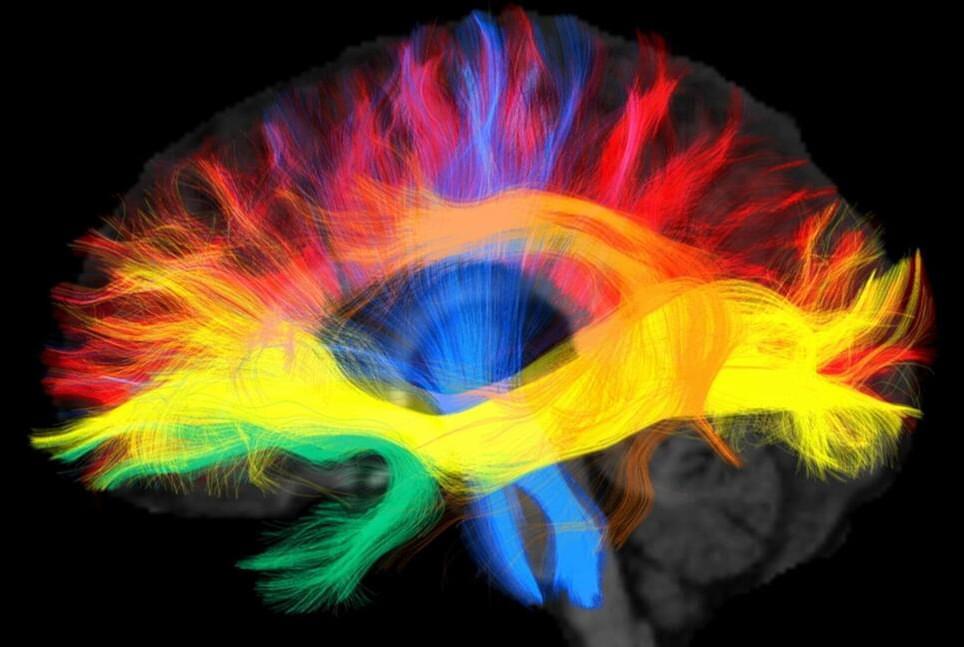
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig have found evidence that the language we speak shapes the connectivity in our brains that may underlie the way we think. With the help of magnetic resonance tomography, they looked deep into the brains of native German and Arabic speakers and discovered differences in the wiring of the language regions in the brain.
Xuehu Wei, who is a doctoral student in the research team around Alfred Anwander and Angela Friederici, compared the brain scans of 94 native speakers of two very different languages and showed that the language we grow up with modulates the wiring in the brain. Two groups of native speakers of German and Arabic respectively were scanned in a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine.
The high-resolution images not only show the anatomy of the brain, but also allow to derive the connectivity between the brain areas using a technique called diffusion-weighted imaging. The data showed that the axonal white matter connections of the language network adapt to the processing demands and difficulties of the mother tongue.