Forget the stereotype. Vegetarianism is becoming a cultural statement.
OpenAI CEO enjoys speculative love-in with Snowflake boss as critics worry over what 1,000X compute would do to the planet
Attention is on AGI taking white-collar jobs. That’s a whammy. But there is a double whammy afoot. AGI embeds with humanoid robots. Here’s the AI insider scoop.
Envision this possible future clinical scenario: a breast cancer patient and her physicians are deciding on the best possible treatment. Their decision is informed by a comprehensive molecular profile of the patient’s cancer samples that predicts the most likely response of the cancer to treatment.
If the profile predicts a high likelihood of a complete positive response and long-term freedom from relapse, then this treatment would be the preferred choice. But if the profile predicts that the tumor would likely be resistant to treatment, alternative treatments must be implemented.
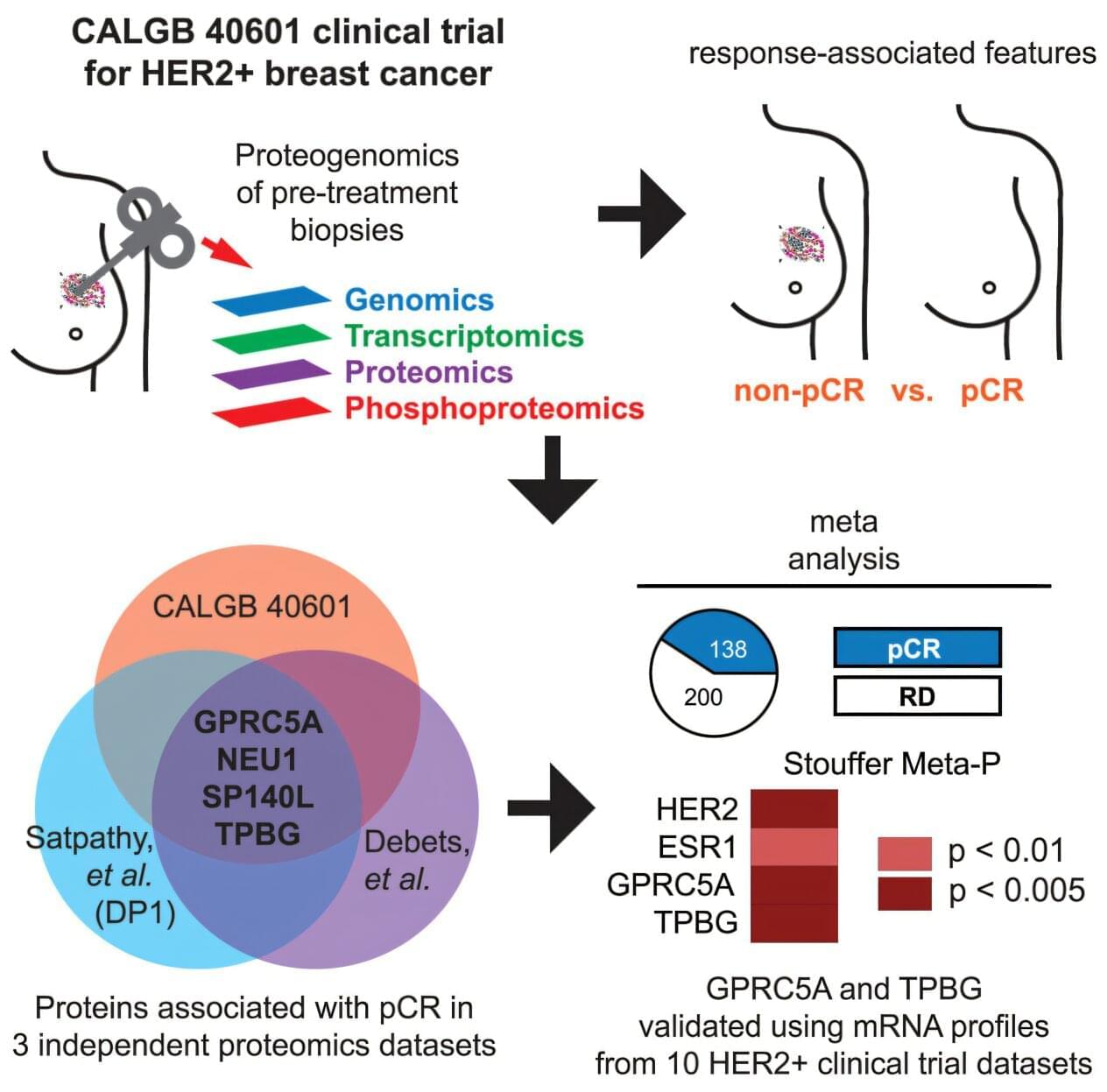
Although this situation is not yet a reality, a team led by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Broad Institute of Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard has taken significant steps in that direction. They report in Cell Reports Medicine that conducting an integrated proteogenomic profiling of cancer cells, which combines the analysis of DNA, RNA, protein and phosphoprotein data, revealed two novel indicators of tumor response to treatment and alternative therapeutic targets for treatment-resistant HER2+ breast cancer.
