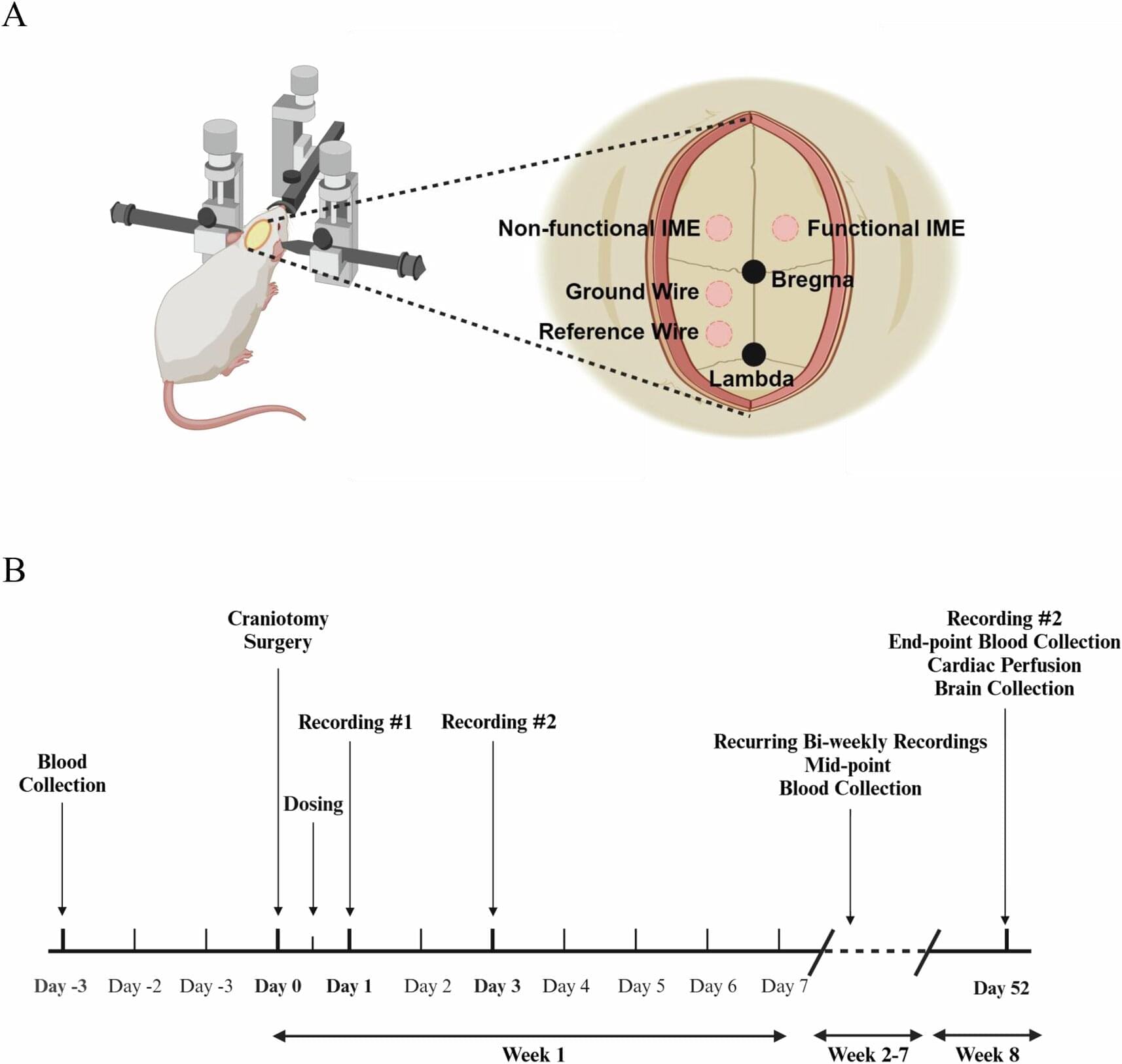
Canine induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells possess the ability to differentiate into any type of cell, making them a useful tool for investigating common canine diseases and disease states, including those of humans.
When culturing iPS cells, a culture substrate is required to serve as a scaffold for the cells, which adhere to it and proliferate. Without the scaffold, the cells die or fail to differentiate.
Currently, recombinant proteins derived primarily from humans are used as culture substrates for canine iPS cells. However, these human-derived elements are an alien substance for dog cells, leading to immune rejection and making clinical use difficult.