Maybe you’re involved in a covert operation. Maybe you’re just curious. Spies have developed their own language of code words in order to keep from being discovered. We don’t need to know, but you should learn the 11 terms used by spies here.
Page 8612
Jun 26, 2019
The Rise of a New Generation of AI Avatars
Posted by Richard Christophr Saragoza in categories: innovation, robotics/AI
I recently discovered it’s possible for someone in their 20s to feel old—just mention Microsoft’s Clippy to anyone born after the late 90s. Weirdly, there is an entire generation of people who never experienced that dancing wide-eyed paper-clip interrupting a Word doc writing project.
For readers who never knew him, Clippy was an interactive virtual assistant that took the form of an animated paperclip designed to be helpful in guiding users through Microsoft Word. As an iconic symbol of its decade, Clippy was also famously terrible. Worldwide consensus decided that Clippy was annoying, intrusive, and Time magazine even named it among the 50 worst inventions of all time (squeezed between ‘New Coke’ and Agent Orange. Not a fun list).
Though Clippy was intended to help users navigate their software lives, it may have been 20 or so years ahead of its time.
Jun 26, 2019
Air Force Wants Neuroweapons to Overwhelm Enemy Minds
Posted by Richard Christophr Saragoza in categories: military, neuroscience
It sounds like something a wild-eyed basement-dweller would come up with, after he complained about the fit of his tinfoil hat. But military bureaucrats really are asking scientists to help them “degrade enemy performance” by attacking the brain’s “chemical pathway[s].” Let the conspiracy theories begin.
You’ve read your last complimentary article this month. To read the full article, SUBSCRIBE NOW. If you’re already a subscriber, please sign in and and verify your subscription.
Jun 26, 2019
Physicists Are Making Solid Light
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: materials, particle physics
Circa 2014
A team of researchers from Princeton University has started doing some very strange things with light. Instead of letting it zip by at incredibly high speed, they’re stopping it dead: freezing it into crystal.
Crucially, they’re not shining light through crystal; rather, they making light into crystal. It’s a process that involves fixing the particles of light known as photons in a single spot, freezing them permanently in one place. It’s never been done before, and it could help develop new exotic materials with weird and wonderful properties.
Jun 26, 2019
Scientists develop unique trap for light
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biological, nuclear energy
Circa 2018
Based at the National Research Nuclear University MEPhI (Russia), a research team led by Prof. Yuri Rakovich has developed a tunable micro-resonator for hybrid energy states between light and matter using light to control the chemical and biological properties of molecules. The results have been published in the Review of Scientific Instruments.
The micro-resonator is a two-mirror trap for the light, with the mirrors facing each other within several hundred nanometers. A photon caught in the trap would form a localized state of an electromagnetic wave. By modifying the resonator’s form and size, operators can control the spatial distribution of the wave, as well as the duration of the photon’s life in the resonator.
Continue reading “Scientists develop unique trap for light” »
Jun 26, 2019
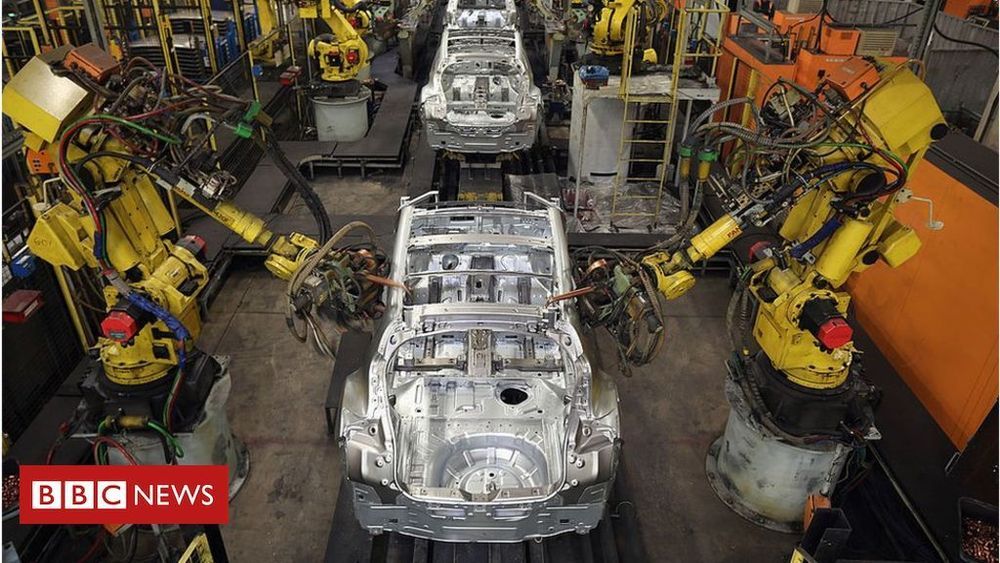
Robots ‘to replace 20 million factory jobs’
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: economics, employment, robotics/AI
A huge acceleration in the use of robots will affect jobs around the world, Oxford Economics says.
