A new study reveals that when interacting with AI tools like ChatGPT, everyone—regardless of skill level—overestimates their performance.


A new report suggests Sam Altman is building a brain interface using sound waves, potentially rivaling Elon Musk’s Neuralink.
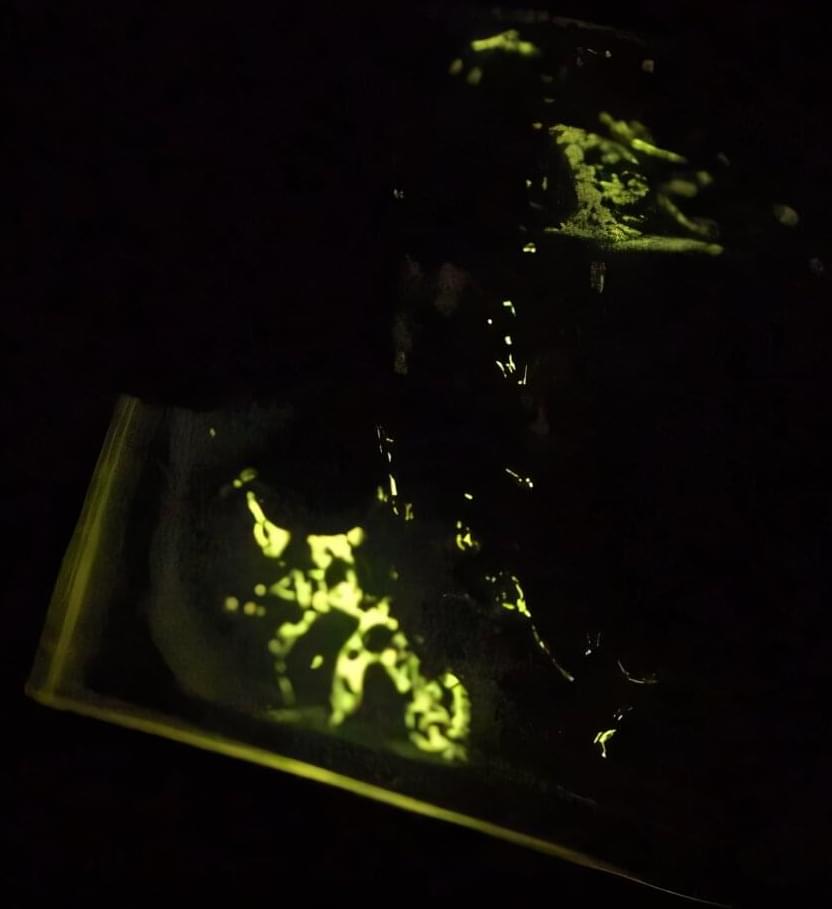
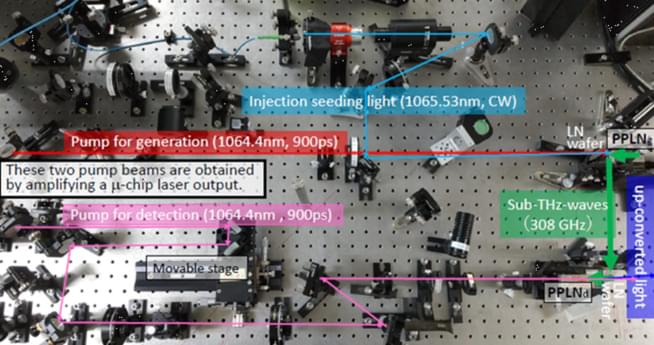

In the 17th century, Francis Bacon described a simple experiment—scraping and fracturing hard sugar in the dark to see sparks of light. This phenomenon is called mechanoluminescence (ML) or triboluminescence (TL), the process of materials emitting light under mechanical stimulation, like grinding or crushing. Usually, ML properties of luminescent compounds are observed in rigid crystalline systems, which limits their real-world applications.
Now, researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have found a way to generate ML in non-crystalline materials, bringing a new wave of potential applications in engineering, industrial safety and beyond.
“Mechanical stimulation of crystals causes fractures. As the crystals are damaged and break down in size, they also start to lose their ML properties, which vastly restricts their application. In crystals, ML is highly dependent on structure and packing, adding complex design requirements. That’s why we were interested in amorphous ML materials with longer-lasting luminescence,” explains Professor Julia Khusnutdinova, head of the Coordination Chemistry and Catalysis Unit at OIST.
