A new “toolkit” to repair damaged DNA that can lead to aging, cancer and motor neuron disease (MND) has been discovered by scientists at the Universities of Sheffield and Oxford.
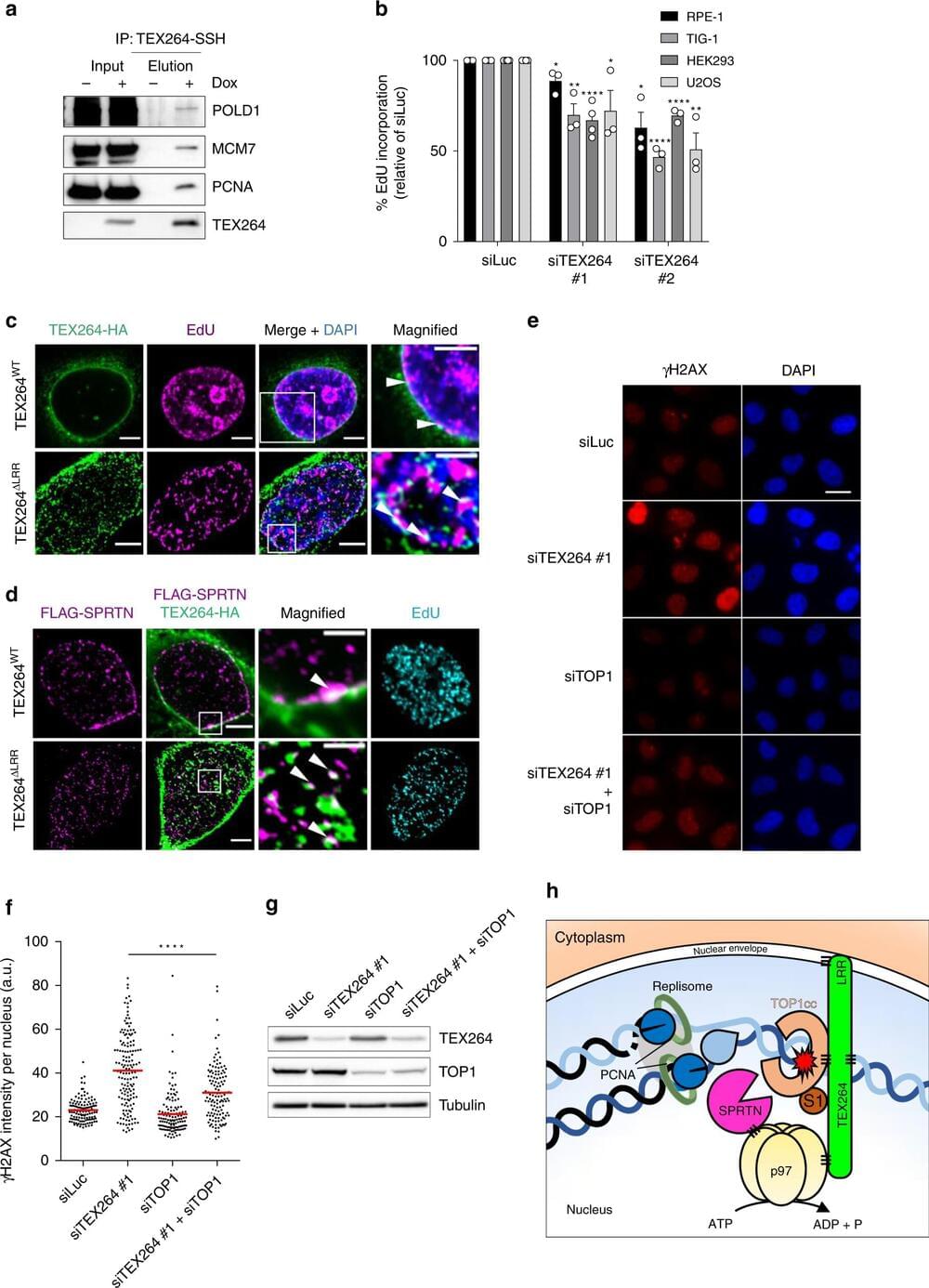
Published in Nature Communications, the research shows that a protein called TEX264, together with other enzymes, is able to recognize and “eat” toxic proteins that can stick to DNA and cause it to become damaged. An accumulation of broken, damaged DNA can cause cellular aging, cancer and neurological diseases such as MND.
Until now, ways of repairing this sort of DNA damage have been poorly understood, but scientists hope to exploit this novel repair toolkit of proteins to protect us from aging, cancer and neurological disease.