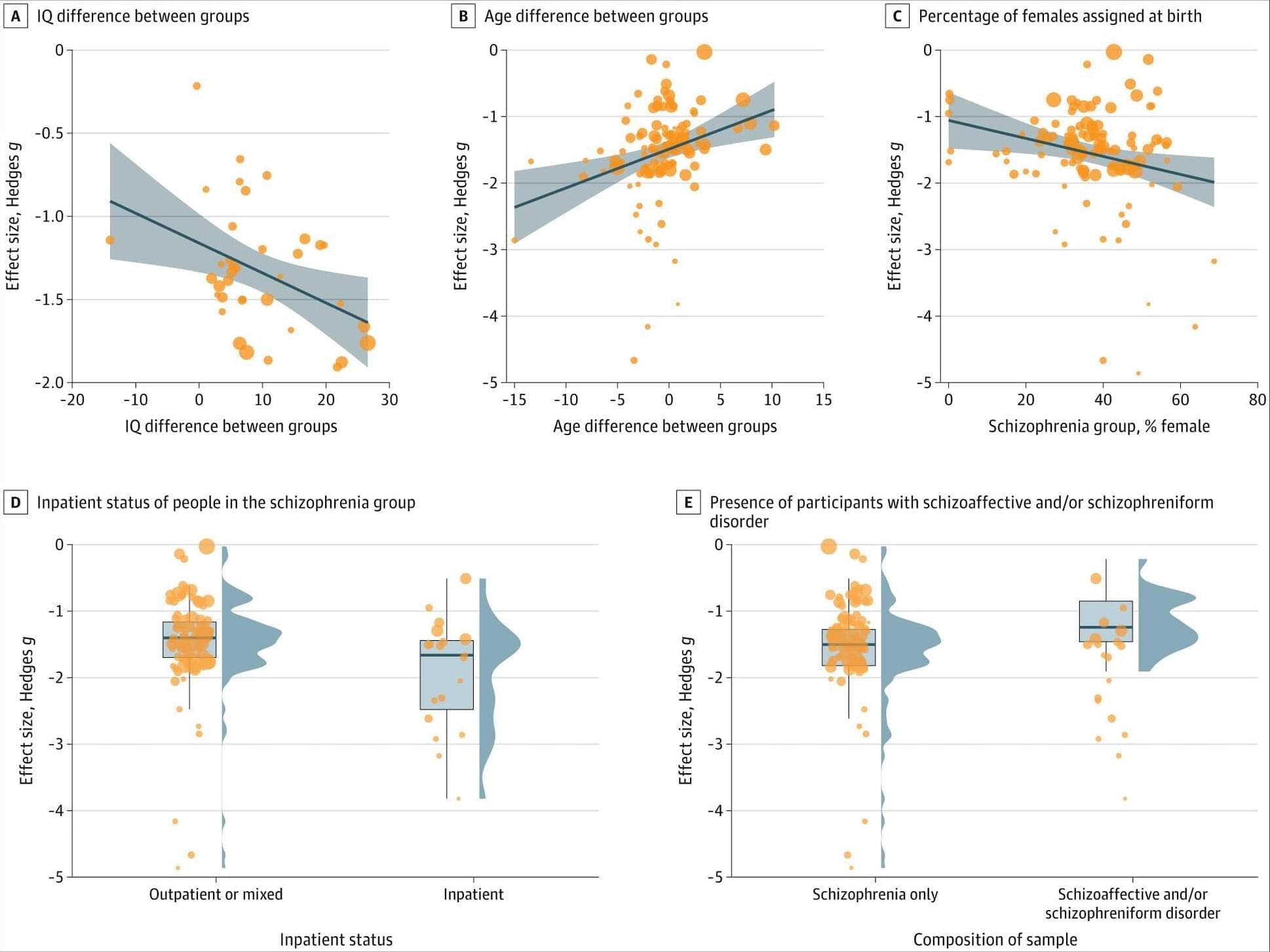
Meta-analysis of 115 studies evaluating cognitive function in people with Schizophrenia confirms that processing speed, especially as measured by symbol coding tasks, remains among the most impaired cognitive domains compared to controls.
This impairment was reliably more severe than that observed in most other tested cognitive domains, suggesting processing speed may be central to broader cognitive deficits in this population and may relate to altered brain connectivity.
This meta-analysis provides an updated review of the evidence for a central processing speed impairment in people with schizophrenia.