May 5, 2024
Generative AI Is Coming for Video Games. Here’s How It Could Change Gaming
Posted by Dan Kummer in categories: blockchains, employment, entertainment, mobile phones, robotics/AI
At the end of the day it just got too expensive to make games, and too risky to release bad ones. Not to mention the political nonsense. AI is now in the wings poised for a take over game development. Will of mostly taken over around 2030. And, it will quickly be back to the old days.
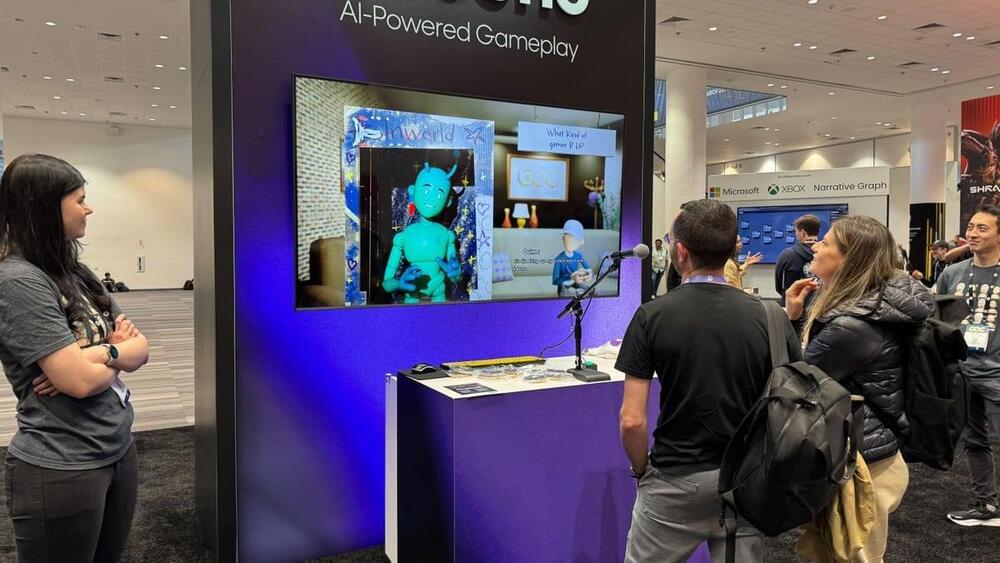
There’s one topic that’s stayed on my mind since the Game Developers Conference in March: generative AI. This year’s GDC wasn’t flooded with announcements that AI is being added to every game — unlike how the technology’s been touted in connection with phones and computers. But artificial intelligence definitely made a splash.
Enthusiasm for generative AI was uneven. Some developers were excited about its possibilities, while others were concerned over its potential for abuse in an industry with shattered morale about jobs and careers.
Continue reading “Generative AI Is Coming for Video Games. Here’s How It Could Change Gaming” »