Discussions among regulators come as Beijing seeks to achieve self-sufficiency in semiconductor production.
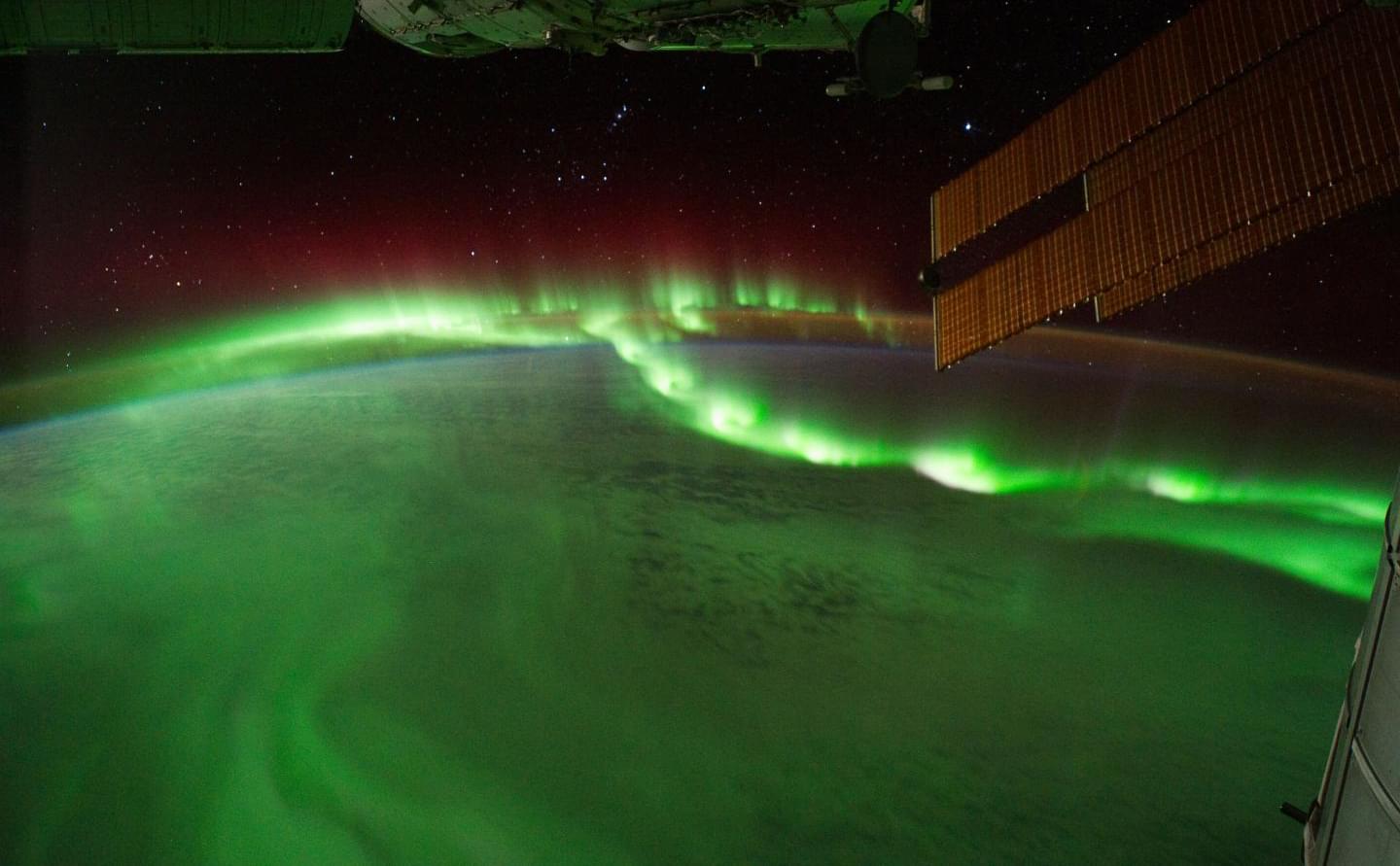



A University of Southampton study has revealed an intriguing new clue in the mystery of what triggers periods of very intense, brightly colored activity during displays of both the southern and northern lights.
