Page 7230
Oct 8, 2020
Optical Matter Machine: Nanoscale Machines Convert Light Into Work
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: nanotechnology, particle physics
Based on optical matter, new machines could be used to move and manipulate tiny particles.
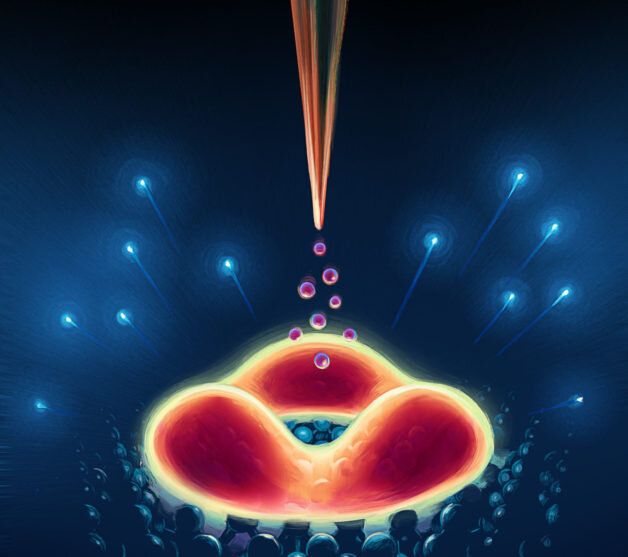
Researchers have developed a tiny new machine that converts laser light into work. These optically powered machines self-assemble and could be used for nanoscale manipulation of tiny cargo for applications such as nanofluidics and particle sorting.
“Our work addresses a long-standing goal in the nanoscience community to create self-assembling nanoscale machines that can perform work in conventional environments such as room temperature liquids,” said research team leader Norbert F. Scherer from the University of Chicago.
Oct 8, 2020
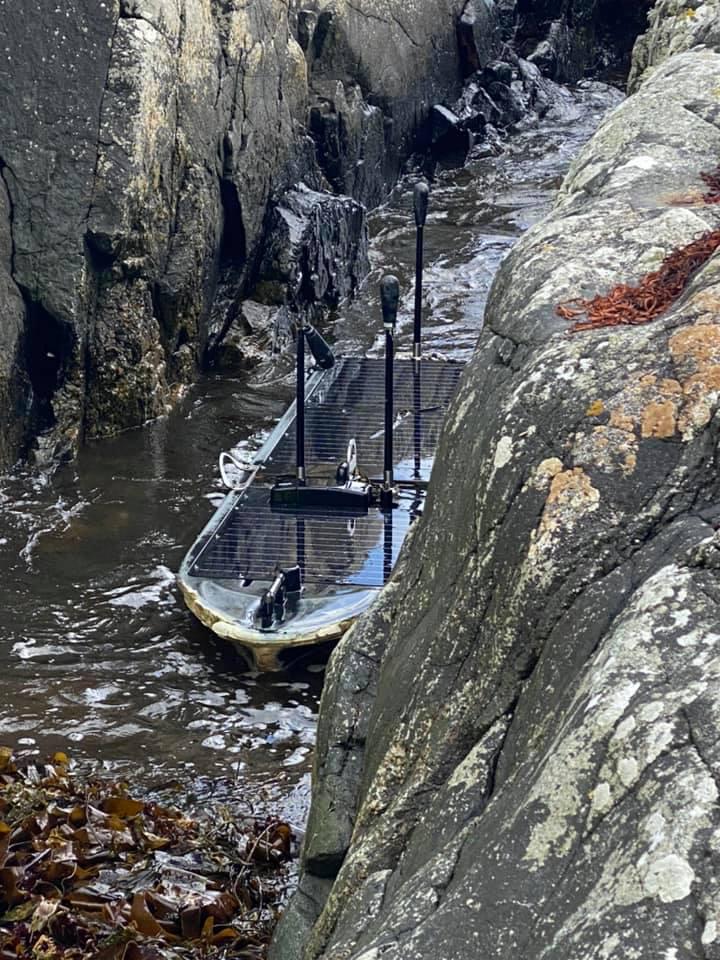
Mystery Deepens Around Unmanned Spy Boat Washed Up In Scotland (Updated)
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: robotics/AI
O,.o.
