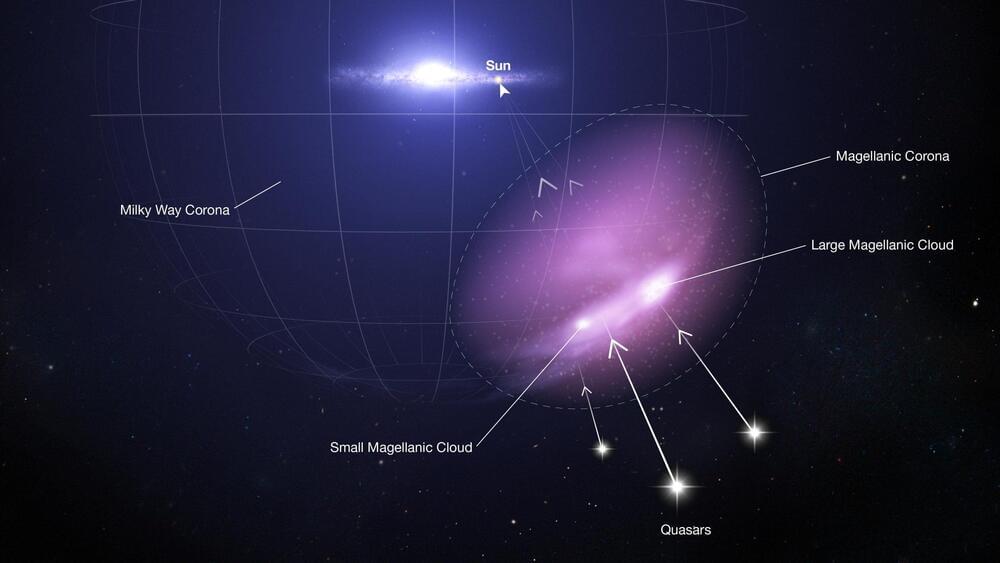
For billions of years, the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds – the Milky Way’s largest satellite galaxies – have followed a perilous journey. Orbiting one another as they are pulled in toward our home galaxy, they have begun to unravel, leaving behind trails of gaseous debris. And yet these dwarf galaxies remain intact, with ongoing vigorous star formation, leaving astronomers baffled.
“A lot of people were struggling to explain how these streams of material could be there,” said Dhanesh Krishnarao, assistant professor at Colorado College. “If this gas was removed from these galaxies, how are they still forming stars?”
A team of astronomers led by Krishnarao has finally found the answer, with the help of data from NASA.