Neuralink reportedly aims to implant its device into 11 humans next year. Elon Musk said it will be inserted by robot.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Astronaut Frank Borman, Who Commanded First Apollo Mission To The Moon, Dead At 95
NASA astronaut Frank Borman, commander of the first Apollo mission to the moon, has died at age 95.

Quantum Wonders: Atomic Dance Transforms Crystal Into a Magnet
Researchers at Rice University found that chiral phonons in a crystal can magnetize the material, aligning electron spins in a way similar to the effect of a strong magnetic field. This discovery challenges established notions in physics, particularly the concept of time-reversal symmetry, and paves the way for advanced research in quantum materials.
Quantum materials hold the key to a future of lightning-speed, energy-efficient information systems. The problem with tapping their transformative potential is that, in solids, the vast number of atoms often drowns out the exotic quantum properties electrons carry.
Rice University researchers in the lab of quantum materials scientist Hanyu Zhu found that when they move in circles, atoms can also work wonders: When the atomic lattice in a rare-earth crystal becomes animated with a corkscrew-shaped vibration known as a chiral phonon, the crystal is transformed into a magnet.
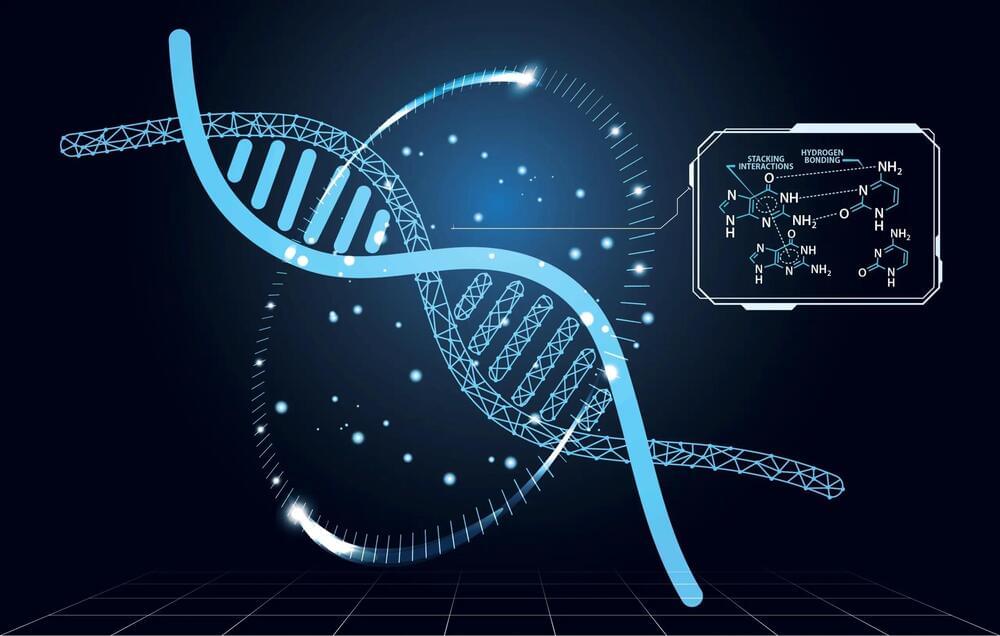
Revolutionizing CRISPR: Quantum Biology and AI Merge to Enhance Genome Editing
Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s research in quantum biology and AI has significantly improved the efficiency of CRISPR Cas9 genome editing in microbes, aiding in renewable energy development.
Scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) used their expertise in quantum biology, artificial intelligence, and bioengineering to improve how CRISPR Cas9 genome editing tools work on organisms like microbes that can be modified to produce renewable fuels and chemicals.
CRISPR is a powerful tool for bioengineering, used to modify genetic code to improve an organism’s performance or to correct mutations. The CRISPR Cas9 tool relies on a single, unique guide RNA.

Turns Out, Rocket Scientists and Brain Surgeons Are Not Smarter Than the Rest
In an interesting revelation, a collaborative team of researchers across various institutions in London has shown that rocket scientists and neurosurgeons, who are often held on a high pedestal for their superior intellect are, in fact, no smarter than the general public, BBC reported.
When failing to complete day-to-day tasks, one often comes across the term “It’s not rocket science”. The phrases that have been used by the public at large tacitly imply that rocket science or brain surgery is not a menial job and requires an individual of a higher intellect. Interestingly, it was a team of neurosurgeons and those involved in studying the human brain who decided to probe whether this held true.

Avascular Necrosis
Osteonecrosis is a disease caused by reduced blood flow to bones in the joints. In people with healthy bones, new bone is always replacing old bone. In osteonecrosis, the lack of blood causes the bone to break down faster than the body can make enough new bone. The bone starts to die and may break down.
You can have osteonecrosis in one or several bones. It is most common in the upper leg. Other common sites are your upper arm and your knees, shoulders and ankles. The disease can affect men and women of any age, but it usually strikes in your thirties, forties or fifties.
At first, you might not have any symptoms. As the disease gets worse, you will probably have joint pain that becomes more severe. You may not be able to bend or move the affected joint very well.


A hyped AI-based restaurant opened to fanfare last month in San Francisco; now its empty
A San Francisco smoothie startup promised to create customers “one-of-a-kind” recipes, but two months after opening, the store was shuttered.
The shop, BetterBlends, used artificial intelligence to generate custom smoothies based on customer preferences. The company only offered one menu item called “Your Smoothie, powered by AI” and claimed to be “the most personalized restaurant, ever,” according to its site.
WHAT IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)?


NVIDIA may soon announce new AI chips for China to get around US export restrictions
The new chips were designed to be less powerful than the models sold in the US, according to sources.
NVIDIA really, really doesn’t want to lose access to China’s massive AI chip market.
NVIDIA really, really doesn’t want to lose access to China’s massive AI chip market. The company is developing three new AI chips especially for China that don’t run afoul of the latest export restrictions in the US, according to The Wall Street Journal and Reuters. Last year, the US government notified the chipmaker that it would restrict the export of computer chips meant for supercomputers and artificial intelligence applications to Russia and China due to concerns that the components could be used for military purposes. That rule prevented NVIDIA from selling certain A100 and H100 chips in the country, so it designed the A800 and H800 chips specifically for the Chinese market.
However, the US government recently issued an updated set of restrictions that puts a limit on how much computing power a chip can have when it’s meant for export to the aforementioned countries. The A800 and the H800 are no longer eligible for export under the new rules, along with NVIDIA’s other products, which include its top-of-the-line RTX 4090 consumer GPU. Some reports even suggest that the company could end up canceling over $5 billion worth of advanced chip orders in China.
The new chips meant for the Chinese market are called the HGX H20, the L20 and the L2, based on the specs sent to distributors. While the H20 is supposed to be the most powerful model out of the three, all of them don’t go beyond the computing power threshold set by the US government’s new export rules. That means customers using them for AI applications may need more chips than they would if they had access to higher-spec models.