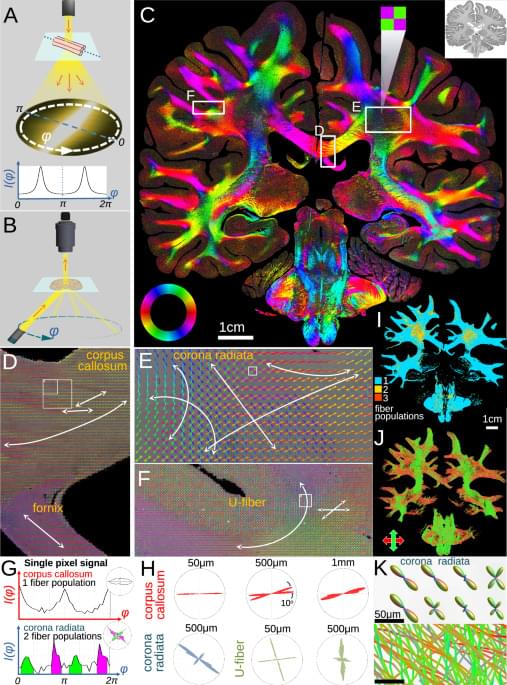
“Extremely massive stars may have played a key role in the formation of the first galaxies,” said Dr. Paolo Padoan.
How did the extremely massive stars (EMS) in the early universe help form the oldest star clusters? This is what a recent study published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society hopes to address as an international team of scientists investigated the role that EMS played in not only forming globular clusters (GCs), but how the latter were responsible for forming the first black holes. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand the conditions of the early universe and what this could mean to better understanding our existence.
For the study, the researchers presented a new computational model to help explain how EMS contributed to GC formation with bodies celestial objects being between 1,000 to 10,000 times as massive as our Sun and containing hundreds of thousands to millions of stars, respectively. Given the massive sizes and short lifetimes of EMS, they go supernova when they die, and the new model postulates they become black holes while releasing massive amounts of chemical and hydrogen that mixes with surrounding gas and dust, resulting in the formation of GCs. Additionally, data obtained from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) discovered nitrogen-rich galaxies had chemical signatures obtained from GCs.