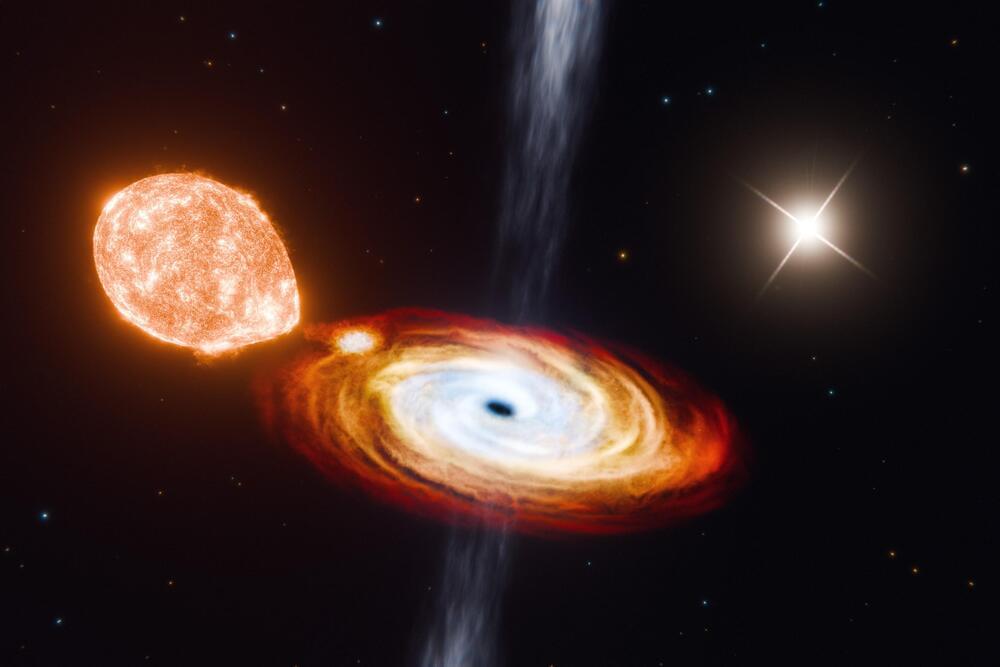
In a recent discovery, astronomers have found that the black hole in the well-known low-mass X-ray binary (LMXB) system V404 Cygni is part of a much larger structure—a wide triple system.
Many black holes detected to date appear to be part of a pair. These binary systems comprise a black hole and a secondary object — such as a star, a much denser neutron star, or another black hole — that spiral around each other, drawn together by the black hole’s gravity to form a tight orbital pair.
Now a surprising discovery is expanding the picture of black holes, the objects they can host, and the way they form.
In a study appearing today in Nature, physicists at MIT and Caltech report that they have observed a “black hole triple” for the first time. The new system holds a central black hole in the act of consuming a small star that’s spiraling in very close to the black hole, every 6.5 days — a configuration similar to most binary systems. But surprisingly, a second star appears to also be circling the black hole, though at a much greater distance. The physicists estimate this far-off companion is orbiting the black hole every 70,000 years.