Scientists have developed tiny metal-oxide particles that push cancer cells past their stress limits while sparing healthy tissue.

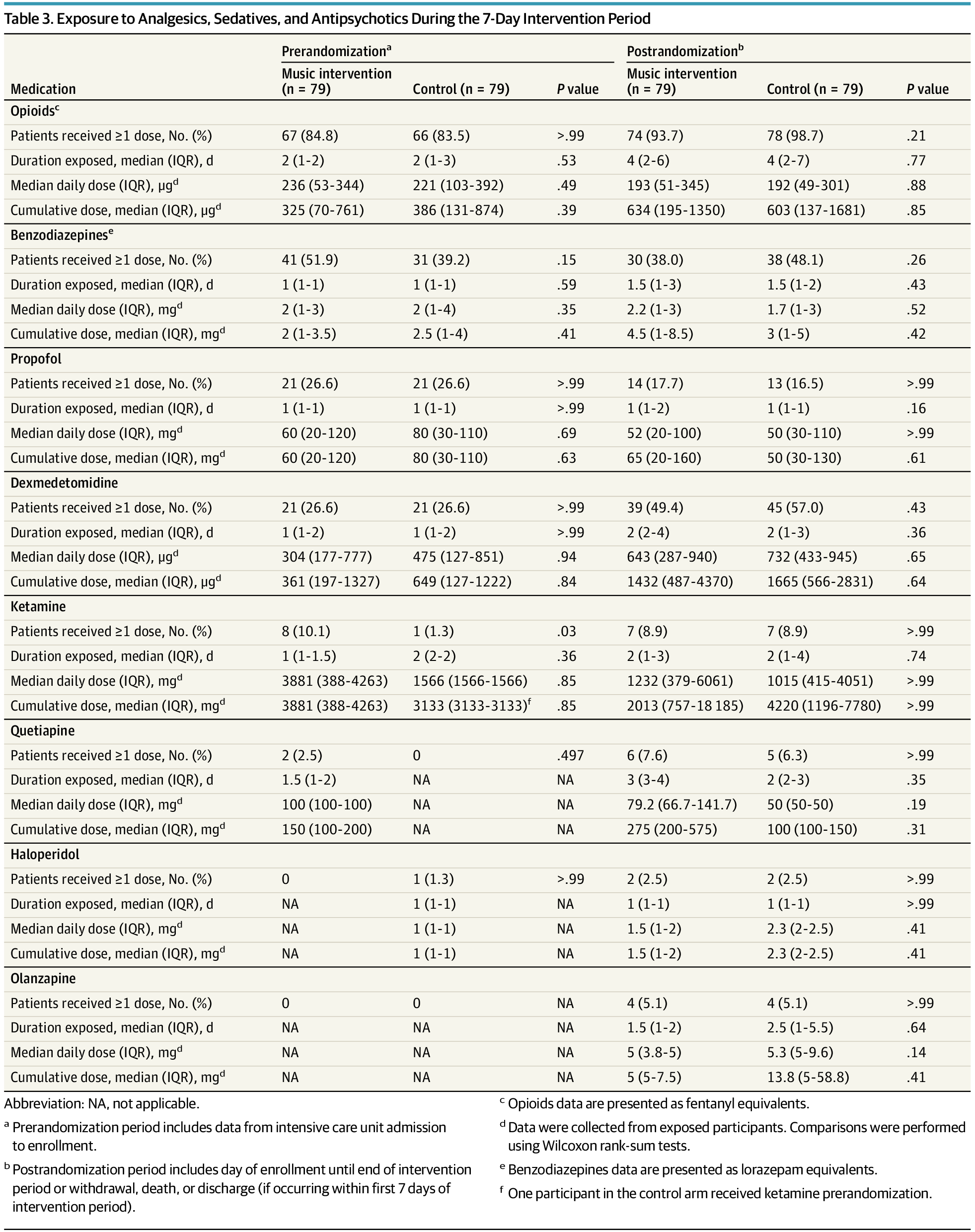
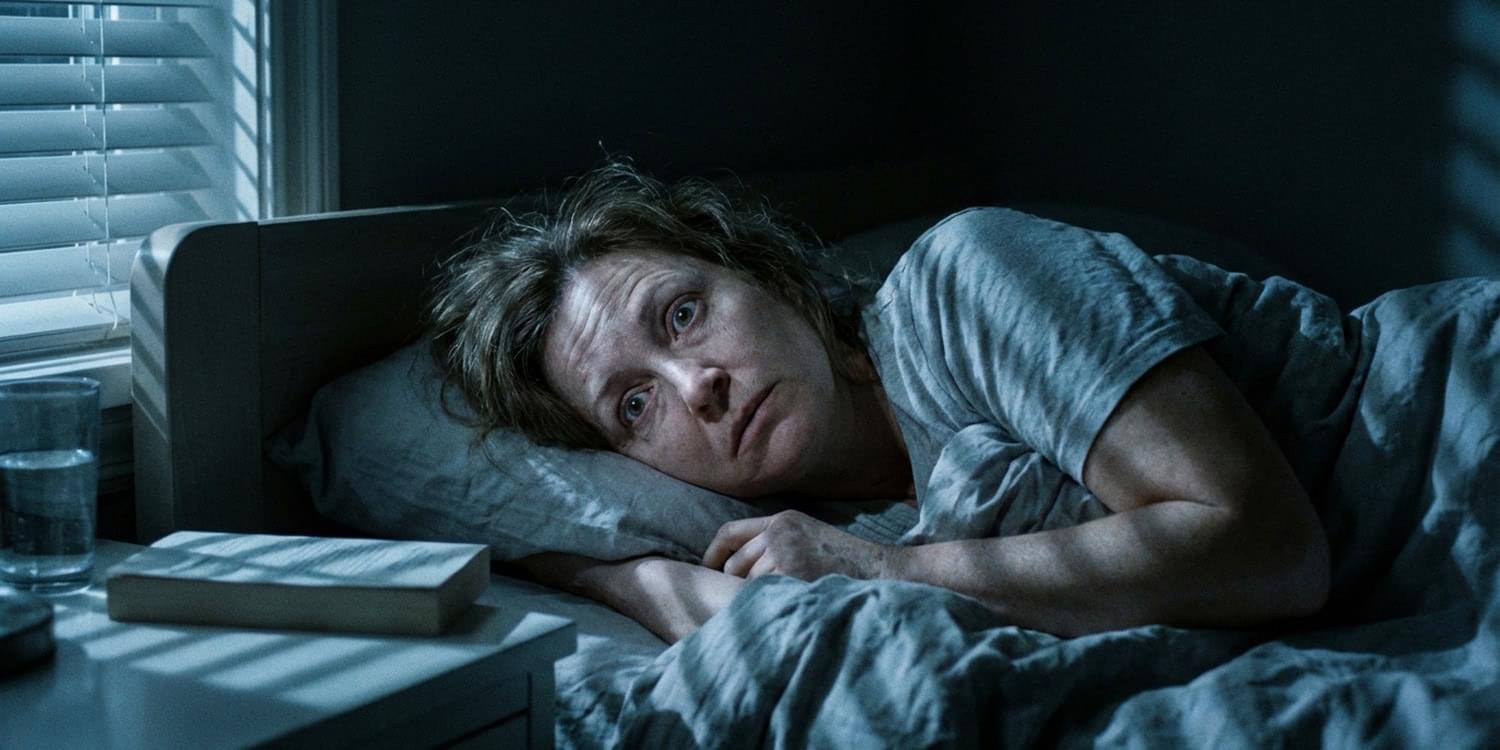
A slow-tempo music intervention did not reduce delirium duration, severity, pain, or anxiety in mechanically ventilated older adults in the ICU.
Question Among critically ill, mechanically ventilated older adults in the intensive care unit, does a music-listening intervention reduce delirium, pain, or anxiety?
