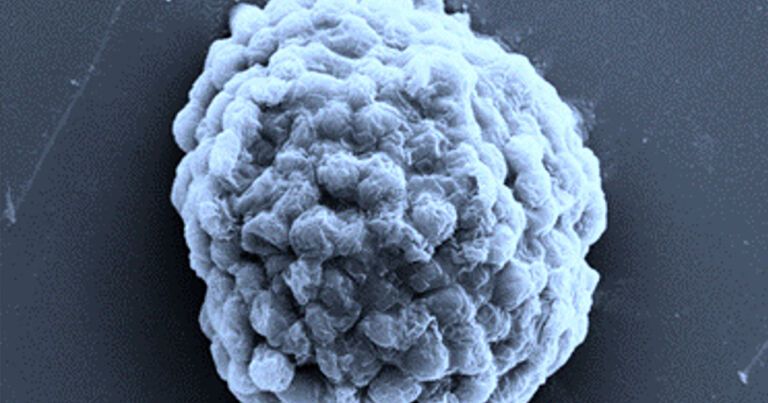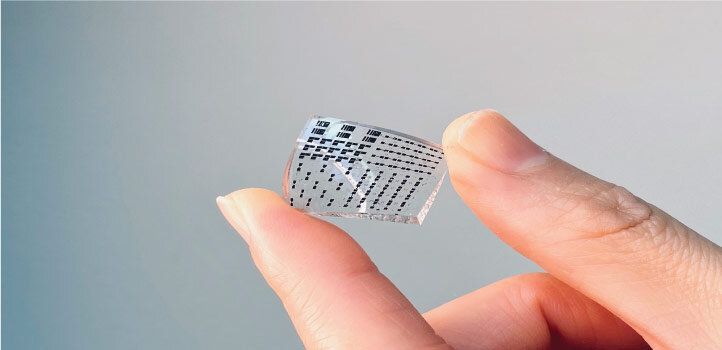
A material that mimics human skin in strength, stretchability and sensitivity could be used to collect biological data in real time. Electronic skin, or e-skin, may play an important role in next-generation prosthetics, personalized medicine, soft robotics and artificial intelligence.
“The ideal e-skin will mimic the many natural functions of human skin, such as sensing temperature and touch, accurately and in real time,” says KAUST postdoc Yichen Cai. However, making suitably flexible electronics that can perform such delicate tasks while also enduring the bumps and scrapes of everyday life is challenging, and each material involved must be carefully engineered.
Most e-skins are made by layering an active nanomaterial (the sensor) on a stretchy surface that attaches to human skin. However, the connection between these layers is often too weak, which reduces the durability and sensitivity of the material; alternatively, if it is too strong, flexibility becomes limited, making it more likely to crack and break the circuit.