The unmanned vessel washed up in Scotland last week does not belong to the Royal Navy. But it may have been on an intelligence-gathering mission for someone else, along with a second craft found last year.
Oct 8, 2020
An electrical trigger fires single, identical photons
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: computing, quantum physics
Secure telecommunications networks and rapid information processing make much of modern life possible. To provide more secure, faster, and higher-performance information sharing than is currently possible, scientists and engineers are designing next-generation devices that harness the rules of quantum physics. Those designs rely on single photons to encode and transmit information across quantum networks and between quantum chips. However, tools for generating single photons do not yet offer the precision and stability required for quantum information technology.
Now, as reported recently in the journal Science Advances, researchers have found a way to generate single, identical photons on demand. By positioning a metallic probe over a designated point in a common 2-D semiconductor material, the team led by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has triggered a photon emission electrically. The photon’s properties may be simply adjusted by changing the applied voltage.
“The demonstration of electrically driven single-photon emission at a precise point constitutes a big step in the quest for integrable quantum technologies,” said Alex Weber-Bargioni, a staff scientist at Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Foundry who led the project. The research is part of the Center for Novel Pathways to Quantum Coherence in Materials (NPQC), an Energy Frontier Research Center sponsored by the Department of Energy, whose overarching goal is to find new approaches to protect and control quantum memory that can provide new insights into novel materials and designs for quantum computing technology.
Oct 8, 2020
Engineers create nanoparticles that deliver gene-editing tools to specific tissues and organs
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, chemistry, genetics, nanotechnology, neuroscience
One of the most remarkable recent advances in biomedical research has been the development of highly targeted gene-editing methods such as CRISPR that can add, remove, or change a gene within a cell with great precision. The method is already being tested or used for the treatment of patients with sickle cell anemia and cancers such as multiple myeloma and liposarcoma, and today, its creators Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna received the Nobel Prize in chemistry.
While gene editing is remarkably precise in finding and altering genes, there is still no way to target treatment to specific locations in the body. The treatments tested so far involve removing blood stem cells or immune system T cells from the body to modify them, and then infusing them back into a patient to repopulate the bloodstream or reconstitute an immune response—an expensive and time-consuming process.
Building on the accomplishments of Charpentier and Doudna, Tufts researchers have for the first time devised a way to directly deliver gene-editing packages efficiently across the blood brain barrier and into specific regions of the brain, into immune system cells, or to specific tissues and organs in mouse models. These applications could open up an entirely new line of strategy in the treatment of neurological conditions, as well as cancer, infectious disease, and autoimmune diseases.
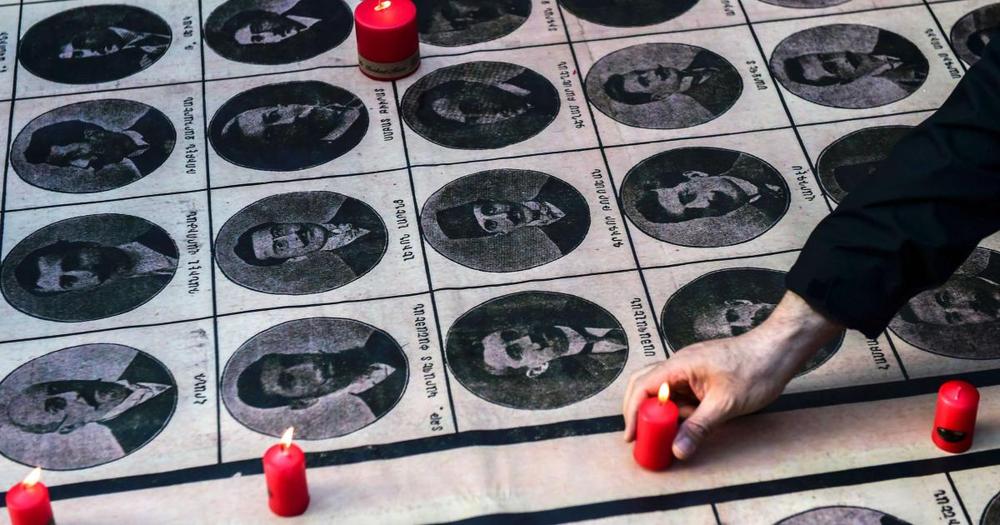
Armenians face the risk of ethnic cleansing after the eruption of clashes with Azerbaijan and Turkey, two countries with a long history of aggression against them, Israel-based political analyst Uzay Bulut said on Tuesday.
