Page 8723
Jun 9, 2019
Chip design drastically reduces energy needed to compute with light
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: robotics/AI
A new photonic chip design drastically reduces energy needed to compute with light, with simulations suggesting it could run optical neural networks 10 million times more efficiently than its electrical counterparts.
Image: courtesy of the researchers, edited by MIT News.
Jun 9, 2019
50 Years Ago, Scientists Wanted to Build Solar Panels on The Moon
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: solar power, space, sustainability
In 1969, scientists proposed building solar panels on the moon to convert the sun’s energy into electricity that can be used on Earth.
Jun 9, 2019
China rockets to forefront of global space race with sea launch success
Posted by Derick Lee in categories: engineering, space travel
The launch was expected to encounter many technical and engineering challenges, including simplified procedures for pre-launch testing, the rocking motion of the ship and heat dissipation in a confined space.
China has become the first nation to fully own and operate a floating launch platform for its space missions.
Jun 9, 2019
How fast is Earth traveling through space?
Posted by Alberto Lao in category: space travel
Jun 9, 2019
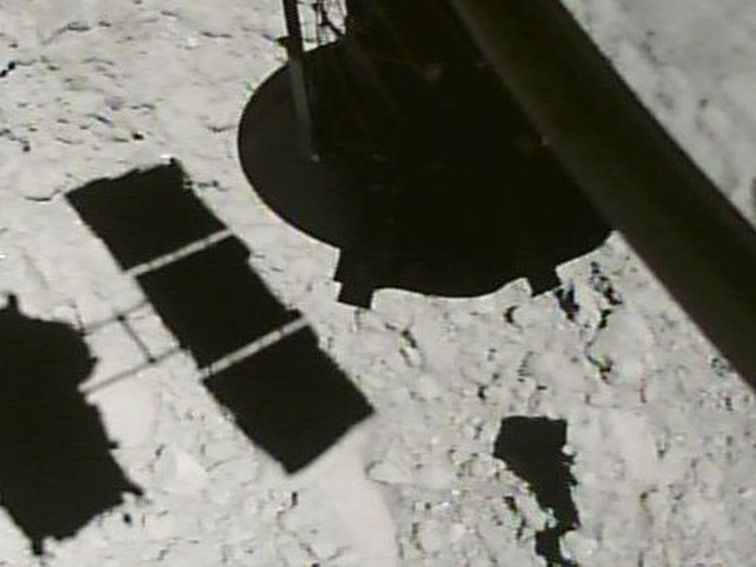
Japan’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft grabs epic close-up just 30 feet above asteroid
Posted by Michael Lance in category: space
The Japanese asteroid-hunter had another photo opportunity when it dropped a target marker on asteroid Ryugu.
Jun 8, 2019
Primordial oscillations, an alternative mechanism to the Big Bang
Posted by Paul Battista in category: cosmology
Jun 8, 2019
5 Intriguing Theories about Dark Matter
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: cosmology, particle physics
Dark matter is a hypothetical invisible mass, which is responsible for the force of gravity among galaxies and other celestial bodies. Although researchers don’t have any concrete information about this puzzling entity, they did come up with a number of intriguing theories about this enigmatic mass. Following is a list of 5 dark matter theories that are quite interesting.
WIMPs are hypothetical particles that are thought to constitute dark matter. These heavy, electromagnetically neutral subatomic particles are hypothesized to make up 22% of the entire universe. They are thought to be heavy and slow-moving because if the dark matter particles were light and fast, they would not have clumped together in the density fluctuations from which galaxies and clusters of galaxies are formed. The precise nature of these particles is currently unknown and they do not abide by the laws of the Standard Model of Particle Physics.
Axions are believed to be neutral, slow-moving particles that are a billion times lighter than electrons. They rarely interact with light and this behavior has urged scientists to believe that Axion could be a building block of the dark matter. An attempt to detect these particles was made in April 2018 by the physicists from the University of Washington. The main idea of this theory suggests that if axions are constantly dashing towards Earth, powerful magnets may be able to convert some of the axions into microwave photons, which are easier to detect. Their work is commonly known as the Axion Dark Matter Experiment (ADMX) and this theory has not enjoyed much success, since then.
Continue reading “5 Intriguing Theories about Dark Matter” »
Jun 8, 2019
Quantum Biology May Help Solve Some of Life’s Greatest Mysteries
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biological, neuroscience, quantum physics
From the remarkable speed of enzyme-catalyzed reactions to the workings of the human brain, numerous biological puzzles are now being explored for evidence of quantum effects.
Jun 8, 2019
Nanotechnology treatment reverses multiple sclerosis in mice
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, nanotechnology
Summary: Extracting nanosized exosomes from bone marrow stem cells and injecting them into mice, researchers reverse symptoms of multiple sclerosis. Source: UC IrvineA nanotechnology treatment.