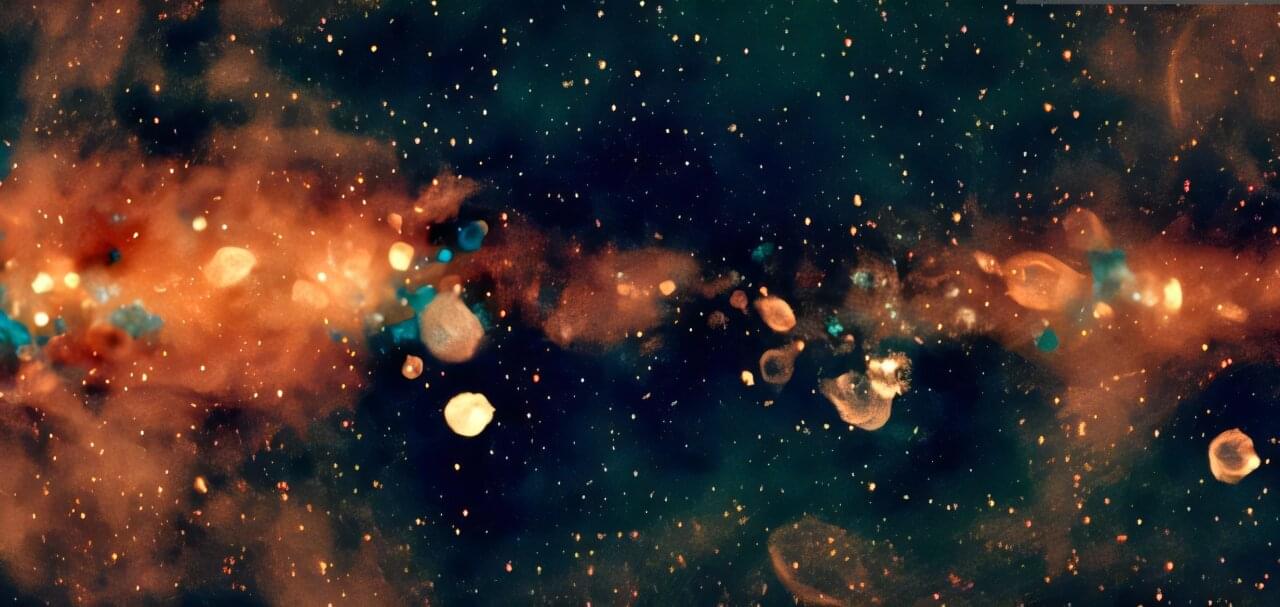


Astronomers from the International Centre of Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) have created the largest low-frequency radio color image of the Milky Way ever assembled. This spectacular new image captures the Southern Hemisphere view of our Milky Way galaxy, revealing it across a wide range of radio wavelengths, the colors of radio light.
A paper describing this work appears in Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia.
It provides astronomers with new ways to explore the birth, evolution, and death of stars in our galaxy.
Deeper insight into PPIs is essential for advancing the development of new treatments and vaccines.
PLM-Interact offers a powerful new lens into these critical mechanisms.
The key to PLM-Interact’s success lies in its training. Leveraging the supercomputer, the researchers trained the model on as many as 421,000 human protein pairs.
