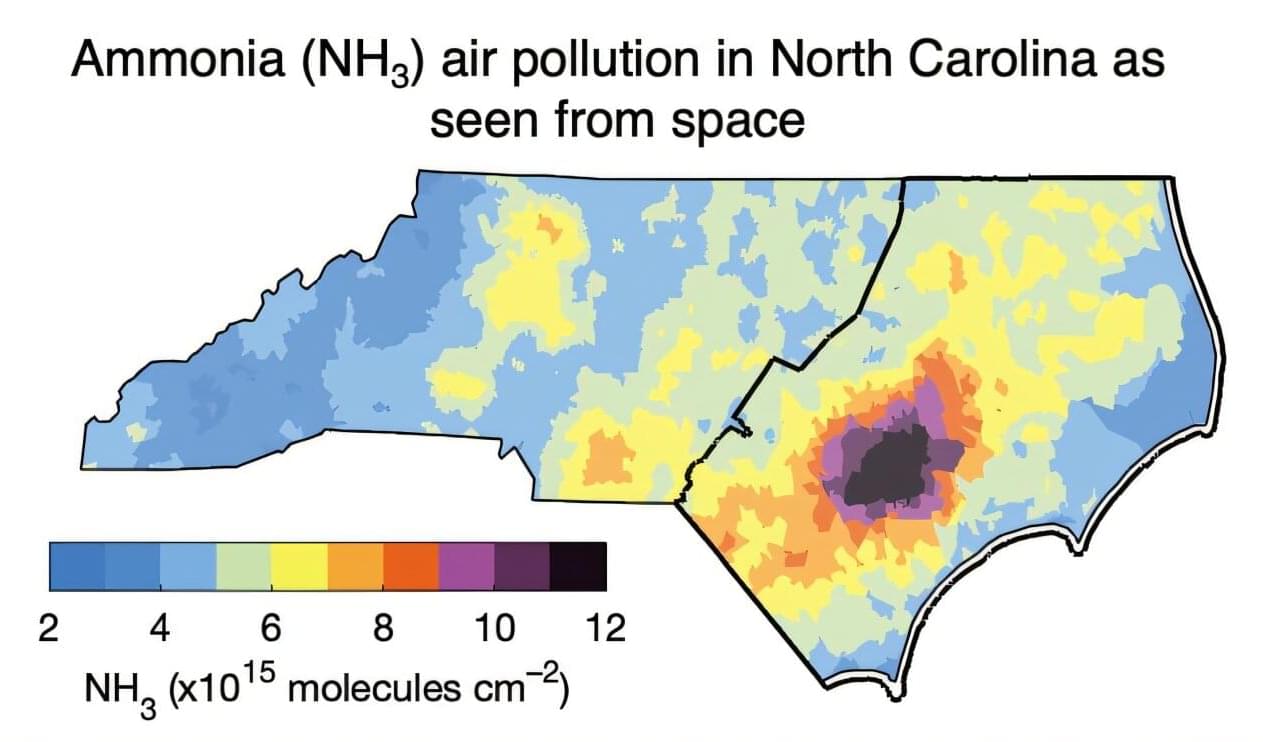
A study led by researchers from the University of Virginia has used satellite measurements to show the long-term persistence of air pollution inequalities tied to industrialized swine facilities in Eastern North Carolina.
Using satellite data spanning a 15-year period from 2008–2023, the study quantifies disparities in ammonia (NH3)—an air pollutant emitted by swine operations—for Black, Hispanic and Indigenous communities. These inequalities, exacerbated by hot and calm weather conditions, extend for multiple kilometers beyond the immediate vicinity of the facilities, highlighting the widespread impact of this environmental issue.
The study, published in Environmental Science & Technology by Sally Pusede and her team in the Department of Environmental Sciences at UVA, uses data from the Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer (IASI) aboard multiple polar-orbiting satellites. By analyzing NH3 levels in the atmosphere, UVA researchers were able to show that emissions from industrial swine operations result in systematic environmental inequalities.