Findings In this randomized clinical trial of 158 mechanically ventilated older adults, a twice-daily music intervention delivered via noise-canceling headphones and tablets for up to 7 days did not demonstrate a statistically significant decrease in delirium duration, delirium severity, pain, or anxiety.
Meaning A music-listening intervention did not improve delirium, pain, or anxiety among critically ill older adults.
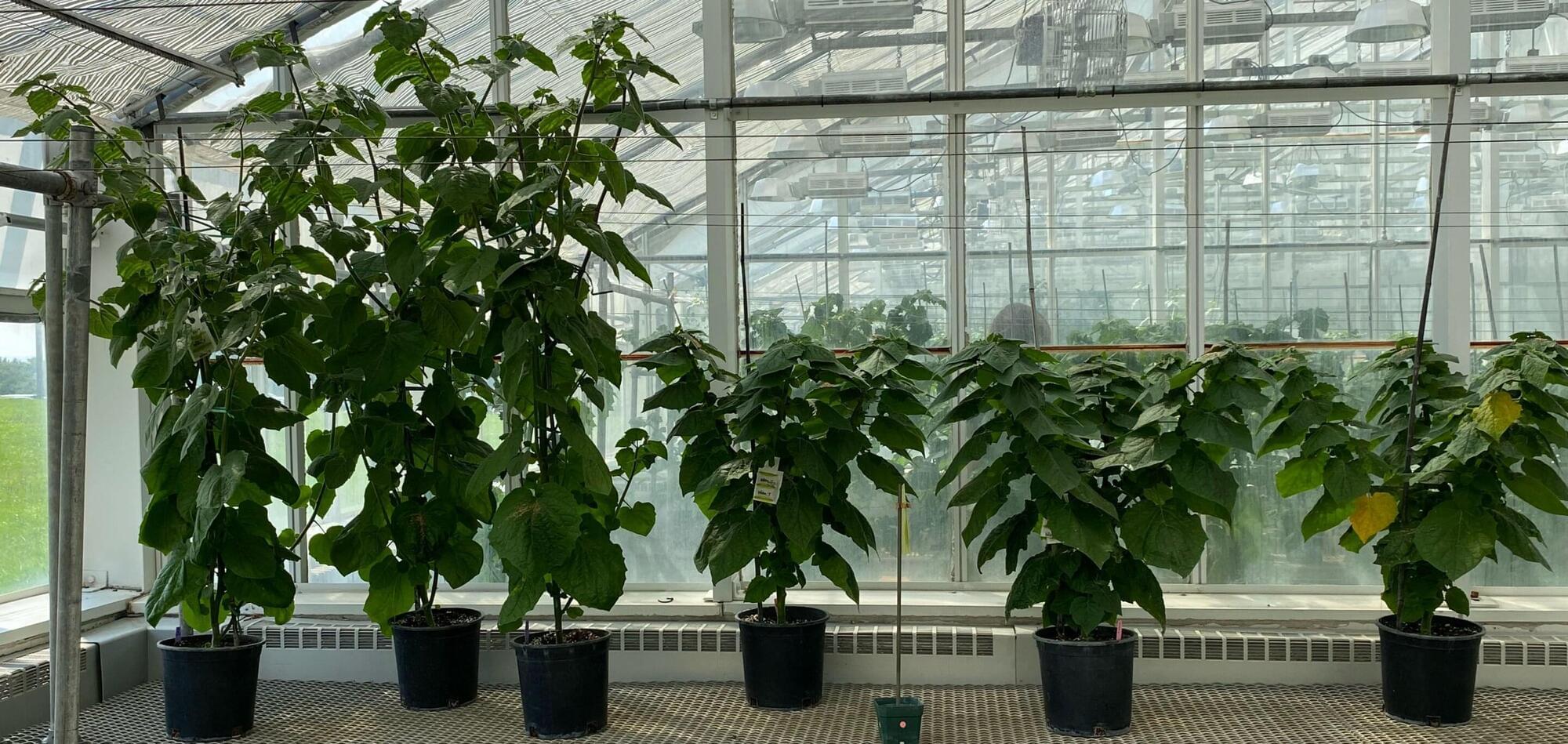

Goldenberries taste like a cross between pineapple and mango, pack the nutritional punch of a superfood, and are increasingly popular in U.S. grocery stores. But the plants that produce these bright yellow-orange fruits grow wild and unruly—reaching heights that make large-scale farming impractical.
