The Talon-A2 vehicle air-launched from the world’s biggest aircraft, piloted itself at hypersonic speeds, and landed in California.


Directly connected to bone, the leg allows wearers to climb stairs, walk at a normal speed, and kick balls.
The hand could lead to advanced prosthetic hands for amputees or robots with the dexterity and strength to perform household task.
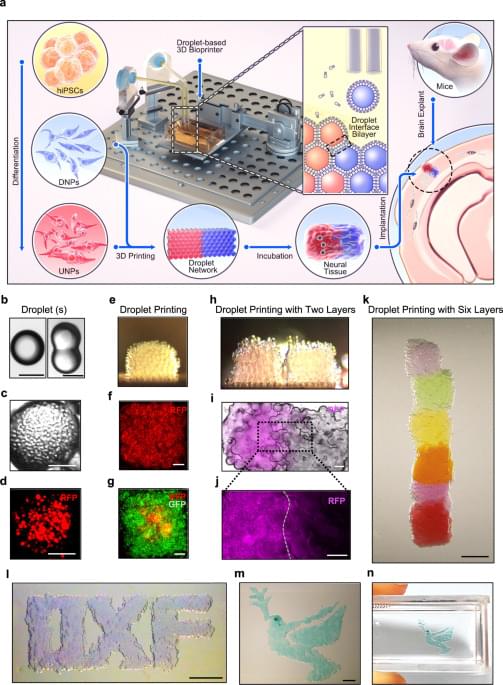
Brain injuries can result in significant damage to the cerebral cortex, and restoring the cellular architecture of the tissue remains challenging. Here, the authors use a droplet printing technique to fabricate a simplified human cerebral cortical column and demonstrate its functionality and potential for future personalized therapy approaches.
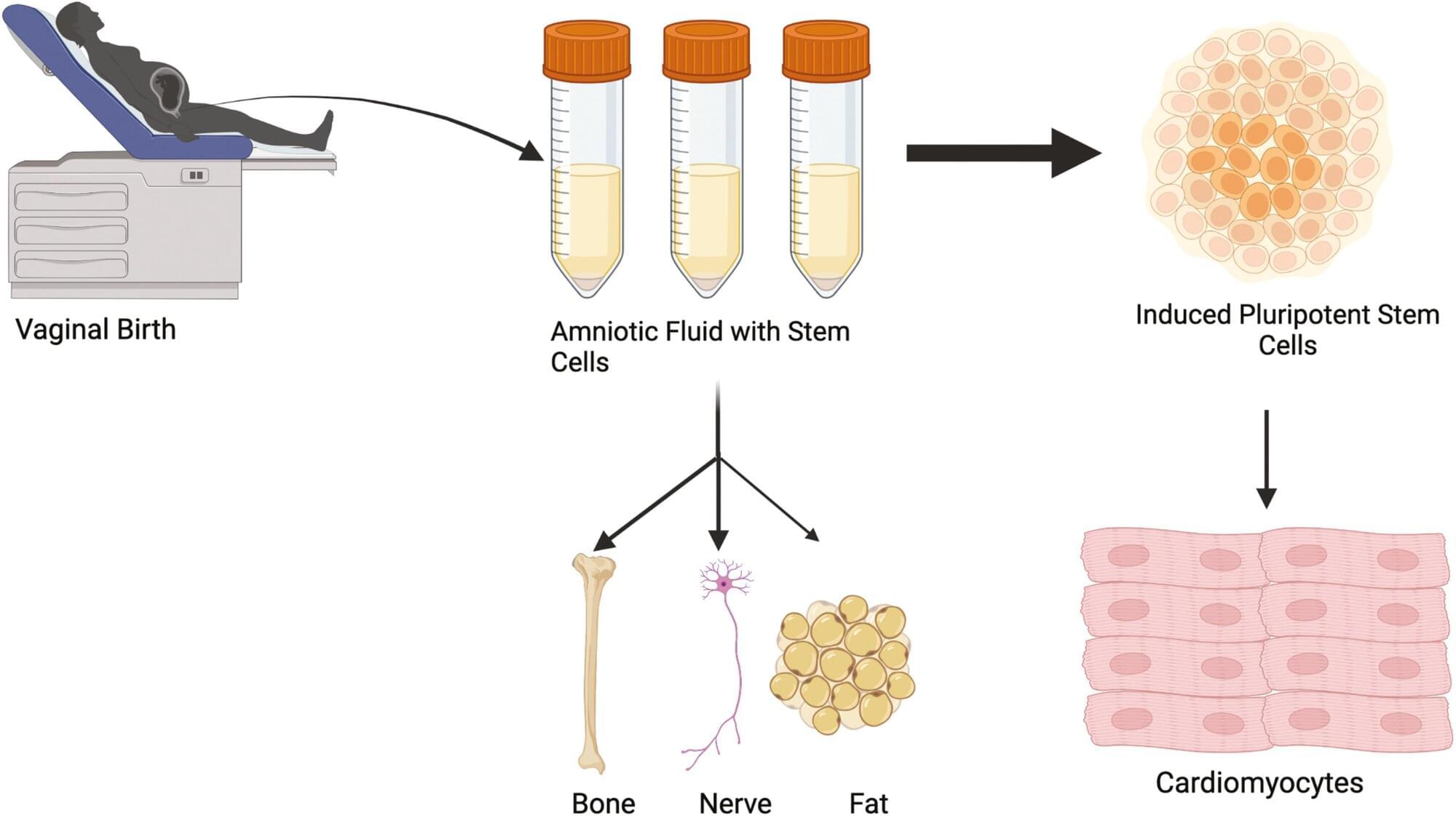
Researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have discovered that amniotic fluid stem cells can be safely collected from vaginal fluid after childbirth rather than relying on more invasive methods that can pose some risk to the mother and fetus.
“We can then turn those cells into beating heart cells and use them later in treating congenital heart defects,” said the study’s senior author Jeffrey Jacot, Ph.D., associate professor of pediatrics and bioengineering at the University of Colorado Center for Bioengineering in the CU School of Medicine. “These results allow for an expanded and readily available source of amniotic stem cells beyond traditional collection through amniocentesis.”
The study was published today in the journal Stem Cells Translational Medicine.
The slimy, segmented, bottom-dwelling California blackworm is about as unappealing as it gets—but get a few dozen or thousand together, and they form a massive, entangled blob that seems to take on a life of its own.
It may be the stuff of nightmares, but it is also the inspiration for a new kind of robot. “We look at the biological system, and we say, ‘Look how cool this is,’” said Senior Research Fellow Justin Werfel, who heads the Designing Emergence Laboratory at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS). Werfel is hooked on creating a robotic platform that’s inspired by a wriggling ball of blackworms and that, like the worms, can accomplish more as a group than as individuals.
