Dec 28, 2019
Scientists finally figure out why the water bear is nearly indestructible
Posted by Brent Ellman in category: futurism
Freeze it, boil it, or expose it to radiation. The water bear shrugs it off. Now we know why.
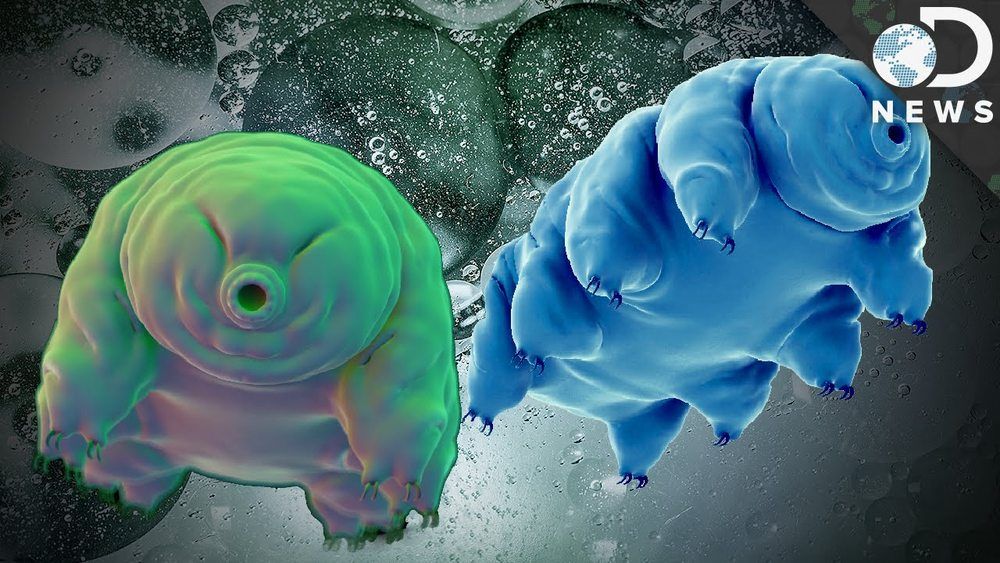
Freeze it, boil it, or expose it to radiation. The water bear shrugs it off. Now we know why.
Many experiencers have been visited by alien mantises. I personally heard their cackling communication and have things stolen without any trace simply teleported away.
This extraterrestrial species resembles a praying mantis and occasionally surface in abduction accounts as overseers. Learn about the Mantid agenda on Earth.
Clumps of harmful proteins that interfere with brain functions have been partially cleared in mice using nothing but light and sound.
Research led by MIT earlier this year found strobe lights and a low pitched buzz can be used to recreate brain waves lost in the disease, which in turn remove plaque and improve cognitive function in mice engineered to display Alzheimer’s-like behaviour.
It’s a little like using light and sound to trigger their own brain waves to help fight the disease.
The second thing to mention is that in many instances, we actually have cracked it, at least medically. There are endless cutting-edge treatments being deployed as we speak, and endless additional cutting-edge research projects being conducted. There are new breakthroughs all the time, much of which are awaiting FDA approval, but one thing many of these treatments and cures have in common is that they are developed in a tiny country smaller than New Jersey that happens to be located in perhaps the worst neighborhood on Earth. When it comes to cancer research, Israel leads the way.
Finally, the last time I wrote about cutting-edge cancer treatments, I was contacted by a close friend who is a leading oncologist. He pointed out that a disclaimer is very much necessary when I write these articles. The last thing oncologists need is for their patients to think there is some magical solution here and show up to their appointments with a cut-out of an article. In fact, the last thing a cancer patient needs is false hope.
So the disclaimer is that this company is in the clinical trial phase, and if all goes according to plan, tumors might be much more manageable and treatable than they are today, but a lot has to happen before we get there.
Professor Varda Shoshan-Barmatz of the Department of Life Sciences and the founding Director of the NIBN, in collaboration with Dr. Jay Chung of the NIH, have successfully demonstrated that the mitochondrial protein VDAC1 is critical for the release of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) associated with the lupus disease.
They demonstrated that restricting of VDAC1 with a newly developed molecule resulted in substantial improvement in pathological aspects of the disease.
“When VDAC1 is over-expressed, as found in several diseases, a large pore composed of several VDAC1 units is formed, allowing the release of pro-cell death factors and mtDNA,” BGU explained in a statement.
We thank Drs. Michel Bernier and Anne E. Burke for valuable input, Mr. Marc Raley for work on previous versions of the figures, Dr. David G. Le Couteur for assistance with the preparation of an earlier version of the manuscript, and the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health, for its support.
That might explain things…
There may soon be serious financial and legal ramifications to the proliferation of deepfake technology. The Wall Street Journal reported last week that a UK energy company’s chief executive was tricked into wiring €200,000 to a Hungarian supplier because he believed his boss was instructing him to do so. Instead, it was a thief using deepfake tech.
For the first time, researchers and scientists from the University of Bristol, in collaboration with the Technical University of Denmark (DTU), have achieved quantum teleportation between two computer chips. The team successfully developed chip-scale devices that are able to harness the applications of quantum physics by generating and manipulating single particles of light within programmable nano-scale circuits.
Unlike regular or science fiction teleportation which transfer particles from one place to another, with quantum teleportation, nothing physical is being transported. Rather, the information necessary to prepare a target system in the same quantum state as the source system is transmitted from one location to another, with the help of classical communication and previously shared quantum entanglement between the sending and receiving location.
In a feat that opens the door for quantum computers and quantum internet, the team managed to send information from one chip to another instantly without them being physically or electronically connected. Their work, published in the journal Nature Physics, contains a range of other quantum demonstrations. This chip-to-chip quantum teleportation was made possible by a phenomenon called quantum entanglement. The entanglement happens between two photons (two light particles) with the interaction taking place for a brief moment and the two photons sharing physical states. Quantum entanglement phenomenon is so strange that physicist Albert Einstein famously described it as ‘spooky action at a distance’.
We all feel the passing of time, but nothing in physics suggests it is a fundamental property of the universe. So where does our sense of time’s flow come from?
Researchers at Princeton University have found a way to make a tokamak nuclear fusion reactor safer using insulating boron powder. The new research appears in the IAEA journal Nuclear Fusion and comes from Princeton’s U.S. Department of Energy-funded Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL).
A tokamak, like the huge one that will reach 200 million Celsius in China next year, is a nuclear fusion plasma reactor where extremely hot, charged plasma spins and generates virtually limitless energy. The Princeton research examines the way boron powder can prevent one of the fundamental flaws in existing plasma reactor technology.
