My seventh installment of interesting research papers that I have read over the past few weeks and would like to share with my community.


Weather forecasting is notoriously wonky — climate modeling even more so. But their increasing ability to predict what the natural world will throw at us humans is largely thanks to two things — better models and increased computing power.
Now, a new paper from researchers led by Daniel Klocke of the Max Planck Institute in Germany describes what some in the climate modeling community have described as the “holy grail” of their field — an almost kilometer-scale resolution model that combines weather forecasting with climate modeling.
Technically the scale of the new model isn’t quite 1 sq km per modeled patch — it’s 1.25 kilometers.
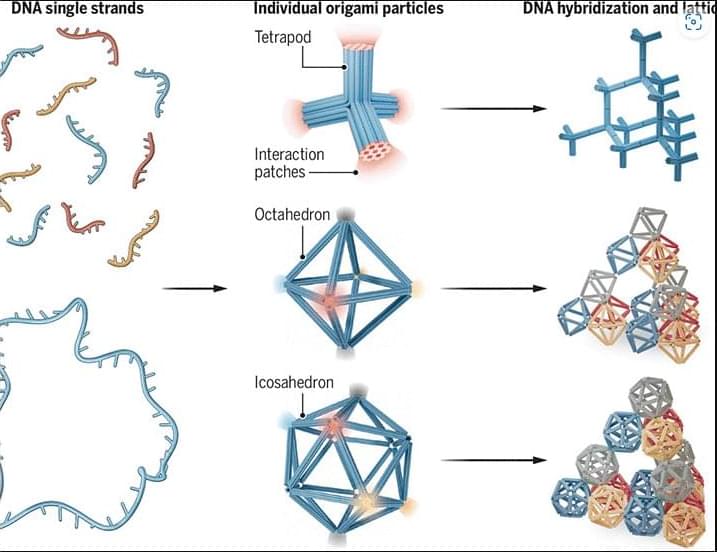
Scientists built these tiny diamond crystals using a technique known as DNA origami, in which DNA molecules fold themselves into elaborate shapes.
Learn more in this 2024 Science Perspective on OrigamiDay.
DNA particles are programmed to assemble with precision into complex lattices.
Zhe Li and Chengde Mao Authors Info & Affiliations
Science
Vol 384, Issue 6697
Pioneering breakthroughs in healthcare — for everyone, everywhere, sustainably.
Komeil Nasrollahi is a seasoned innovation and business‐development leader currently serving as Senior Director of Innovation & Venture Partnerships at Siemens Healthineers (https://www.siemens-healthineers.com/), where he is charged with forging strategic collaborations, identifying new venture opportunities and accelerating transformative healthcare technologies.
With an academic foundation in industrial engineering from Tsinghua University (and additional studies in the Chinese language) and undergraduate work in civil engineering from Azad University in Iran, Komeil blends technical fluency with global business acumen.
Prior to his current role, Komeil held senior positions driving business engagement and international investment, including leading market‐entry and growth initiatives across China and the U.S., demonstrating a strong ability to navigate cross‐cultural, high‐stakes innovation ecosystems.
In his current role, Komeil works at the intersection of healthcare, technology and venture creation—identifying high-impact innovations that align with Siemens Healthineers’ mission to “pioneer breakthroughs in healthcare, for everyone, everywhere, sustainably.”
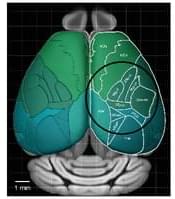
Our ability to perceive, think, or act relies on coordinated activity in large networks of neurons in the brain. This review examines recent progress in connecting ideas from statistical physics, such as maximum entropy methods and the renormalization group, to quantitative experiments that record the electrical activity of thousands of neurons simultaneously. This quantitative bridge between the new data and statistical physics models uncovers new, quantitatively reproducible behaviors and makes clear that abstract theoretical principles in studies of the brain can have the level of predictive power that we expect in other areas of physics.

Imagine you’re watching a movie, in which a character puts a chocolate bar in a box, closes the box and leaves the room. Another person, also in the room, moves the bar from a box to a desk drawer. You, as an observer, know that the treat is now in the drawer, and you also know that when the first person returns, they will look for the treat in the box because they don’t know it has been moved.
You know that because as a human, you have the cognitive capacity to infer and reason about the minds of other people—in this case, the person’s lack of awareness regarding where the chocolate is. In scientific terms, this ability is described as Theory of Mind (ToM). This “mind-reading” ability allows us to predict and explain the behavior of others by considering their mental states.
We develop this capacity at about the age of four, and our brains are really good at it.

Could a tunnel through space and time—long a dream of science fiction—ever exist in theory? According to Arya Dutta, a Ph.D. student in Mathematics at the Katz School, the answer might be yes, at least on paper.
Accepted for publication in the International Journal of Geometric Methods in Modern Physics, Dutta’s study, “Thin-shell Wormhole with a Background Kalb–Ramond Field,” explored a mathematical model of a wormhole—a hypothetical shortcut through spacetime that could, in theory, connect two distant regions of the universe. “A wormhole allows faster-than-light travel or even time travel,” said Dutta. “It hasn’t been observed yet, but theoretical research has advanced a lot.”