Researchers have developed a retinal prosthesis made of tellurium nanowires that restores partial vision in blind mice and enables near-infrared vision in primates.
The space agency relies on Elon Musk’s rockets for crucial missions to the International Space Station. Who will replace them when competitors are still playing catch up?
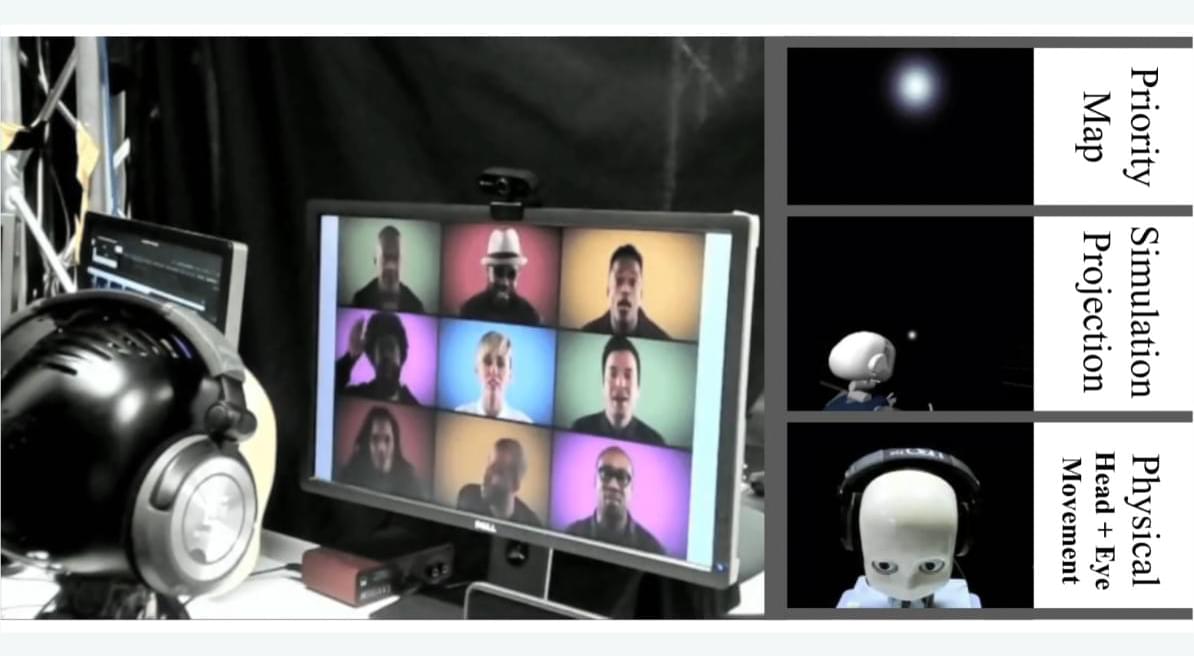
Humans no longer have exclusive control over training social robots to interact effectively, thanks to a new study from the University of Surrey and the University of Hamburg.
The study, which will be presented at this year’s IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), introduces a new simulation method that lets researchers test their social robots without needing human participants, making research faster and scalable.
Using a humanoid robot, the research team developed a dynamic scanpath prediction model to help the robot predict where a person would look in a social setting.
Can one person run a business like a team of ten? In this episode, we explore how AI empowers solopreneurs to scale faster, automate smarter, and compete at…
By Chuck Brooks
Dear Friends and Colleagues, in this issue of the Security and Tech Insights newsletter, I focus on the risk management of expecting the unexpected. The focus of this issue is on potential Black and Gray Swan events.
Critically ill patients with sepsis who are given statins may be more likely to survive, new research suggests.
Researchers set out to explore whether the cholesterol-busting drugs may bring additional benefits for patients.
The new study examined information on sepsis patients who received statins during a stint in intensive care and compared it with patients in a similar situation who did not receive statins.