Known as a “magnetospheric substorm,” this awe-inspiring phenomenon, which blankets the night sky in green and purple, is almost always preceded by what space scientists call “auroral beads”—a necklace-like wave of multiple luminous points of light which eventually evolve into the storm.
Southampton scientists have now shown there is a link between these auroral beads and the intensity of low frequency radio waves above the aurora in Earth’s magnetosphere—a vast area around our planet that is dominated by its magnetic field. Their findings are published in Nature Communications.
An exploration of ten spooky aspects of the multiverse and our universe within it.
https://www.patreon.com/johnmichaelgodier.
Music:
Cylinder Eight by Chris Zabriskie is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/.…
Source: http://chriszabriskie.com/cylinders/
Artist: http://chriszabriskie.com/
Cylinder Five by Chris Zabriskie is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/.…
Source: http://chriszabriskie.com/cylinders/
Artist: http://chriszabriskie.com/
Darkest Child by Kevin MacLeod is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
I hope this message finds you well. My name is Nick, and I am writing to you in the spirit of openness and honesty. In 2025 I underwent emergency medical treatment for a skull tumor, and after initial interventions failed I received CAR T-cell therapy at City of Hope Cancer Centers in California. This journey along with the rest of the year has been one of the most challenging years of my life.
Because of cancer treatments and multiple hardships throughout the year, medical bills, recovery needs, a car accident, and not allowed to return to work yet, I established a GoFundMe campaign to help cover necessary expenses and give myself a chance at recovery and Here’s the link to the campaign:
I understand Lifeboat core values and mission is towards making the world a better place and after years of growing with this community, which is why I believe that human life, is a part of what makes our future worth safeguarding.
I’m reaching out because we all have our own personal humanitarian crisis and unfortunate this year is mine. I appreciate any support, be it words of encouragement or donating to my campaign is all deeply appreciated. Thank you for letting me a part of this community. The link is posted in a comment.
A special THANK YOU to Eric Klien for being supportive and donating.
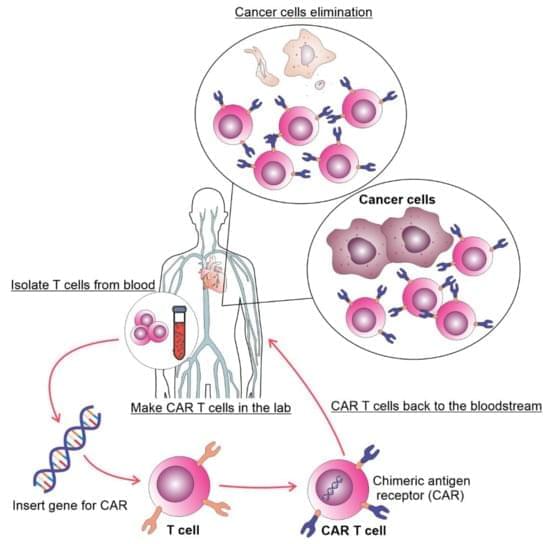
Chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR T) cell therapy achieved remarkable success in B-cell leukemia and lymphoma which led to its incorporation in treatment protocols for these diseases. CAR T cell therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients showed less success compared to other malignant tumors. In this review, we discuss the published results regarding CAR T cell therapy of CLL, possible mechanisms of failures and expected developments.
