May 11, 2024
Discovering optimal conditions for mass production of ultraviolet holograms
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: chemistry, engineering, holograms
Professor Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, and Electrical Engineering, Hyunjung Kang and Nara Jeon, PhD candidates, from Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dongkyo Oh, a PhD student, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) successfully conducted a thorough quantitative analysis. Their aim is to determine the ideal printing material for crafting ultraviolet metasurfaces.
Their findings featured in the journal Microsystems & Nanoengineering (“Tailoring high-refractive-index nanocomposites for manufacturing of ultraviolet metasurfaces”).
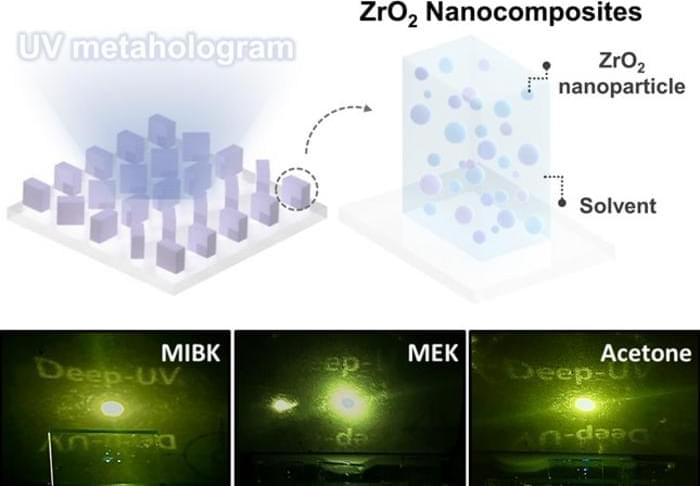
Diagram illustrating the composition of nanocomposites for ultraviolet metasurface fabrication. (Top) Diagram illustrating the ZrO 2 nanocomposite’s role in achieving high transfer fidelity ultraviolet metaholograms. (Bottom) Comparison of UV holograms under various solvent conditions. (Image: POSTECH)