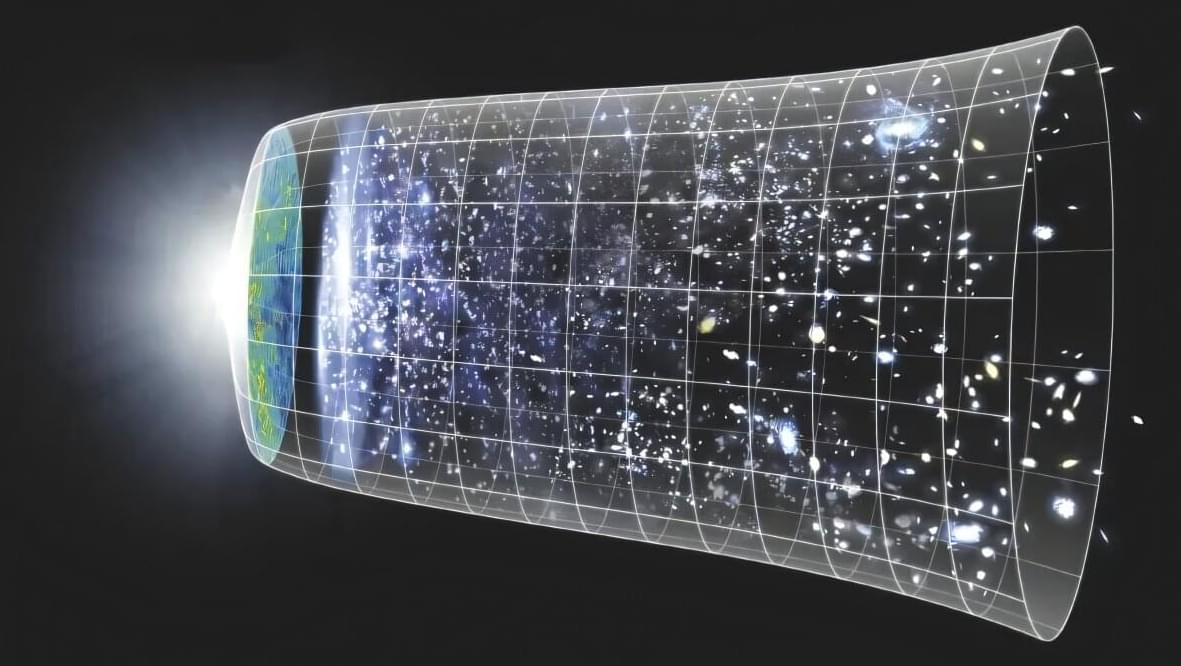
We have known for several decades that the universe is expanding. Scientists use multiple techniques to measure the present-day expansion rate of the universe, known as the Hubble constant. These methods are internally consistent and based on the same physics, so all observed values of the Hubble constant should agree. But those that come from early-universe datasets disagree with those that come from late-universe datasets. This problem is known as the Hubble tension and is considered to be one of the most significant open questions in cosmology.
Now a team of astrophysicists, cosmologists, and physicists at The Grainger College of Engineering at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and at the University of Chicago has developed a novel way to compute the Hubble constant using gravitational waves—tiny ripples in the spacetime fabric. The researchers were able to improve upon the accuracy of prior gravitational-wave methods of measuring the Hubble constant. As our capability to observe gravitational waves improves in the future, this new method can be used to make even more accurate measurements of the Hubble constant, bringing scientists closer to resolving the Hubble tension.
Illinois Physics Professor Nicolás Yunes said, “This result is very significant—it’s important to obtain an independent measurement of the Hubble constant to resolve the current Hubble tension. Our method is an innovative way to enhance the accuracy of Hubble constant inferences using gravitational waves.” Yunes is the founding director of the Illinois Center for Advanced Studies of the Universe (ICASU) on the Urbana campus.