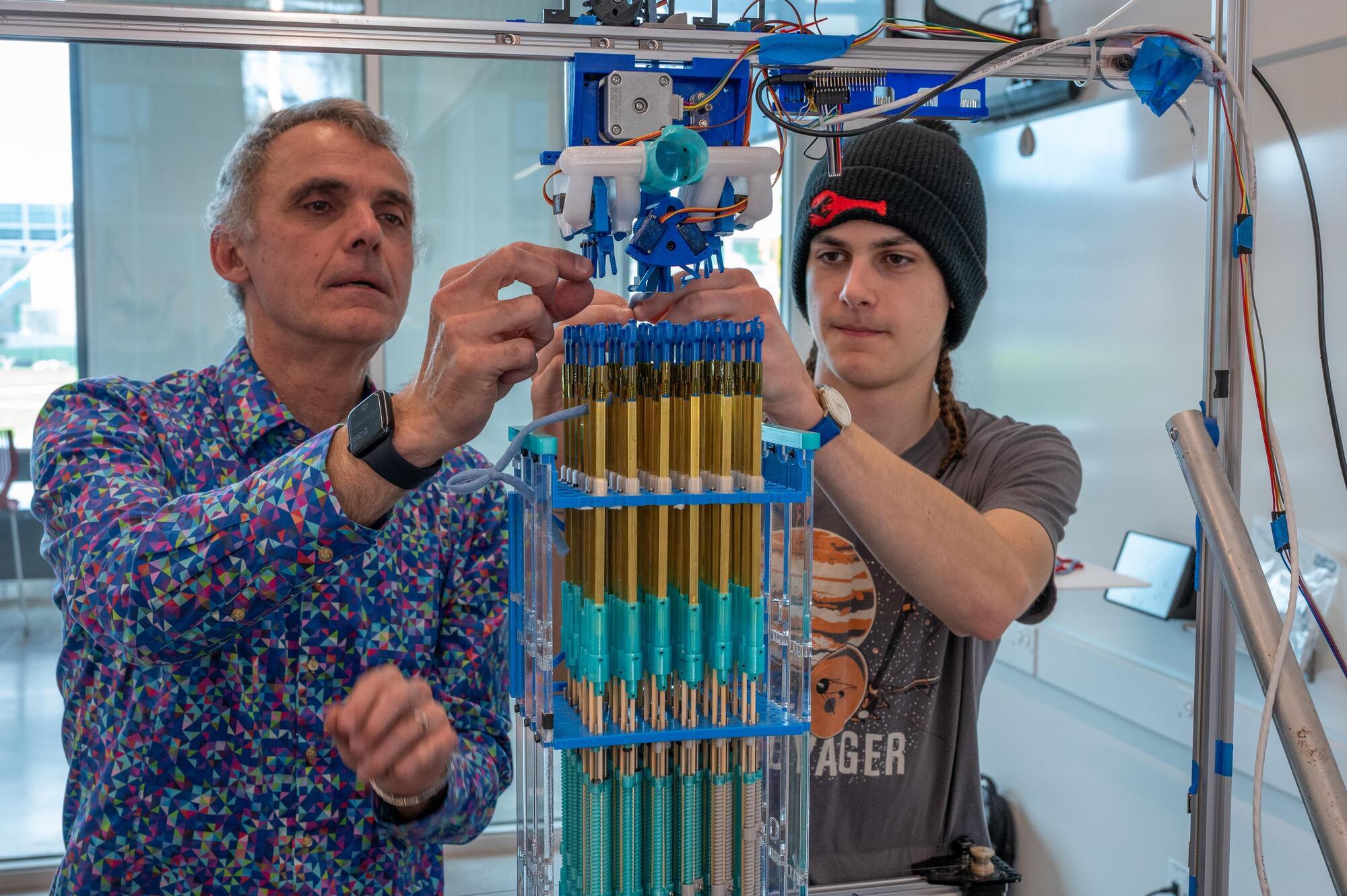
If you find 3D printers to be just a little too coldly futuristic, this contraption might be more to your liking. Scientists from Cornell University have created a machine that knits solid 3D objects out of nice old-timey conventional yarn.
The prototype device is made mainly of 3D-printed components, and incorporates a bed of knitting needles arranged in a 6 × 6 block. A motorized knitting head dispenses yarn to any of those needles in sequence, as determined by a program on a computer that’s controlling it.
Each of the needles in turn consists of a 3D-printed symmetrical double hook connected to a brass support tube. Because the front and rear sections of the hook move independently, it’s possible for the device to either knit or purl, depending on which section of the hook picks up the first loop of yarn.