May 10, 2024
Astronomers spot ‘sleeping giant’ black hole Gaia BH3 in Milky Way
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: cosmology, materials
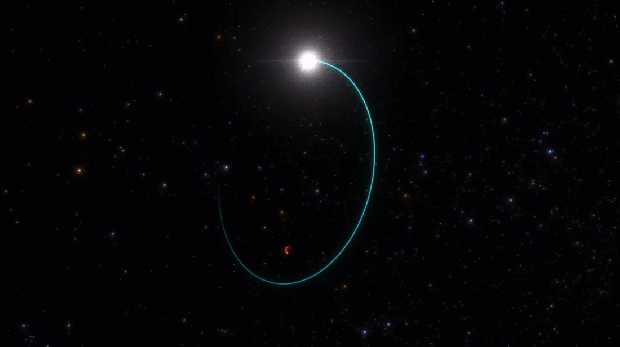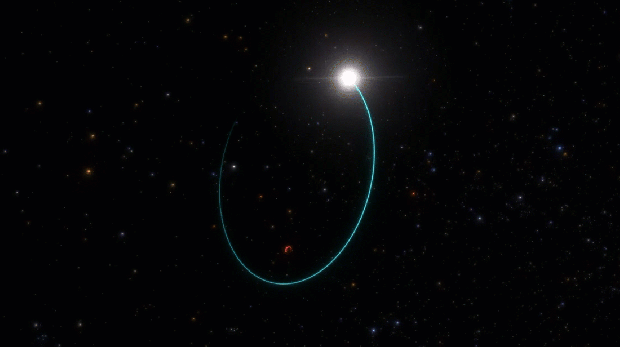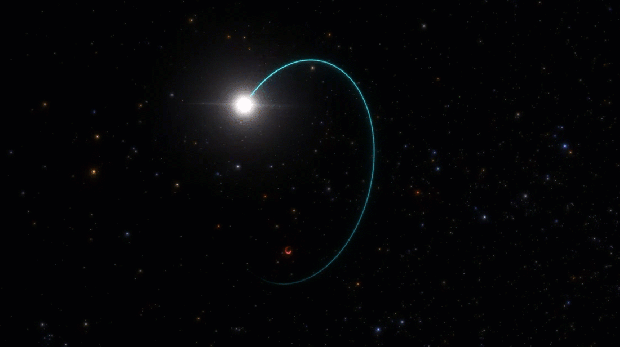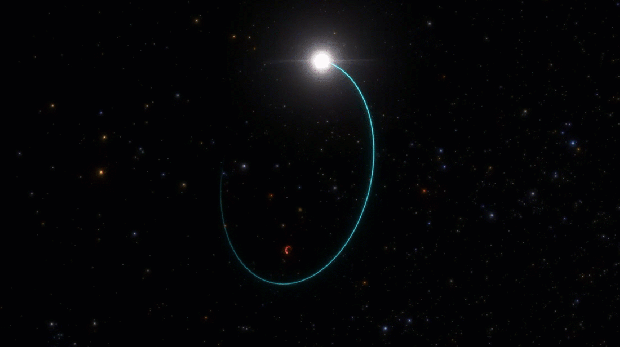
The newfound black hole, an intense, light-trapping abyss which has been named Gaia BH3, lurks just 1,926 light-years from Earth in the Aquila constellation. (That makes it the second closest black hole to Earth after Gaia BH1, which resides at 1,500 light-years away and is three times lighter than Gaia BH3.) The so-called “sleeping giant” — so named because unlike its ilk, the dormant black hole doesn’t appear to be shredding its companion star to pieces — birthed out of the imminent collapse of a once-massive star. It is the first direct link between a black hole and a progenitor star that was deprived of metals heavier than hydrogen and helium, according to the new study published in April in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics.
The discovery confirms a leading theory of stellar evolution that posits high-mass black holes are remnants of stars that are low on metals. Such metal-poor stars have damped mass-eroding winds compared to their metal-rich counterparts, and thus have more material available to form heavier black holes. Astronomers normally time announcements of science discoveries at the same time as data release, in this case no sooner than early 2026, but “you cannot hide this kind of discovery from the community for two years,” says Panuzzo. “It is a unique case of publication based on the preliminary data because the data is exceptional and also something that’s very interesting for the community.”