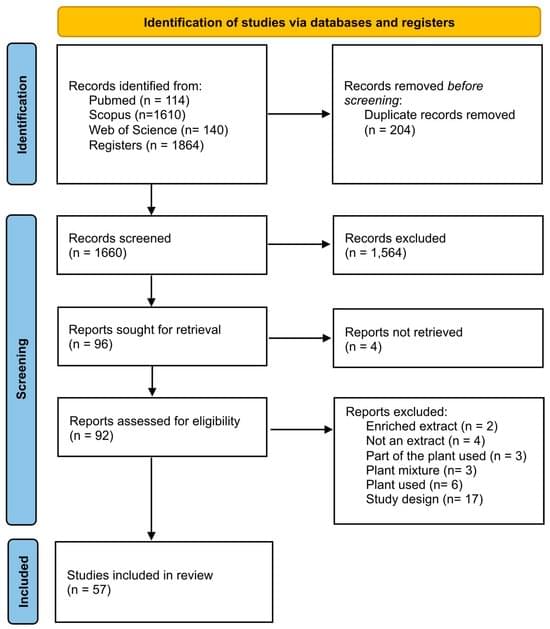
Background/Objectives: The species Mikania glomerata and Mikania laevigata are commonly referred to as guaco. Their preparations are used in traditional Brazilian medicine, mainly to address respiratory conditions affecting the upper airways. Considering the wide popular use of this species, the present study aims to survey the biological activities of guaco that have already been proven in the literature and to generate an evidence gap map for these biological activities. Methods: A scoping review was conducted using the electronic databases PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science (7 October 2024), which included all studies that have evaluated the biological activities of the leaves of the M. glomerata or M. laevigata species. Results: A total of 57 studies (31 assessed only M. glomerata, 17 assessed only M.

Using a CRISPRa-based approach, Elvir Becirovic & team activated retinal disease-related genes in isolated human cells, establishing a minimally invasive diagnostic method for inherited retinal diseases:
The fundus autofluorescence image is from a patient with confirmed ABCA4-associated retinal disease (STGD1).
1Laboratory for Retinal Gene Ther apy, Department of Ophthalmology, University Hospital Zurich, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland.
2Department of Ophthalmology, LMU University Hospital, LMU Munich, Munich, Germany.
3Department of Pharmacy – Center for Drug Research, LMU Munich, Munich, Germany.

Most patients with lung cancer are diagnosed when they present with symptoms, they have advanced stage disease, and curative treatment is no longer an option. An effective screening test has long been desired for early detection with the goal of reducing mortality from lung cancer. Sputum cytology, chest radiography, and computed tomography (CT) scan have been studied as potential screening tests. The National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) demonstrated a 20% reduction in mortality with low-dose CT (LDCT) screening, and guidelines now endorse annual LDCT for those at high risk. Implementation of screening is underway with the desire that the benefits be seen in clinical practice outside of a research study format. Concerns include management of false positives, cost, incidental findings, radiation exposure, and overdiagnosis.
Cigarette smoking is the number one risk factor for lung cancer. In the United States, cigarette smoking is linked to about 80% to 90% of lung cancer deaths. Using other tobacco products such as cigars or pipes also increases the risk for lung cancer. Tobacco smoke is a toxic mix of more than 7,000 chemicals. Many are poisons. At least 70 are known to cause cancer in people or animals.
People who smoke cigarettes are 15 to 30 times more likely to get lung cancer or die from lung cancer than people who do not smoke. Even smoking a few cigarettes a day or smoking occasionally increases the risk of lung cancer. The more years a person smokes and the more cigarettes smoked each day, the more risk goes up.
People who quit smoking have a lower risk of lung cancer than if they had continued to smoke, but their risk is higher than the risk for people who never smoked. Quitting smoking at any age can lower the risk of lung cancer.

Scientists have unveiled a technique that uses ‘molecular antennas’ to direct electrical energy into insulating nanoparticles. This approach creates a new family of ultra-pure near-infrared LEDs that could be used in medical diagnostics, optical communication systems, and sensitive detectors.
Researchers at the Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge have discovered how to drive electrical current into materials that normally do not conduct, a feat previously thought impossible under normal conditions. By attaching carefully chosen organic molecules that act like tiny antennas, they have built the first light-emitting diodes (LEDs) from insulating nanoparticles. Their work, reported in Nature, points toward a new generation of devices for deep-tissue biomedical imaging and high-speed data transmission.