Sep 23, 2020
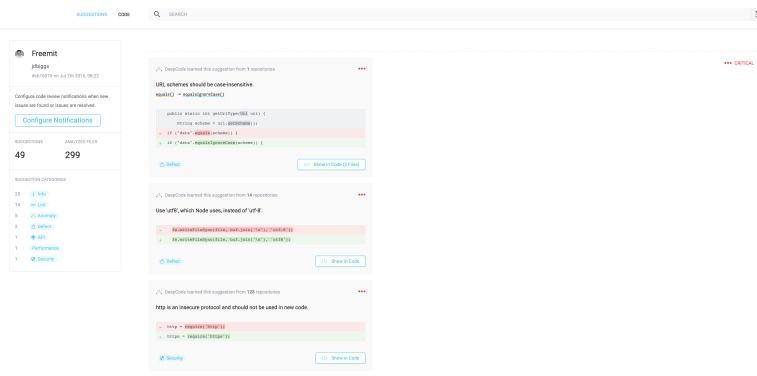
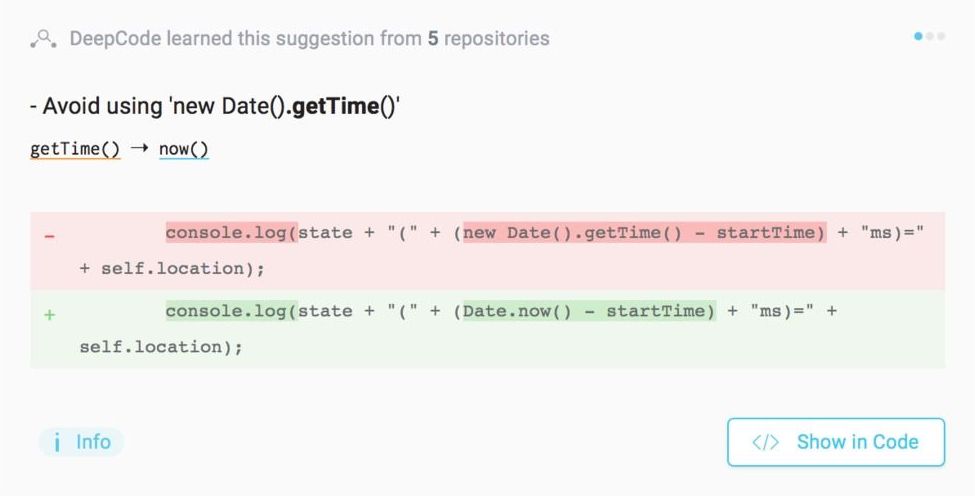
Microsoft AI boasts 97% accuracy in detecting software bugs
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, cybercrime/malcode, robotics/AI
Software bugs are a tale as old as time — which, in the case of programming, means about 75 years. In 1947, programmer Grace Murray Hopper was working on a Mark II Computer at Harvard University when she noticed a moth that was stuck in the relay, preventing the computer program from running. It was the first “bug”, and countless others have followed since then.
In the history of programming, bugs have ranged from harmless to absolutely catastrophic. In 1986 and 1987, several patients were killed after a Therac-25 radiation therapy device malfunctioned due to an error by an inexperienced programmer, and a software bug might have also triggered one of the largest non-nuclear explosions in history, at a Soviet trans-Siberian gas pipeline.
While events such as this are rare, it’s safe to say that software bugs can do a lot of damage and waste a lot of time (and resources). According to recent analysis, the average programmer produces 70 bugs per 1,000 lines of code, with each bug demanding 30 times more time to fix than it took to write the code in the first place. In the US alone, an estimated $113 billion is spent identifying and fixing code bugs…