Researchers at the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) helped solve that problem. Using CRISPR gene editing, a collaborative team including BTI professor Joyce Van Eck engineered compact goldenberry plants that are 35% shorter than their wild relatives, making them viable for commercial agriculture.
“Goldenberry has tremendous potential as a nutritious crop, but its large, bushy growth habit has hindered commercial production,” said Van Eck. “These new compact plants can be grown at higher density, don’t require extensive staking or trellising, and are much easier to maintain and harvest.”
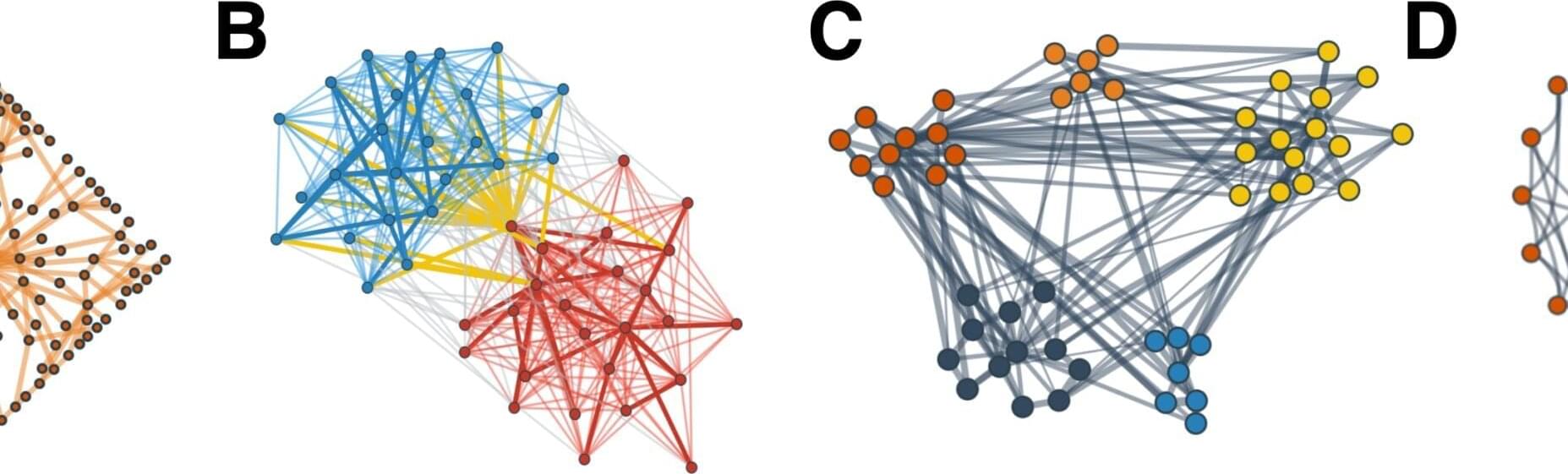
When large language models (LLMs) make decisions about networking and friendship, the models tend to act like people, across both synthetic simulations and real-world network contexts.
Marios Papachristou and Yuan Yuan developed a framework to study network formation behaviors of multiple LLM agents and compared these behaviors against human behaviors. The paper is published in the journal PNAS Nexus.

Interactions among viruses can help them succeed inside their hosts or impart vulnerabilities that make them easier to treat. Scientists are learning the ways viruses mingle inside the cells they infect, as well as the consequences of their socializing.
Ph.D. student Alexander J. Robertson in the Molecular & Cellular Biology program at the University of Washington is among those scientists.
“I study the evolution of antimicrobial resistance through mechanisms which require interaction between microbes,” he explained.