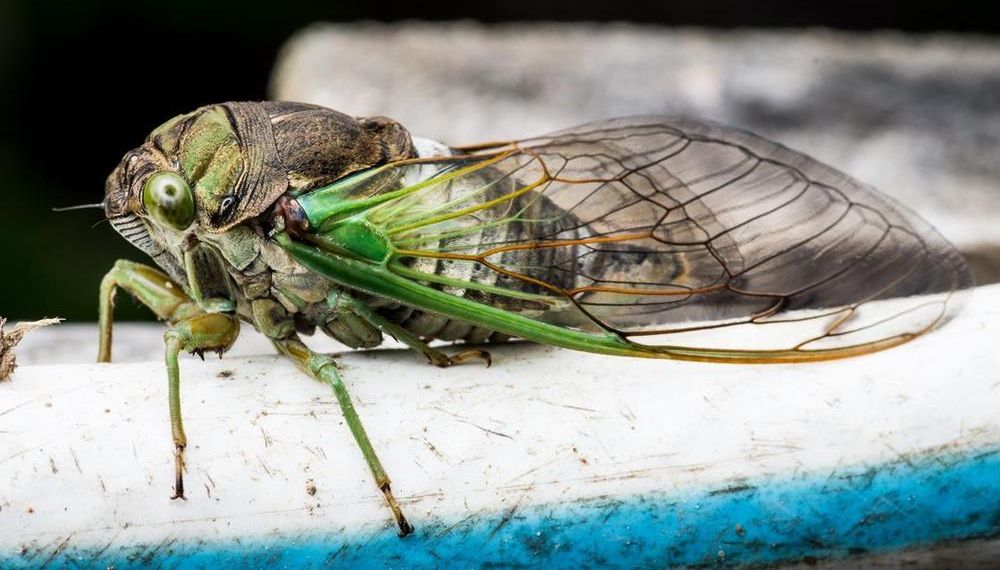
Meticulously organised fatty acids are responsible for the bacteria-killing, superhydrophobic nanostructures on cicada wings. The team behind the discovery hopes that its work will inspire antimicrobial surfaces that mimic cicada wings for use in settings such as hospitals.
When in contact with dust, pollen and – importantly – water, the cicadas’ superhydrophobic wings repel matter to self-clean. These extraordinary properties are down to fatty acid nanopillars, periodically spaced and of nearly uniform height, that cover the wings.
Past work has generally only described cicadas’ wings as ‘waxy’ and not explained how these fatty acids nanopillars give rise to unique traits. Nor is it known exactly why cicada wings evolved antibacterial nanostructures. These gaps in our knowledge exist, in part, because of how diverse the cicada family is. But Marianne Alleyne’s group at the University of Illinois, Urbana–Champaign, along with colleagues at Sandia National Labs, set out to understand what role chemistry plays in the wings of two evolutionarily divergent species.