The nascent autonomous-vehicle industry is being reshaped by consolidation. Amazon, which committed to buying 100,000 Rivian electric vehicles, announced today that it is buying Zoox, the self-driving car tech start-up, for $1 billion. Ford and Volkswagen made multi-billion dollar investments in Argo. General Motors purchased Cruise Automation in 2016, while Hyundai is working with tier-one supplier Aptiv to deploy a robotaxi service in multiple global markets.
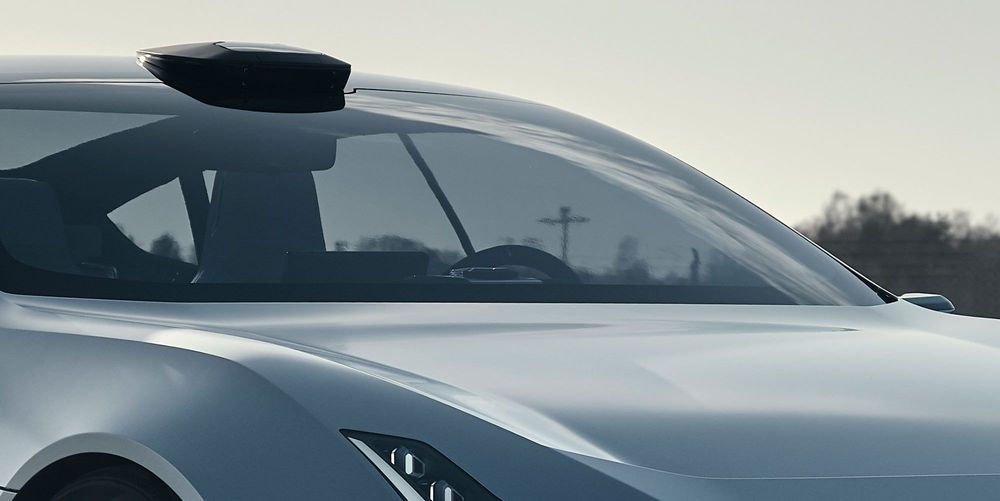
The tie-up between Waymo and Volvo (with its three brands all aggressive pursuing electric vehicles) could reshape the competitive landscape, although it’s too early to tell.
Google started its self-driving program more than a decade ago but paused the development of its own vehicle in 2016. A tight partnership between Waymo and Volvo to develop ground-up cars, if that’s what materializes, could put those plans back on track – this time with an established auto manufacturer known for high-quality production and safety.