Jul 11, 2024
Overcoming Longstanding Quantum Computing Roadblock: Scientists Develop Efficient 2D Device for Quantum Cooling
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: computing, nanotechnology, quantum physics, space
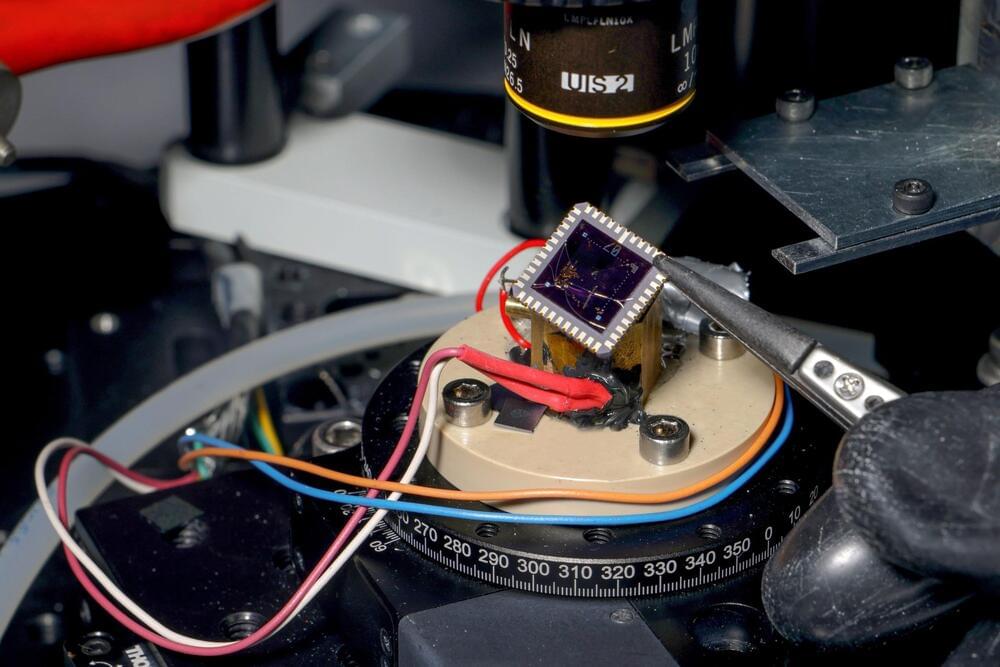
Engineers at EPFL have developed a device capable of transforming heat into electrical voltage efficiently at temperatures even colder than those found in outer space. This breakthrough could significantly advance quantum computing technologies by addressing a major obstacle.
To perform quantum computations, quantum bits (qubits) need to be cooled to temperatures in the millikelvin range (close to-273 degrees Celsius) to reduce atomic motion and minimize noise. However, the electronics used to control these quantum circuits generate heat, which is challenging to dissipate at such low temperatures. Consequently, most current technologies must separate the quantum circuits from their electronic components, resulting in noise and inefficiencies that impede the development of larger quantum systems beyond the laboratory.
Researchers in EPFL’s Laboratory of Nanoscale Electronics and Structures (LANES), led by Andras Kis, in the School of Engineering have now fabricated a device that not only operates at extremely low temperatures, but does so with efficiency comparable to current technologies at room temperature.