Sep 17, 2021
Bispecific antibodies targeting distinct regions of the spike protein potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in category: biotech/medical
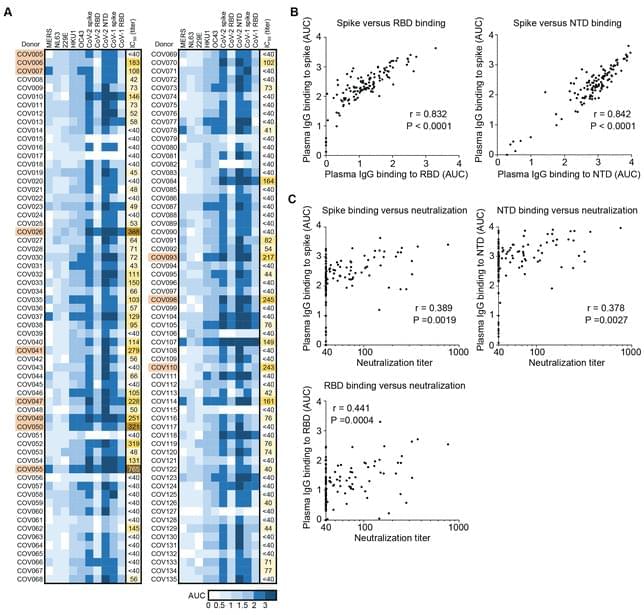
The emergence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants of concern threatens the efficacy of existing vaccines and therapeutic antibodies and underscores the need for additional antibody-based tools that potently neutralize variants by targeting multiple sites of the spike protein. We isolated 216 monoclonal antibodies targeting SARS-CoV-2 from plasmablasts and memory B cells collected from patients with coronavirus disease 2019. The three most potent antibodies targeted distinct regions of the receptor-binding domain (RBD), and all three neutralized the SARS-CoV-2 Alpha and Beta variants. The crystal structure of the most potent antibody, CV503, revealed that it binds to the ridge region of SARS-CoV-2 RBD, competes with the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor, and has limited contact with key variant residues K417, E484 and N501. We designed bispecific antibodies by combining non-overlapping specificities and identified five bispecific antibodies that inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection at concentrations of less than 1 ng/mL. Through a distinct mode of action, three bispecific antibodies cross-linked adjacent spike proteins using dual N-terminal domain-RBD specificities. One bispecific antibody was greater than 100-fold more potent than a cocktail of its parent monoclonals in vitro and prevented clinical disease in a hamster model at a 2.5 mg/kg dose. Notably, two bispecific antibodies in our panel comparably neutralized the Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta variants and wild-type virus. Furthermore, a bispecific antibody that neutralized the Beta variant protected hamsters against SARS-CoV-2 expressing the E484K mutation. Thus, bispecific antibodies represent a promising next-generation countermeasure against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern.
Bispecific antibodies targeting multiple regions of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein comparably neutralize variants of concern and wild-type virus.