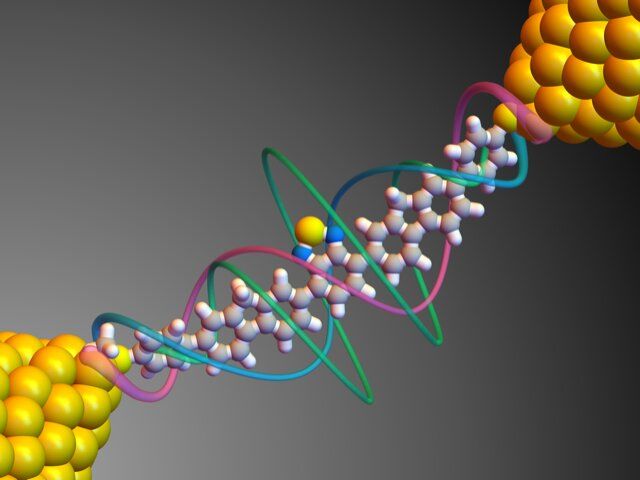
Columbia team discovers 6-nanometer-long single-molecule circuit with enormous on/off ratio due to quantum interference; finding could enable faster, smaller, and more energy-efficient devices.
Researchers, led by Columbia Engineering Professor Latha Venkataraman, report today that they have discovered a new chemical design principle for exploiting destructive quantum interference. They used their approach to create a six-nanometer single-molecule switch where the on-state current is more than 10,000 times greater than the off-state current–the largest change in current achieved for a single-molecule circuit to date.
This new switch relies on a type of quantum interference that has not, up to now, been explored. The researchers used long molecules with a special central unit to enhance destructive quantum interference between different electronic energy levels. They demonstrated that their approach can be used to produce very stable and reproducible single-molecule switches at room temperature that can carry currents exceeding 0.1 microamps in the on-state. The length of the switch is similar to the size of the smallest computer chips currently on the market and its properties approach those of commercial switches. The study is published today in Nature Nanotechnology.