Jun 26, 2019
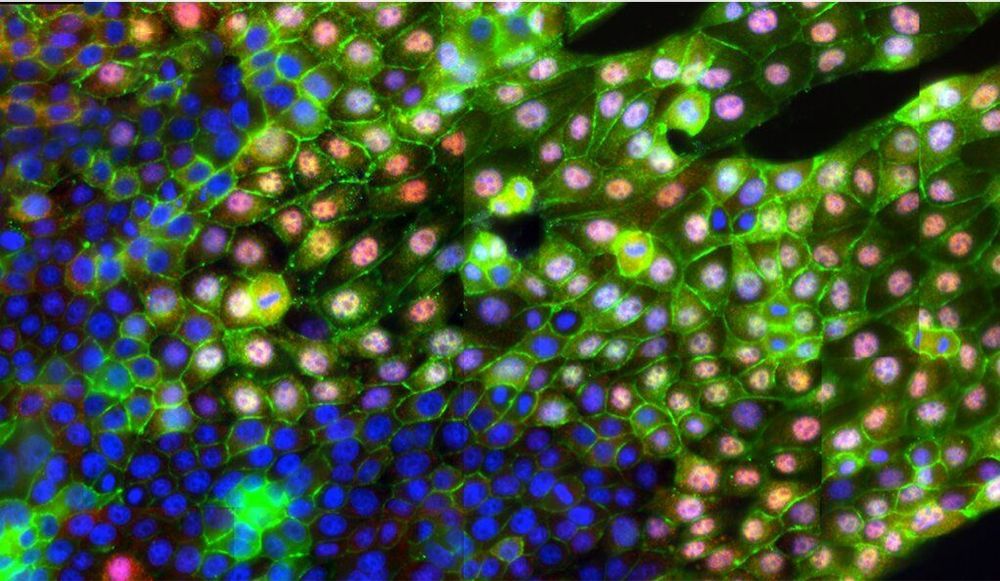
Scientists discover molecular key to how cancer spreads
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
Yale researchers have discovered how metastasis, the spread of cancer cells throughout the body, is triggered on the molecular level, and have developed a tool with the potential to detect those triggers in patients with certain cancers. The discovery could lead to new ways for treating cancer.
The study was led by Andre Levchenko, the John C. Malone Professor of Biomedical Engineering and director of the Yale Systems Biology Institute at Yale’s West Campus. It was published June 26 in the journal Nature Communications. Levchenko is a member of the Yale Cancer Center.
One way metastasis occurs is through epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process that breaks neighboring cells apart from each other and sets them in motion. It’s been long assumed that chemical signals or genetic changes in the cells trigger EMT. But Levchenko’s research team found that it could be caused by a simple change in the texture of the extracellular matrix (ECM), which acts as a scaffold for cells. They discovered that an alignment of the matrix’s fibers (a common biological occurrence) can trigger the EMT process without or other stimuli.
Jun 26, 2019
Mars 2020 “Name the Rover” Contest, Seeks Judges
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: space
NASA has selected two partner organizations to run a nationwide contest giving K-12 students in U.S. schools a chance to make history by naming the Mars 2020 rover. An application to become a judge of the contest also is now available online.
Jun 26, 2019
Retailers Are Judging Consumers
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: business, education, government, information science, surveillance
China isn’t the only country with a draconian “social credit score” system — there’s one quite a bit like it operating in the U.S. Except that it’s being run by American businesses, not the government.
There’s plenty of evidence that retailers have been using a technique called “surveillance scoring” for decades in which consumers are given a secret score by an algorithm to give them a different price — but for the same goods and services.
But the practice might be illegal after all: a California nonprofit called Consumer Education Foundation (CEF) filed a petition yesterday asking for the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to look into the shady practice.
Jun 26, 2019
Incredible Observation Links Two Different Radioactive Phenomena Inside a Thunderstorm
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: climatology, physics
Scientists in Japan reported seeing two radioactive weather phenomena at the same time, for the first time, according to a new paper. The observation establishes a link between the two, adding to our knowledge of the wild physics that takes place inside thunderstorms.
The researchers reported the “unequivocal simultaneous detection” of a minute-long “gamma-ray glow” followed by a powerful, millisecond-long “terrestrial gamma-ray flash,” or TGF. Though scientists have observed these two events before, they don’t quite understand the connection between—the glows and flashes have never been observed together. That is, until now.