The fighting started between Armenia and Azerbaijan on Sept. 27, marking the biggest escalation in a decades-old conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh, also known as Artsakh. Armenian officials allege that Turkey is involved in the conflict on the side of Baku and is sending mercenaries from Syria to the region.
“Through these assaults, Azerbaijan and Turkey are once again endangering the existence of Artsakh and the survival of Armenia,” Bulut said.
Oct 8, 2020
Fusing cytokines with antibodies found to be effective at treating brain tumors in mice
Posted by Kevin Huang in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
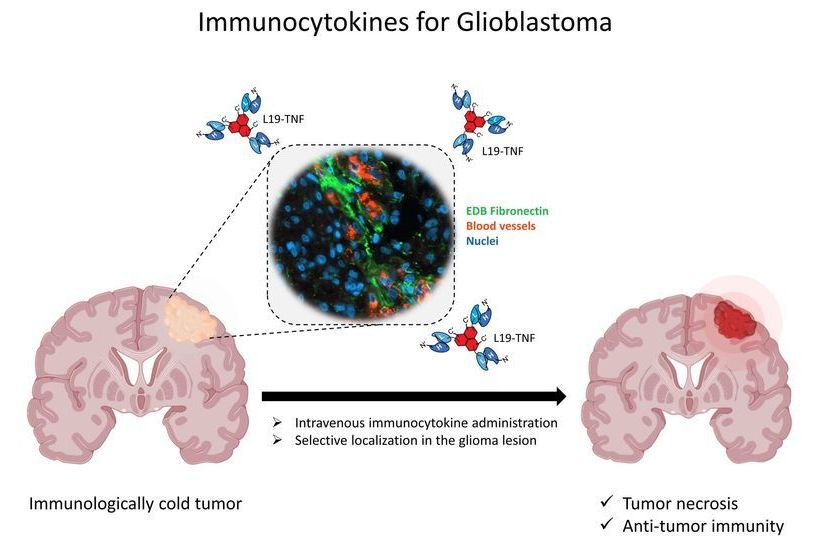
A team of researchers from University Hospital Zurich and the University of Zurich, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology and biotechnology company Philochem, has found fusing cytokines with antibodies to be an effective treatment for glioblastoma in mice. In their paper published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, the group describes their technique and how well it worked when tested with mouse models.
Glioblastoma is a type of cancerous brain tumor that is notoriously difficult to treat. Surgery to remove it is difficult and fraught with side effects, and drugs have little impact. In recent years, researchers have tried using drugs that alert the immune system to the presence of the tumor but they have not worked as hoped, either. In this new effort, the researchers tried another approach—fusing cytokines with antibodies as a way to attack the tumor. The hope was that together, the two would incite the immune system to attack the tumor more strongly and hopefully get rid of it.
Cytokines are small protein cells secreted by the immune system. Their usual job is to send signals to other cells in the immune system. And antibodies are Y-shaped proteins produced by plasma cells, the workhorses of the immune system that attack viruses and bacteria. In this new effort, the researchers fused L19 antibodies to cytokines. L19 was chosen because prior research has shown that it is able to seek out markers for glioblastoma. Fusing the two proteins together proved to be a more formidable therapeutic approach than using either alone. The resulting (L19TNF) immunocytokines were injected into mice with induced glioblastoma and were then monitored to determine their impact on the brain tumors.

