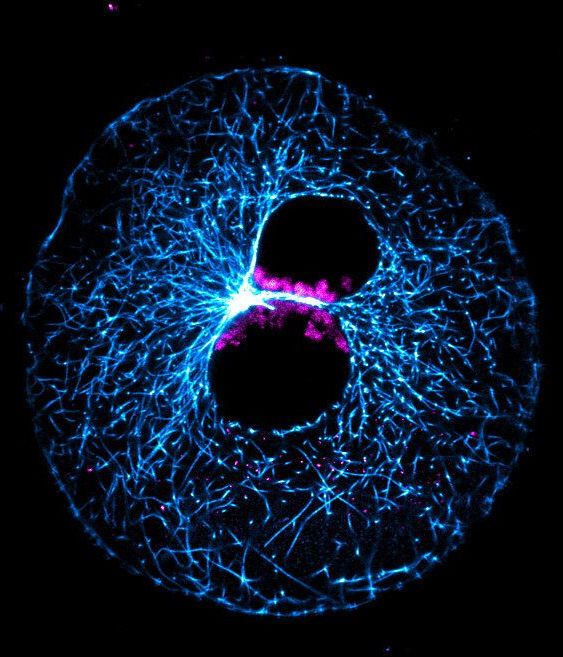
Only one in three fertilizations leads to a successful pregnancy. Many embryos fail to progress beyond early development. Cell biologists at the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Biophysical Chemistry in Göttingen (Germany), together with researchers at the Institute of Farm Animal Genetics in Mariensee and other international colleagues, have now developed a new model system for studying early embryonic development. With the help of this system, they discovered that errors often occur when the genetic material from each parent combines immediately after fertilization. This is due to a remarkably inefficient process.
Human somatic cells typically have 46 chromosomes, which together carry the genetic information. These chromosomes are first brought together at fertilization, 23 from the father’s sperm, and 23 from the mother’s egg. After fertilization, the parental chromosomes initially exist in two separate compartments, known as pronuclei. These pronuclei slowly move towards each other until they come into contact. The pronuclear envelopes then dissolve, and the parental chromosomes unite.
The majority of human embryos, however, end up with an incorrect number of chromosomes. These embryos are often not viable, making erroneous genome unification a leading cause of miscarriage and infertility.