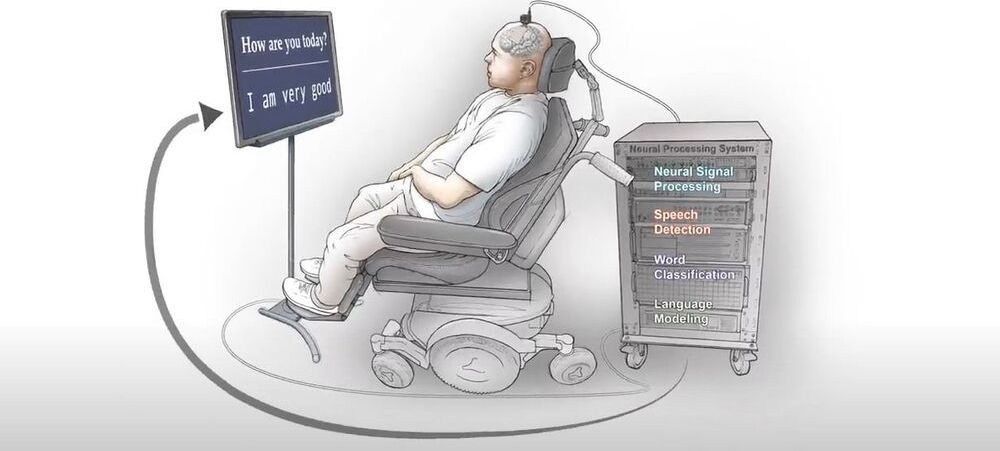
New research out of the University of California, San Francisco has given a paralyzed man the ability to communicate by translating his brain signals into computer generated writing. The study, published in The New England Journal of Medicine, marks a significant milestone toward restoring communication for people who have lost the ability to speak.
“To our knowledge, this is the first successful demonstration of direct decoding of full words from the brain activity of someone who is paralyzed and cannot speak,” senior author and the Joan and Sanford Weill Chair of Neurological Surgery at UCSF, Edward Chang said in a press release. “It shows strong promise to restore communication by tapping into the brain’s natural speech machinery.”
Some with speech limitations use assistive devices–such as touchscreens, keyboards, or speech-generating computers to communicate. However, every year thousands lose their speech ability from paralysis or brain damage, leaving them unable to use assistive technologies.


