Brains (mammalian, avian, reptilian) are analog, not digital/ hardwired for good evolutionary reasons (MVT). I have become interested in building synths recently — “Anyone with any passing interest in the synthesizer will have noticed not one, but three trends over the last decade. The first is a return to analogue… You can now get a phenomenal number of astounding synths — many of them ‘proper’ analogues — for an easy three digits. If you are as old as me, you’ll remember a time before when this was unthinkable. In fact, the whole idea of a return to analogue was unthinkable. “It would simply cost too much to (re) manufacture all of those analogue components,” they used to say, “and because everyone uses software, why would anyone be interested?”
Well, it turned out that analogue components could be cheap, and not everyone was interested in software (and if they were, they were also interested in hardware).”
Oct 8, 2020
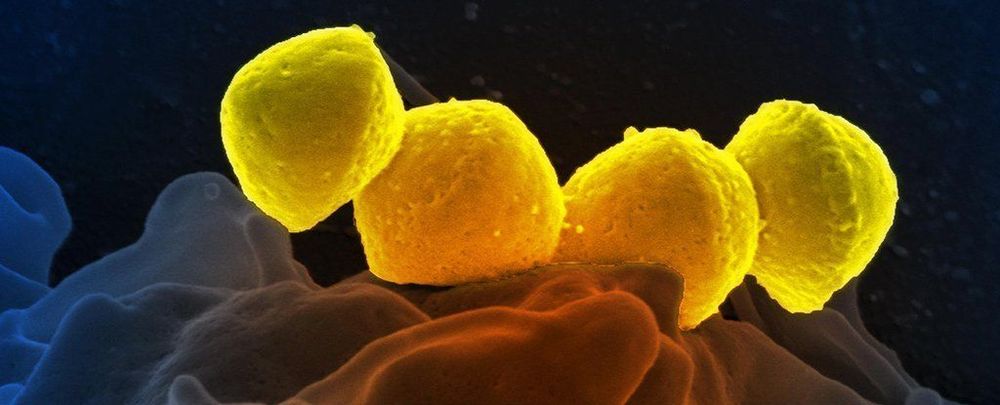
A Historical Epidemic Has Been Making a Scary Comeback Due to a Bacterial ‘Clone’
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: biotech/medical
Once a leading cause of death for children across the western world, scarlet fever was nearly eradicated thanks to 20th century medicine. But fresh outbreaks in the UK and North East Asia over recent years suggest we’ve still got a long way to go.
Just why we’re experiencing a resurgence of the deadly pathogen is a mystery. A new study has uncovered clues in the genome of one of the bacterial strains responsible, showing just how complex the family tree of infectious diseases can be.
The species behind the illness is group A strep, or Streptococcus pyogenes; a ball-shaped microbe that can churn out toxic compounds called superantigens, capable of wreaking havoc inside the body. Especially in children.
Oct 8, 2020
SpaceX’s Starman cruising space in a Tesla makes a close approach to Mars
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: alien life, Elon Musk, sustainability, transportation

Yes, it is True! A Tesla car is cruising space! The founder of SpaceX Elon Musk wanted to launch a ‘silly’ payload for SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy rocket debut flight because a rocket’s first flight has potential to fail. Typically, aerospace companies launch massive concrete blocks as mass simulators during risky rocket flights. As the dreamer that Musk is, he opted to launch something that would inspire the public to dream big and look at the stars — his flashy midnight cherry Tesla Roadster. The electric vehicle became the crazy payload for the rocket’s launch.
On February 6, 2018, SpaceX conducted Falcon Heavy’s debut flight; It lifted-off from historic launch Pad 39A at NASA Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida. The successful test turned Falcon Heavy into the most powerful rocket in operation, it produced about five million pounds of thrust (22MN). During the mission, SpaceX shared Live footage as the Tesla Roadster was placed into orbit. It was a very inspiring to watch an actual car orbiting around Earth with, a mannequin dressed as an astronaut, positioned in the Tesla driver’s seat; while the radio played “Life on Mars” by David Bowie (video below). After the awe-inspiring launch, Musk wholeheartedly said — “Life cannot just be about solving one sad problem after another. There need to be things that inspire you, that make you glad to wake up in the morning and be part of humanity. That is why we did it. We did for you.”