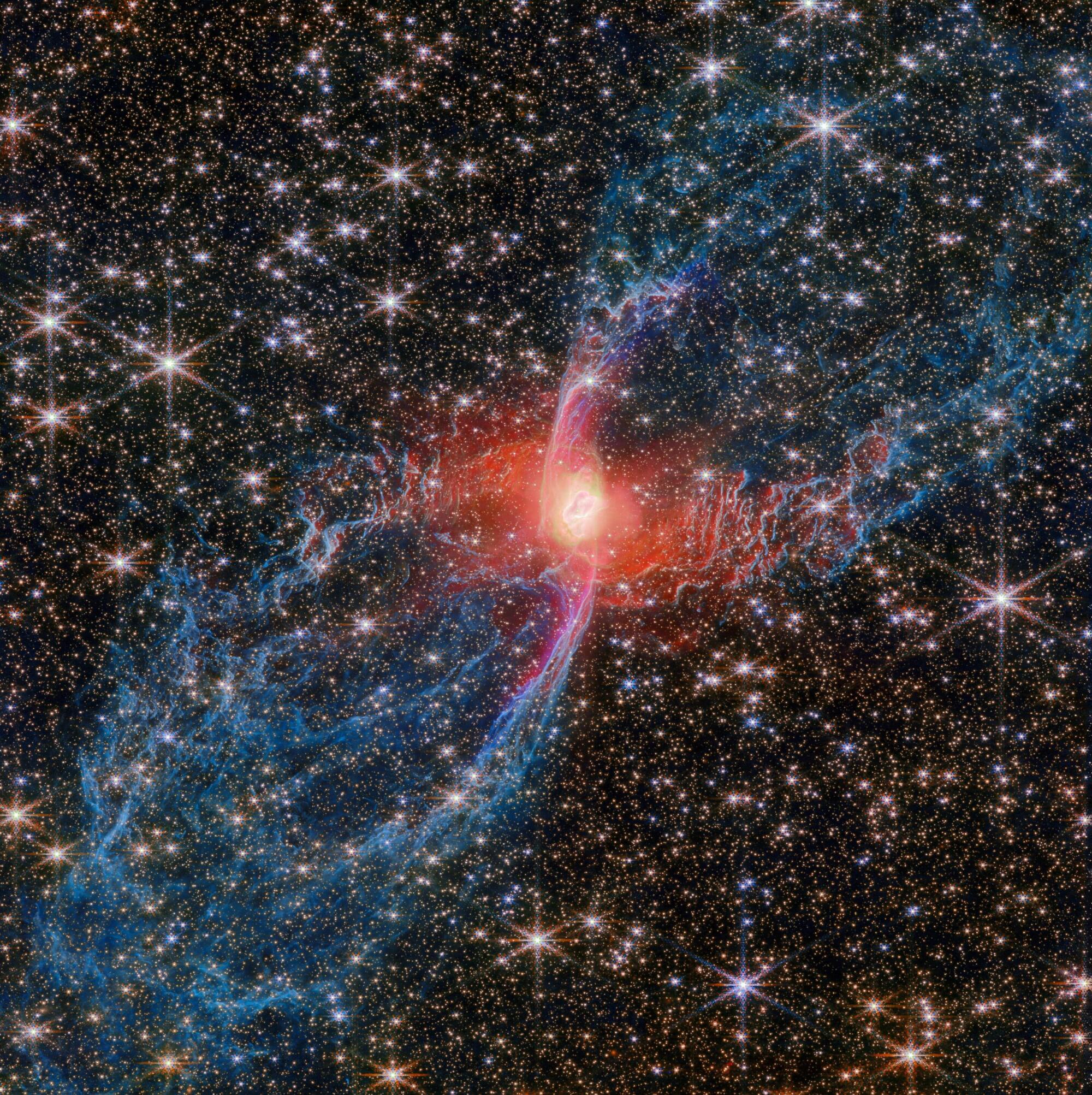


This new NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope Picture of the Month features a cosmic creepy-crawly called NGC 6537—the Red Spider Nebula. Using its Near-InfraRed Camera (NIRCam), Webb has revealed never-before-seen details in this picturesque planetary nebula with a rich backdrop of thousands of stars.
Planetary nebulae like the Red Spider Nebula form when ordinary stars like the sun reach the end of their lives. After ballooning into cool red giants, these stars shed their outer layers and cast them into space, exposing their white-hot cores. Ultraviolet light from the central star ionizes the cast-off material, causing it to glow. The planetary nebula phase of a star’s life is as fleeting as it is beautiful, lasting only a few tens of thousands of years.
The central star of the Red Spider Nebula is visible in this image, glowing just brighter than the webs of dusty gas that surround it. The surprising nature of the nebula’s tremendously hot and luminous central star has been revealed by Webb’s NIRCam.