Recently garnering a Best Paper on Mechanisms and Design award at the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, the Harvard team’s blackworm-inspired robotic platform consists of soft, thin, worm-like threads made out of synthetic polymer materials that can quickly tangle together and untangle.

Modern-day computers have proved to be quite powerful in what they can do. The rise of AI has made things we previously only imagined possible. And the rate at which computers are increasing their computational power certainly makes it seem like we will be able to do almost anything with them. But as we’ve seen before, there are fundamental limits to what computers can do regardless of the processors or algorithms they use. This naturally leads us to ask what computers are capable of doing at their best and what their limits are. Which requires formalizing various definitions in computing.
This is exactly what happened in the early 20th century. Logicians & mathematicians were trying to formalize the foundations of mathematics through logic. One famous challenge based on this was the Entscheidungsproblem posed by David Hilbert and Wilhelm Ackermann. The problem asked if there exists an algorithm that can verify whether any mathematical statement is true or false based on provided axioms. Such an algorithm could be used to verify if any mathematical system is internally consistent. Kurt Gödel proved in 1931 that this problem could not be answered one way or the other through his incompleteness theorems.
Years later, Alan Turing and Alonzo Church proved the same through separate, independent means. Turing did so by developing Turing machines (called automatic machines at the time) and the Halting problem. Church did so by developing lambda calculus. Later on, it was proved that Turing machines and lambda calculus are mathematically equivalent. This led many mathematicians to theorize that computability could be defined by either of these systems. That in turn caused Turing and Church to make their thesis: every effectively calculable function is a computable function. In simpler terms, it states that any computation from any model can be carried out by a Turing machine or lambda calculus. To better understand the implications of the Church-Turing thesis, we need to explore the different kinds of computational machines.
