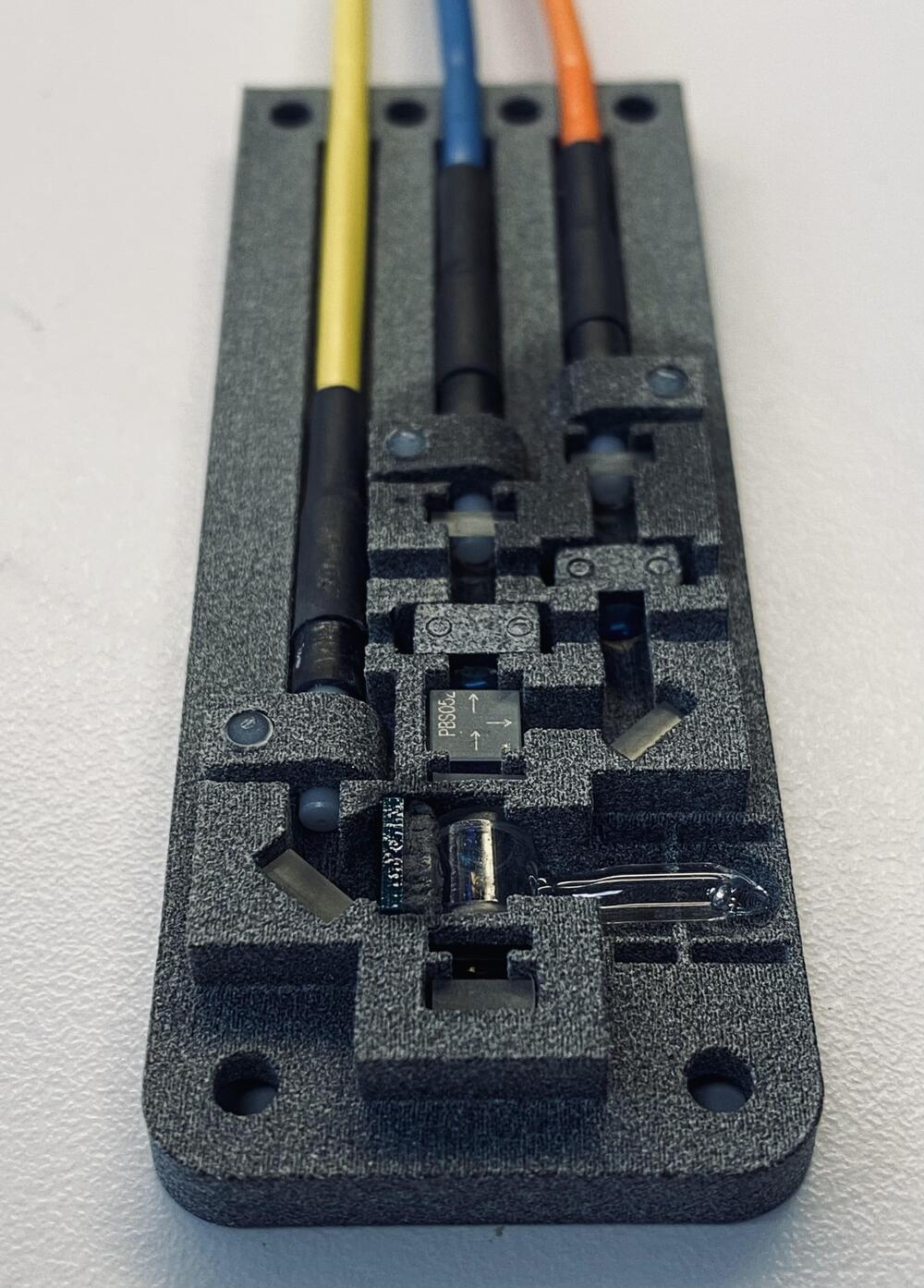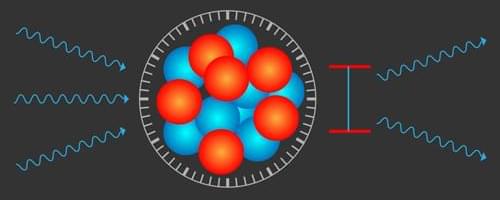
Researchers use a laser to excite and precisely measure a long-sought exotic nuclear state, paving the way for precise timekeeping and ultrasensitive quantum sensing.
Any reliably produced, periodic phenomenon—from the swing of a pendulum to the vibrations of a single atom—can form the basis of a clock. Today’s most precise timekeeping is based on extremely narrow electronic transitions in atoms, which resonate at optical frequencies. These stupendously precise optical atomic clocks lose just 1 second (s) in about 30 billion years. However, they could potentially be outperformed by a nuclear clock, which would instead “tick” to the resonant frequency of a transition that occurs in the atomic nucleus instead of in the electronic shell. The most promising candidate for this nuclear standard is an exceptionally low-energy and long-lived excited state, or isomer, of the isotope thorium-229 (229 Th). Researchers have now achieved the long-sought goal of exciting this transition with ultraviolet light.