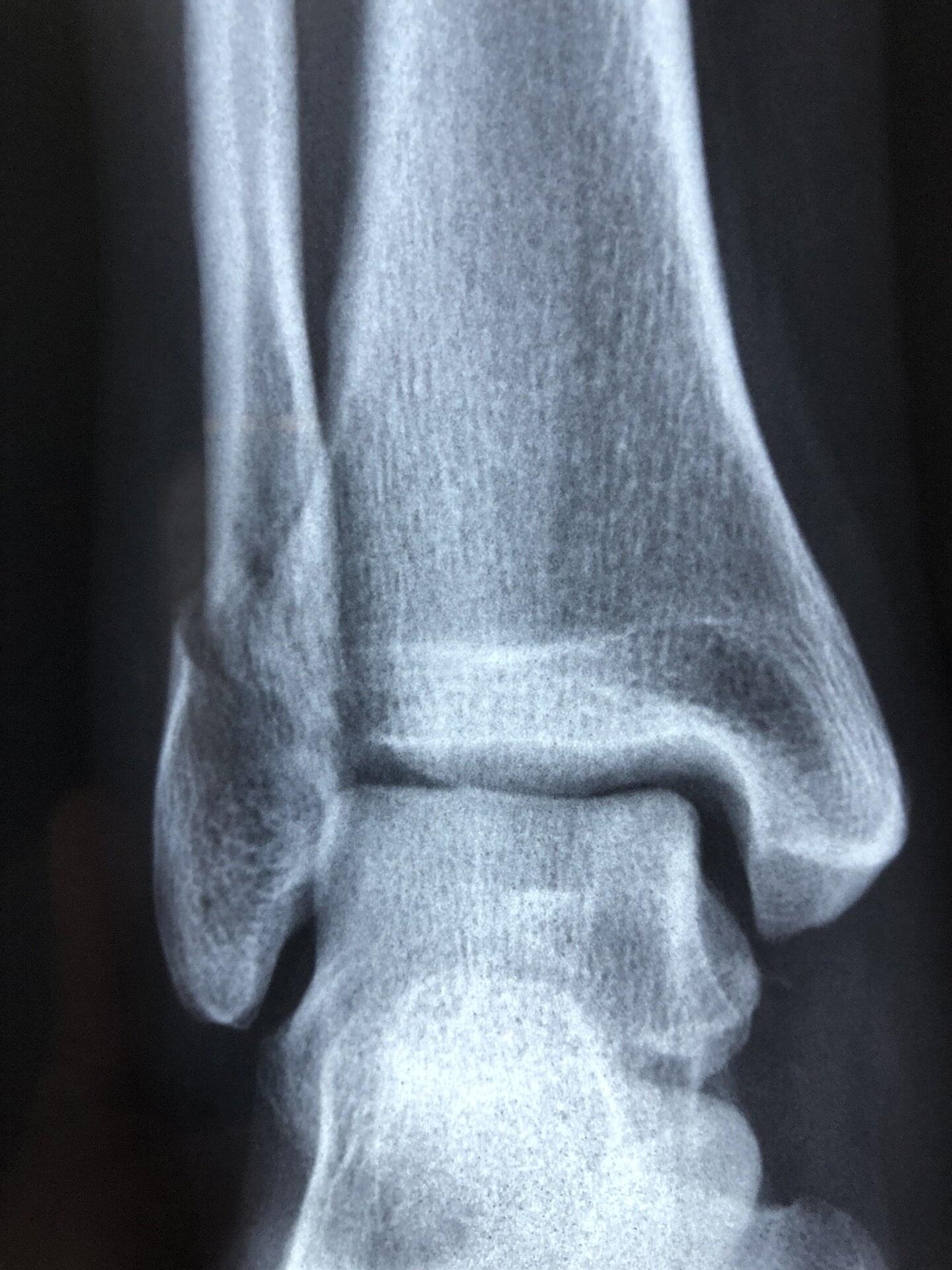
Peripheral afferent neurons—nerves that send signals from all areas of the body to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)—are known to infiltrate and grow within malignant bone tumors called osteosarcomas, often accompanied by severe pain.
In a study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a multicenter research team led by Johns Hopkins Medicine reports that two analgesic drugs, bupivacaine and rimegepant, which are used to inhibit the formation and functioning of these neurons, not only relieve tumor-associated pain in laboratory mice, but also slow the unchecked growth of the cancer.
“Our findings suggest that these two medications—already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration [FDA] for relieving nerve pain [bupivacaine] and migraines [rimegepant]—might one day be repurposed as anti-tumor therapies,” says study lead author Sowmya Ramesh, Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher in pathology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.