Dec 1, 2021
Physicists Confirm The Existence of Time Crystals in Epic Quantum Computer Simulation
Posted by Kelvin Dafiaghor in categories: computing, particle physics, quantum physics
Are you in the market for a loophole in the laws that forbid perpetual motion? Knowing you’ve got yourself an authentic time crystal takes more than a keen eye for high-quality gems.
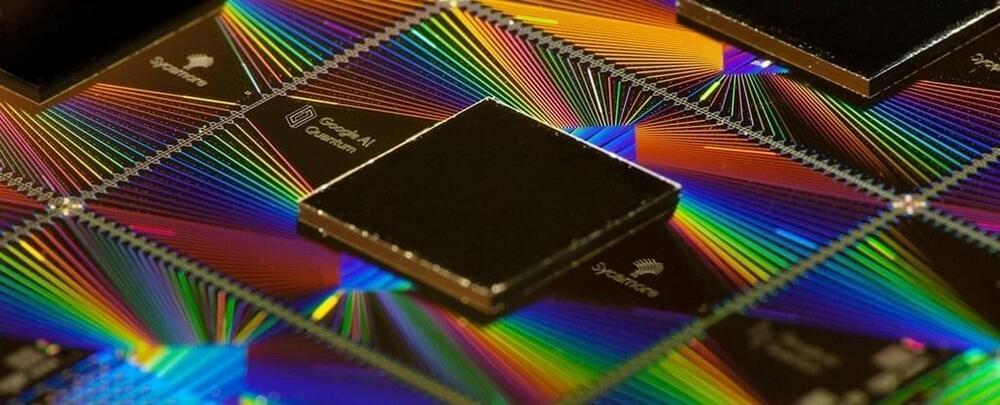
In a new study, an international team of researchers used Google’s Sycamore quantum computing hardware to double-check their theoretical vision of a time crystal, confirming it ticks all of the right boxes for an emerging form of technology we’re still getting our head around.
Similar to conventional crystals made of endlessly repeating units of atoms, a time crystal is an infinitely repeating change in a system, one that remarkably doesn’t require energy to enter or leave.