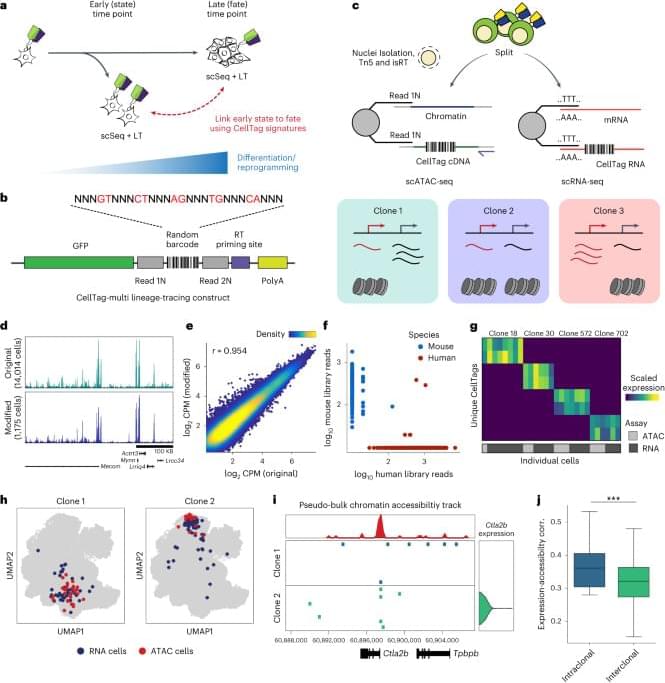
To enable prospective lineage tracing with chromatin accessibility capture, we have developed ‘CellTag-multi’. CellTag-multi is based on our previous CellTagging technology, which uses sequential lentiviral delivery of CellTags (heritable random barcodes) to enable the construction of multilevel lineage trees7,16. Here we introduce a strategy in which CellTags, expressed as polyadenylated transcripts, can be captured in both scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq assays allowing for independent tracking of clonal transcriptional and epigenomic state.
We validate this method using in vitro hematopoiesis, a well-characterized model of multilineage differentiation, and demonstrate highly accurate reconstruction of lineage relationships and capture of lineage-specific progenitor cell states across scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq. Moreover, the addition of chromatin accessibility information to gene expression allows for an improvement in the prediction of differentiation outcome from early progenitor state. We also deploy CellTag-multi in the direct lineage reprogramming of fibroblasts to iEPs, to characterize early gene regulatory changes in rare subpopulations of cells that successfully reprogram. This application reveals how chromatin is remodeled following the expression of reprogramming TFs, enabling deeper insight into gene regulatory network reconfiguration. We uncover the TF Foxd2 as a facilitator of on-target reprogramming, increasing the efficiency of MEF to iEP conversion.