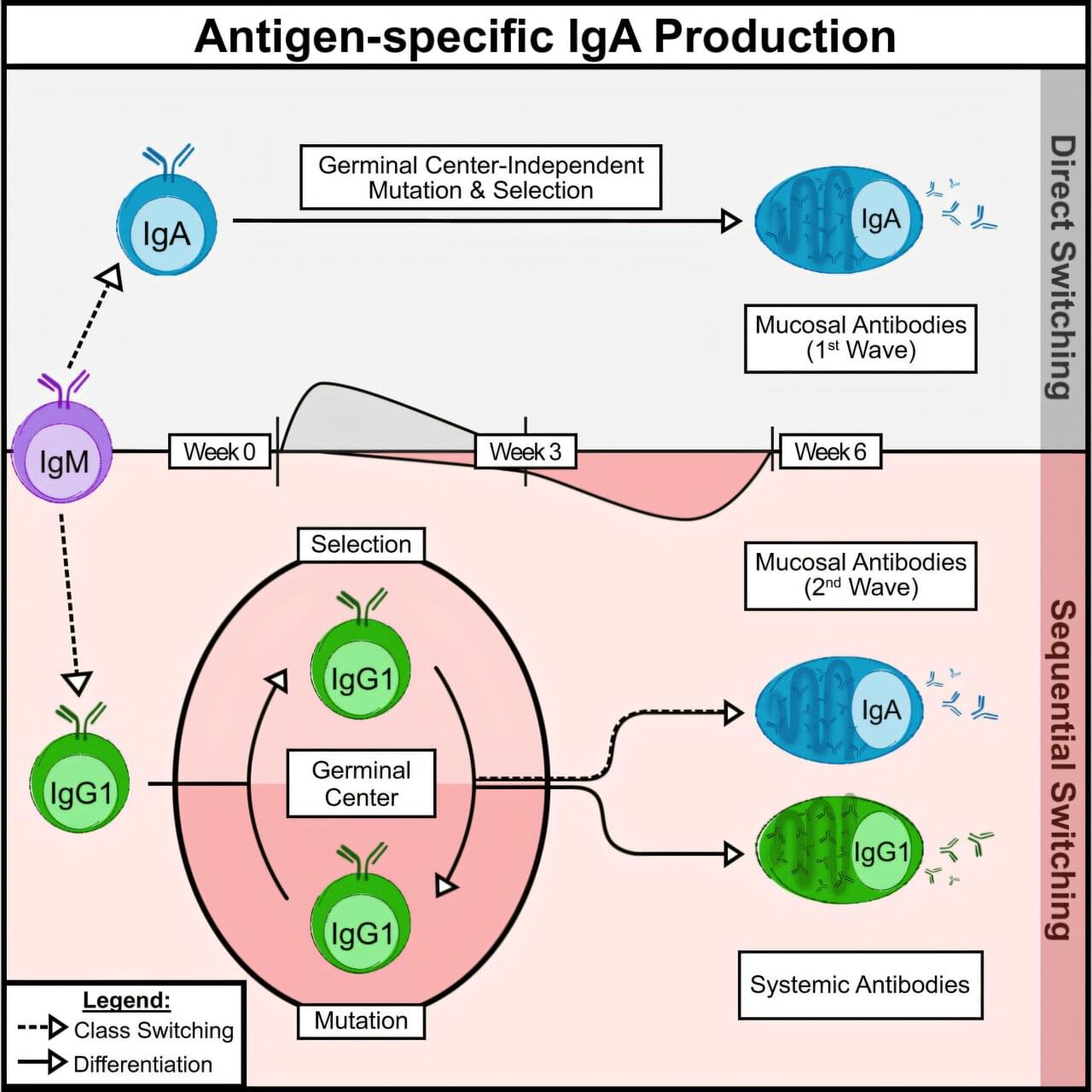
Scientists led by Stephanie Eisenbarth, MD, Ph.D., the Roy and Elaine Patterson Professor of Medicine and director of the Center for Human Immunobiology, have discovered how critical IgA antibodies are produced through unexpected cellular pathways, findings that may help inform the design of more effective vaccines to prevent infections, according to a recent study published in Immunity.
Immunoglobulin (Ig)A is an antibody that serves as the first line of defense for mucosal tissues that comprise the inner lining of organs in the respiratory system and digestive system. IgA antibodies play a role in humoral immunity, in which IgA and other antibodies produced by B-cells fight off and prevent the spread of infection.
However, inducing an IgA-specific immune response, particularly through vaccines, has remained unsuccessful, according to Eisenbarth.