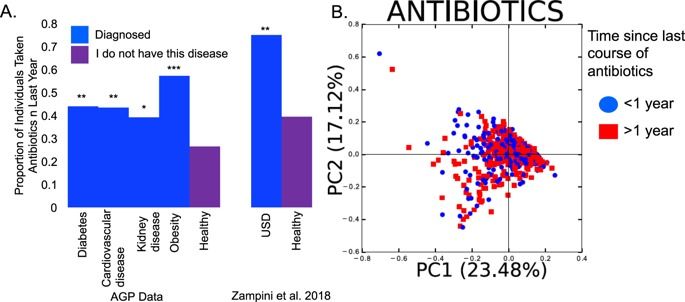
Researchers from Chalmers University of Technology and Politecnico di Milano have identified a crucial new aspect of charge density modulations in cuprate high critical temperature superconductors. They have identified a new electron wave which could help reveal some of the mysteries about superconducting materials. The findings are published in the journal Science.
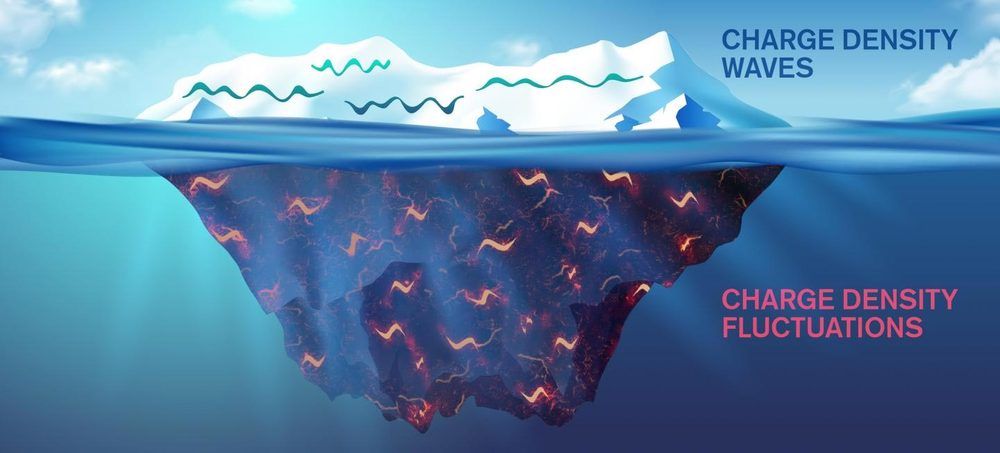
High critical temperature superconductors have a variable charge density, meaning that their electrical charge is unevenly distributed. This partly results from what are known as ‘charge density waves’, which were discovered a few years ago. But these have only been observed to exist sporadically, under certain conditions. Therefore, they were not believed to be a contributing factor to the materials’ superconducting properties.
What the researchers have now discovered, however, is an additional aspect to the variable charge density, which they term “charge density fluctuations”. These have been identified as an additional charge modulation, collective and with a shorter correlation length. They are very pervasive, meaning that compared to the conventional charge density waves, they are present at a much greater range of temperatures, up to room temperature and beyond, and at different levels of oxygen doping.