Sep 14, 2022
New insights revealed through century-old photochemistry technique
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: chemistry, energy, food
As the poet Dylan Thomas once explained, it is “the force that through the green fuse drives the flower.”
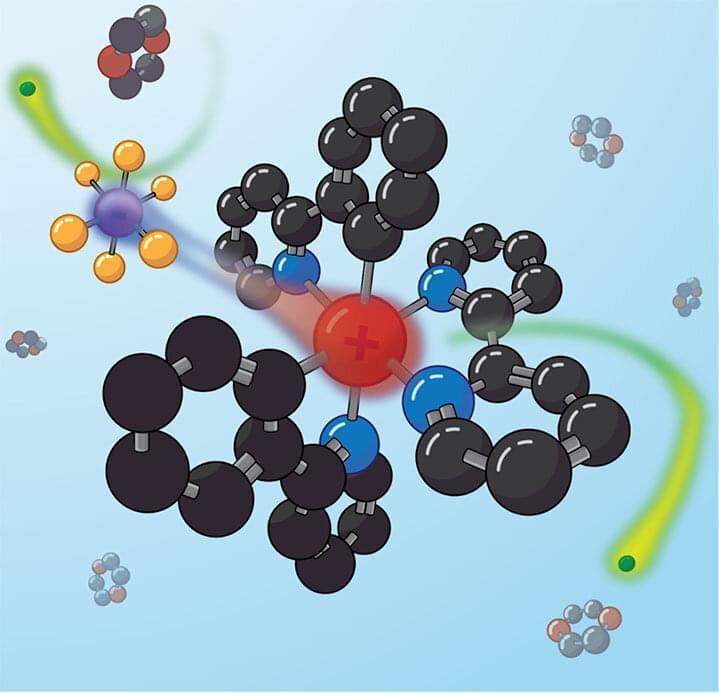
Organic photochemistry brings life to Earth, allowing plants to “eat” sunlight. Using this power of light to make new molecules in the lab instead of the leaf, from fuel to pharmaceuticals, is one of the grand challenges of photochemical research.
What is old is new again. Sometimes gaining new insight requires a return to old tools, with a modern twist. Now, a collaborative team from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and Princeton University has resurrected a century-old microwave technique to reveal a surprising feature of well-established light-driven chemistry.