Aug 3, 2020
New Integrated 3D-Circuit Architecture With Spiraling Memory for More Efficient AI
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: climatology, information science, robotics/AI, sustainability
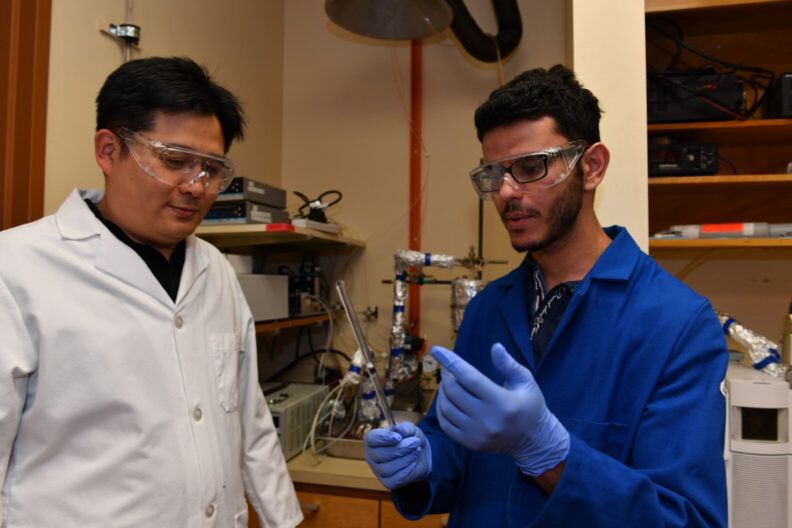
Researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science at The University of Tokyo designed and built specialized computer hardware consisting of stacks of memory modules arranged in a 3D-spiral for artificial intelligence (AI) applications. This research may open the way for the next generation of energy-efficient AI devices.
Machine learning is a type of AI that allows computers to be trained by example data to make predictions for new instances. For example, a smart speaker algorithm like Alexa can learn to understand your voice commands, so it can understand you even when you ask for something for the first time. However, AI tends to require a great deal of electrical energy to train, which raises concerns about adding to climate change.
Now, scientists from the Institute of Industrial Science at The University of Tokyo have developed a novel design for stacking resistive random-access memory modules with oxide semiconductor (IGZO) access transistor in a three-dimensional spiral. Having on-chip nonvolatile memory placed close to the processors makes the machine learning training process much faster and more energy-efficient. This is because electrical signals have a much shorter distance to travel compared with conventional computer hardware. Stacking multiple layers of circuits is a natural step, since training the algorithm often requires many operations to be run in parallel at the same time.